------ are responsible for supplying organs with blood, while ------ are responsible for draining organs of blood
Arteries and veins
2 circuits that compose the cardiovascular system
Pulmonary and systemic circuits
This is responsible for immune surveillance of the blood
The spleen
The process of creating the formed elements is called what?
Where does it take place?
Hemopoiesis
Red bone marrow
Coelom and viscera are alternate names for what
The ventral body cavity and the organs within the ventral body cavity
Blood 45% formed elements, what is the rest?
The first chamber in the heart blood hits upon returning from the LUNGS
The left atrium
one function of the lymphatic system is to drain excess ISF and return it to the blood
What is another function?
immune surveillance of the lymph
Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils all have what specific connection?
They belong to the granulocyte sub group of leukocytes
What is the difference between visceral serous membranes and parietal serous membranes?
Visceral serous membrane line organs while parietal serous membrane lines the body wall
The cardiac muscle of the heart is thickest in the walls of the left ventricle, from a functional perspective why is that necessary?
The left ventricle needs to supply the whole body (minus the lungs) with blood, so the cardiac muscle is thicker for stronger contractions to pump more blood
The 2 functions of the spleen
Immune surveillance of the blood and it acts as a blood reservoir
T lymphocytes reach immunocompetence in the
A. red bone marrow
B. thymus
C. Spleen
D. Lymph nodes
B. Thymus
what structure prevents back blow of blood back into the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary semi lunar valve
All of the following can be found in the tunica interna of an ELASTIC artery except
A. endothelium
B. basement membrane
C. internal elastic lamina
D. areolar CT
E. These are all found in elastic Arteries
C. internal elastic lamina
adrenal glands, inferior vena cava and the duodenum all have what in common?
They are all retroperitoneal
The name of 2 capillary beds in a row
a portal system
The appendix, Peyer's patches and tonsils fall under what category of lymphatic structure?
A. Primary lymphatic organ
B. secondary lymphatic organ
C. lymphatic nodules
D. Lymph nodes
C. Lymphatic nodules
Which protein is the primary carrier for oxygen in the blood
A. fibrin
B. Elastin
C. Collagen
D. Hemoglobin
D. Hemoglobin
What does M.A.L.T stand for?
What lymphatic structure is responsible for performing immune surveillance on mucous membranes
Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
Lymphoid nodules
list the layers of a muscular artery as well as the composition of each layer.
Tunica interna- endothelium, basement membrane, areolar CT and internal elastic lamina
tunica media- smooth muscle
External elastic lamina between media and externa
Tunica externa- vaso vasorum, collagen
All of the following are true of serous membranes except
A. provide lubrication
B. Made of simple squamous ET and areolar CT
C. lines certain organs
D. keeps surfaces open to the outside world moist
E. lines certain body cavities
D
Name the 3 embryonic germ layers from most superficial to deepest
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
What is responsible for the formation of platelets in the blood?
Megakaryocytes
Primary lymphatic organs are where the immune response occurs in the immune system.
TRUE or FALSE
False
Primary lymphatic organs are the site of maturation for lymphocytes
Based on the given descriptions, ID the structure.
A. Connects the transverse colon to the greater curvature of the stomach
B. Anchors the the sigmoid and transverse colon to the posterior body wall
C. anchors the ileum and jejunum to posterior body wall
D. connects the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach
A. greater omentum
B. Meso colon
C. mesentery proper
D. Lesser omentum
Pleura, pericardium, peritoneum are all examples of what?
Names of serous membranes in specific cavities of the body
Which structures house b lymphocytes inside of a lymph node
A. Medullary cords and lymphoid nodule
B. trabeculae and lymphoid nodule
C. Germinal center and cortical sinuses
D. Germinal center and medullary cords
E. Medullary sinuses and medullary cords
D. Germinal center and medullary cords
The composition of plasma
mostly water, proteins, solutes and waste
The germinal center in a lymphoid nodule contains all of the following except
A. dendritic cells
B. Macrophages
C. B-Lymphocytes
D. It contains all the above
D. It contains all the above
These anatomical features aid in venous return
The skeletal muscle pump, arteries pulsing against veins and venous valves.
which of the following are transported via the cardiovascular system?
A. hormones
B. oxygen
C. nutrients
D. CO2
E. all of the above
E. all the above
Which statements are correct? select all that apply
A. Bicuspid valve separates left atrium from the aorta
B. Tricuspid valve separates right atrium from right ventricle.
C. Pulmonary semi lunar valve separates pulmonary trunk and left ventricle
D. Aortic semi lunar valve separates the ascending aorta and the left ventricle
E. Bicuspid valve separates left atrium and left ventricle
B, D, E
The -------- monitors arteriole blood coming into the spleen for antigen covered pathogens and the ------- acts as a blood reservoir housing RBC's and platelets
White pulp and red pulp
Nervous tissue derives from what embryonic germ layer?
A. ectoderm
B. mesoderm
C. endoderm
A. Ectoderm
The round ligament in females and spermic cords in males pass through this structure
the inguinal canal
In its simplest of terms, what is the path of blood leaving the heart all the way back to the heart?
Leaves the heart through arteries then arterioles then exchange happens at capillaries then to venules then returning to the heart through veins.
The openings in the diaphragm, and what passes though them
The caval hiatus- inferior vena cava
Aortic hiatus-abdominal aorta
Esophageal hiatus- esophagus and vagus nerve
The name of serous membrane associated with THE HEART?
Visceral pericardium and parietal pericardium
List all intraperitoneal organs
Stomach, spleen, sigmoid colon, liver, gallbladder, transverse colon, ilium, jejunum
Match the description to the correct capillary
1. small pore like openings allow for more filtration
2. A complete basement membrane, allows no leakage
3. Incomplete basement membrane, with large openings in the epithelial layer
1. Fenestrated capillary
2. continuous capillary
3. sinusoidal capillary
including the pericardial sac, name the layers of the heart from most superficial to deepest?
Fibrous pericardium, parietal pericardium, Pericardial cavity, epicardium (OR visceral pericardium), myocardium, and endocardium
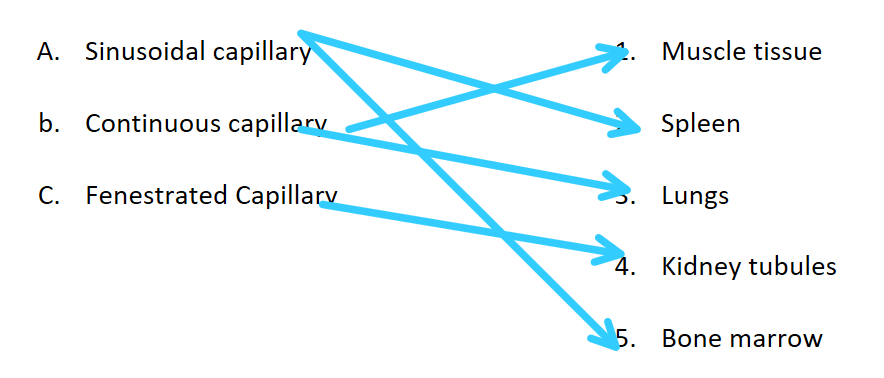
Match the type of capillary with its location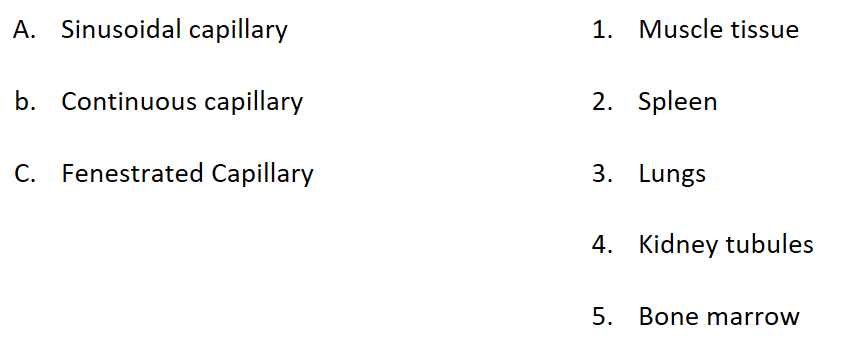
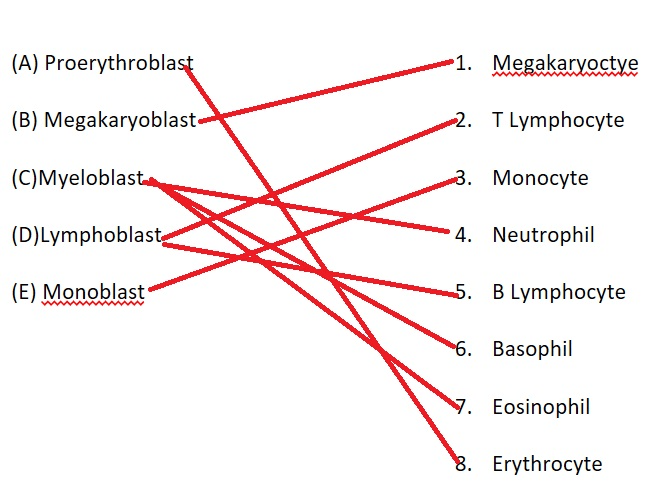
Match the progenitor cells to mature cells 
Arteries have thick layers of smooth muscle in there tunica media, while veins do not. What is the purpose of this difference from a functional perspective?
Arteries are under higher pressure and must constrict or dilate to maintain BP, veins are under much lower pressure so they do not require the thick layer of muscle