What are the 4 factors that can affect the rate of a reaction?
Concentration, temperature, surface area, catalyst
What are the surnames of the two people who defined the definitions of acids and bases that we use at Yr 12
Bronsted and Lowry
Define Kc
The ratio of products/reactants
Why is nitrogen gas inert?
Strong triple bond
What is the bond angle around carbon in methanoic acid?
120
IF using a powdered reactant instead of a lump - how will this affect the rate?
What keywords should you use?
More reactant particles available/exposed to take part in reaction
more successful collisions per second
faster rate of reaction
What is the definition of a base?
Proton acceptor
What species do we not include in Kc expressions?
solids and liquids
Describe the trend of thermal stability of hydrogen halide. (From HF to HI)
It becomes less thermally stable.
What is the catalyst for hydrogenation of alkene?
Ni or Pt
If you used 1 mol/L HCl instead of 2 mol/L in a reaction what keywords would you use to explain the effect?
in 1 mol/L there are less reactant particles/L which results in less successful collisions per second
slower rate of reaction
What is the definition of an acid?
Proton donator
IF Kc is greater than 1 which species are present in higher concentration?
If Kc is greater than 1 there are more products than reactants
Why does reactivity of Group 2 metal increase down the group?
first ionisatiion decrease down the group
What is the condition (temperature and pressure) of the contact process?
450 degrees and 1-2atm
Discuss the relative amounts of reactants and products in this graph
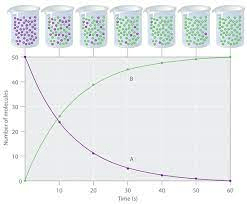
At the beginning there are high concentrations of reactant particles - more collisions per second
As the reactants turn into products, the reactant concentration decreases until it is all used up
The green line shows the rapid production of products, tailing off as all reactants are used up
What is the name for a substance that can both accept and donate a proton?
Amphiprotic
What are the 4 conditions you can change that affect equilibriums?
Concentration
Pressure
Temperature
Catalyst
What is the product formed when Silicon reacts slowly with chlorine gas? Give the formula.
SiCl4
What kind of structure is a fullerene?
Molecular
What affect will increasing the number of reactant particles per volume have on a reaction?
Increasing concentration - more collisions per second, faster rate of reaction
In the following question, what is the concentration of H3O+?
Calculate the pH of a 0.0500mol/L solution of HCl
0.0500mol/L
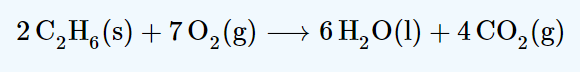 How would increasing pressure affect this equilbrium?
How would increasing pressure affect this equilbrium?
Increasing pressure favours the side with the least moles of gas. The reactants side has 7 moles of gas and the products side has 4. The reaction will shift to the right favouring the products.
Describe and explain the trend of boiling point of halogens
boiling point of halogens increases down the group because of bigger molecules and stronger intermolecular attractions
What does S and n represent in sn1 mechanism?
Substitution
Nucleophilic
Where do we usually write the formula for catalysts in chemical equations?
On the arrow
Calculate the pH of a 0.0500mol/L solution of HCl
-log 0.0500 = 1.3
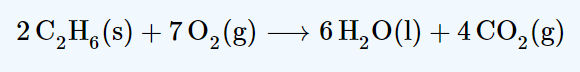
If the concentration of oxygen is increased what affect will this have on the value of Kc.
No affect.
The only thing that will affect the value of Kc is temperature
What is the product formed when aluminium oxide react with hot sodium hydroxide? Give the formula.
NaAl(OH)4
In expressions Kc and Kp, c and p stand for two different things. What do they stand for?
What is (p)ressure and (c)oncentration?
What is collision theory?
That particles must collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation in order to react
Calculate the pH of a 0.160mol/L solution of KOH
[OH-] = 0.160mol/L
[H3O+] = 1x 10-14/0.160 = 6.25x 10-14mol/L
pH = -log 6.25x 10-14mol/L
= 13.2
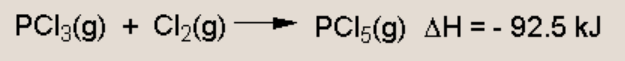
Discuss the effect on this equilibrium if temperature is increased and the value of Kc
Increasing temperature favours the endothermic reactions (which will absorb the excess heat). The forward reaction is exothermic (delta H is -) so the reverse reaction is endothermic, hence an increase in temperature will favour the reverse reaction (the reactants). This will lower the value of Kc
What are the chlorine containing products when chlorine react in cold alkali?
NaCl and NaClO
If one or more factors that affect equilibrium are changed, the position of equilibrium will shift in the direction which reduces the effect of the change.
What is Le Chatlier's Principle?
What materials are commonly used as catalysts in industry?
Transition metals
What is the main difference between a strong and weak base?
Strong - fully dissociates (use -->) into ions
Weak - only partially dissociates into ions (use ⇋ )
Discuss how a decrease in pressure will affect this equilibrium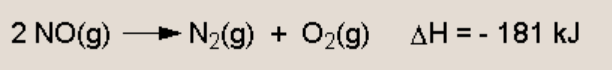
Decreasing pressure favours the side with the most moles of gas - both sides have 2 moles of gas so this will have no effect on the equilibrium
What are the observations when Calcium nitrate is heated in a boiling tube? (Two observations)
Solid melts and brown gas formed
The ratio of moles of one substance in a mixture to the total number of moles of all substances.
What is a Mole Fraction?
How does a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction?
* provides an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
* now more reactant particles will have energy> Ea and be able to collide successfully = more collisions per second, faster rate of reaction
CH3COONa is a salt. Use equation(s) to show if it is acidic or basic.
CH3COONa --> CH3COO- + Na+
Salt fully dissociates into ions when mixed with H2O
CH3COO- + H2O ⇋ CH3COOH + OH-
Ethanoate ions then go on to partially dissociate with some accepting a proton from water to produce hydroxide ions = basic salt
Is the forwards reaction exo or endo-thermic?
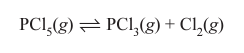
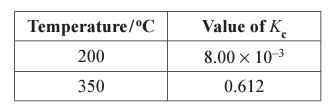
Endothermic - temperature increases favour the endothermic reaction (which will absorb excess heat) as the value of Kc increases as temperature increases, the equilibrium must be producing more products - i.e. it has shifted in the forwards direction which must be the endothermic reaction
What are two products formed when PCl5 reacts with water? What is the observation seen?
H3PO4 + HCl and white fumes
What is the reagent required to form 2-hydroxyproanenitrile from ethanal?
KCN/HCN
How does an increase in temperature affect the rate of reaction? Link to the activation energy
Increasing temperature - increased the Ek of particles, move faster, more collisions per second, faster rate of reaction as now more reactant particles have energy > Ea and will collide successfully
NH3 KOH
Which one would be a better electrical conductor and why?
NH3 is a weak base - partially dissociates to produce a low concentration of ions - poor conductor
KOH is a strong base - fully dissociates to produce a high concentration of ions - good electrical conductor
What is the name of the person who came up with the principle we have been learning that governs changes to equilibriums - first and last name
Henri Le Chatelier
What are all the sulfur containing products formed when iodide reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid?
(There are 4)
NaHSO4, SO2, S, H2S
What would be the two tests carried out to distinguish between propan-1-ol, propanal and propanone?
1. 2,4 DNPH
2. Tollen's or Fehling's reagent