Describe the position of the LoG to the joint axis, the external moment, internal moment, muscle forces, and passive support for:
Upper and lower cervical spine
LOG to upper cervical: anterior to atlanto-occipital joint
External moment: flexion
Internal moment: extension
Dynamic forces: suboccipital muscles (rectus capitis posterior major/minor, obliquus capitis superior/inferior, semispinalis cap/cerv, splenius cap/cerv)
Passive: alar ligament, lig nuchae
LOG to lower cervical: posterior
External moment: extension
Internal moment: flexion
Dynamic forces: scalenes, SCM, longus colli/capitis
Passive: ALL
Describe 3 differences between global muscles and deep segmental muscles’ effect on stability.
Global muscles: superficial, cross multiple vertebral segments, provide motion, “large guy wire function”
Deep segmental: closer to axis, attach to each vertebral segment, control segmental motion, “segmental guy wire function”, > Type I fibers for endurance
Patients are at risk of different physical stressors in the workplace. Describe how these are made worse by the properties of (1) magnitude, (2) repetition, and (3) duration.
Magnitude: forceful exertions, extreme postures/motions, high vibration level, cold temperature
Repetition: repetitive exertions, repetitive motions, repeated vibration exposure, repeated cold exposure
Duration: sustained exertions, sustained postures, long vibration exposure, long cold exposure
What are some postural changes that occur in pregnancy? List at least 5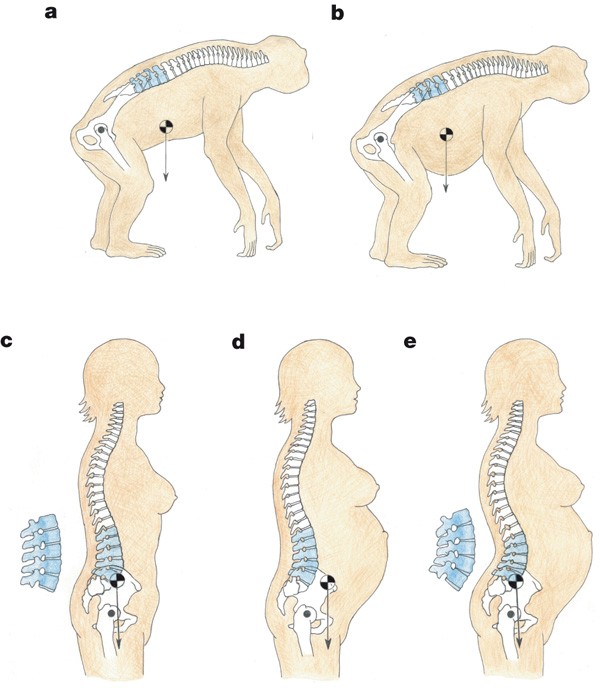
Increase lumbar lordosis because of weight gain
Increase cervical lordosis ot keep head in line
Increase lumbosacral angle
Anterior pelvic tilt
Upper back extension
Scapular protraction
What are the (1) tight, facilitated muscles and the (2) weak, inhibited muscles of UPPER Crossed Syndrome?
Tight, facilitated: pec major, pec minor, SCM (anterior) and upper trap, levator scapulae (posterior)
Weak, inhibited: deep neck flexors (anterior) and serratus anterior, rhomboids, lower trap (posterior)
Describe the position of the LoG to the joint axis, the external moment, internal moment, muscle forces, and passive support for:
Thoracic
LOG to thoracic: anterior
External moment: flexion
Internal moment: extension
Dynamic forces: erector spinae (longissimus, iliocostalis, spinalis) semispinalis thoracis
Passive: PLL
What are global muscles vs. deep segmental muscles for the (1) cervical region and (2) lumbar region that influence stability?
Cervical global muscles: SCM, scalenes, levator scap, upper trap, erector spinae
Cervical deep muscles: rectus capitis anterior/lateralis, longus colli/capitis
Lumbar global muscles: rectus ab, external/internal obliques, quad lumborum (superficial)
Lumbar deep muscles: TVA, multifidus, quad lumborum (deep), intersegmental rotators, intertransversarii
What tips would you give to a patient who has to move a heavy cart at work in terms of body mechanics?
Carry object as close to the CoG as possible (decrease lever arm of the resistance)
Push rather than pull (easier to stabilize proximally than pulling distally)
Why does knee hyperextension occur with pregnancy to address the degrees of freedom problem?
Pregnant person will hyperextend knees to avoid falling
Less muscle response because it’s the close-packed position
Decrease degrees of freedom by preserving some muscle energy since pregnancy is fatiguing
Leads to decreased mobility, instability, increased stress on the capsule and ligaments
What are postural deformities associated with Upper Crossed Syndrome?
Scapular protraction
Scapular winging
DJD
Forward head
Describe the position of the LoG to the joint axis, the external moment, internal moment, muscle forces, and passive support for:
Lumbar and SI
LOG to lumbar: posterior (thru L5)
External moment: extension
Internal moment: flexion
Dynamic forces: rectus ab, obliques
Passive: ALL
LOG to SI: anterior
External moment: nutation
Internal moment: counternutation
Dynamic forces: TVA
Passive: sacrotuberous ligament
Describe the factors associated with chronic pain/disability through the biospychosocial model.
If I have a poor understanding of my pain, my affective response (fear) will change my behavior (avoidance). I should address the root of this issue by changing the belief (my understanding of the cause of my pain).
What are the effects of prolonged standing posture and vibration in a moving work environment, i.e. a fisherman?
Increased disc loading (L4-L5)
Increased risk for hip and knee OA
Bend knee stance to reduce shock loading
What postural changes occur in forward head posture, i.e. LoG, external moment, internal moment?
LoG moves posterior to both upper and lower cervical spine
Anterior to thoracic joint axis
Overall creates a large external flexion moment because of anterior COM shift
What kind of exercises can we use to address the inhibited and facilitated muscle problems in Upper Crossed Syndrome?
Stretch out the tight muscles
Strengthen the DEEP neck flexors (not SCM, it will get fatigued
Keep it functional (chin tucks)
The goal of this position is to keep the eyes up
Describe the position of the LoG to the joint axis, the external moment, internal moment, muscle forces, and passive support for:
Hip
LOG to hip: thru greater trochanter, posterior to axis
External moment: extension
Internal moment: flexion
Dynamic forces: iliopsoas
Passive: iliofemoral, ischiofemoral, pubofemoral ligaments
What landmarks should we look for in postural symmetry for the frontal plane, (1) anterior and (2) posterior views?
Anterior: eyes, shoulders, waist (flank space), knees, 2nd toe
Posterior: ears, scapula, waist (flank space, gluteal fold, popliteal fossa, malleoli, Achilles tendon
What are some postural risks for pain in the upper extremities with overhead work, e.g., using a hammer above eye level or working on ceiling pipes?
Sustained postures
Decreased subacromial space from reaching up
Looking up = increased cervical lordosis
What are the overworked/lengthened/weakened muscles in a forward head posture?
Upper trap, levator scapulae (isometric head hold support)
Scapula retractor muscles (rhomboids, mid trap)
Neck flexors (longus capitis/colli, rectus capitis anterior/lateral)
What are the (1) tight, facilitated muscles and the (2) weak, inhibited muscles of Lower Crossed Syndrome?
Tight (facilitated muscles): lumbar erector spinae, hip flexors (rectus fem, iliopsoas); hamstrings may also be tight to accomodate for Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Weak (inhibited muscle): abdominal muscles, glutes (max, med, min)
Describe the position of the LoG to the joint axis, the external moment, internal moment, muscle forces, and passive support for:
Knee and ankle
LOG to knee: anterior to axis (posterior to patella)
External moment: extension
Internal moment: flexion
Dynamic forces: hamstrings, gastroc
Passive: posterior capsule
LOG to ankle: anterior to axis
External moment: dorsiflexion
Internal moment: plantar flexion
Dynamic forces: gastroc, soleus
Explain how we have feedback responses to address postural sway even in fixed support strategies.
Postural adjustments are activated before voluntary movements to minimize the potential balance disturbances from outside factors. --> Anticipatory postural control
Cone of stability: if the sway remains within the limits, then we have postural stability. Therefore, we activate ankle and hip strategies for a fixed base of support. If sway exceeds the limit of stability, then we have compensation by activating stepping and grasping strategies for change-in-support.
A lot of people we know have sedentary jobs that require sitting for long periods and therefore increase the risk of LBP. Describe at least 3 biomechanical effects of this.
Increased IVD shear force
Increased tensile force on posterior annulus
Increased compressive force on anterior annulus
Increased stress on P.L.L.
Increased hydrostatic pressure
What are some reasons that forward head posture might cause TMJ issues for patients?
Forward head will increase gravity load on the jaw
TMJ muscles need to work harder to keep the jaw closed and therefore fatigue
Discuss the postural changes for Lower Crossed Syndrome.
LOG: Posterior to cervical spine, anterior to thoracic spine, posterior to lumbar spine
Postural deformities:
Increase in lumbosacral angle
Increased anterior pelvic tilt
Increased hip flexion