What magnification level is the eyepiece?
10X
WHAT CELL TYPE ARE WE?
EUKARYOTE
This makes up the DNA
Nucleus
What is the term for a "scientific guess"
Hypothesis
Negative and Positive
What are the 3 total magnification levels?
40, 100, and 400x
What is this type of cell: 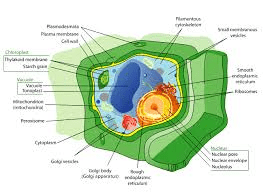
Plant cell - Eukaryote
Name 3 organelles that are not found in prokaryotes
nucleus, golgi apparatus, SER, RER, Mitochondria
Describe a control group
The part of the experiment that you compare to. Receives no treatment or change.
What are the 2 types of metabolic processes
anabolic and catabolic
What are the two dials that move the stage up and down?
Coarse and Fine adjustment
Is this a eukaryote or a prokaryote?
Prokaryote
What is the purpose of a lysosome?
Waste station. Cleans out the cells
What is an independent variable?
The part of the experiment that you change or manipulate.
Define Evolution
Change of genetic information within a population over generations.
What is the purpose of the diaphragm?
Allows a certain amount of light in
How long ago did the first cells come around?
3.5-4 billion years ago
Which type of cell has a larger vacuole and what does a vacuole do?
Plant cells, stores water
What is the "p-word" we never use in science?
Prove
Difference between growth and development
Growth: has to do with size
Development: actual change in structure or function
As you increase the magnification levels, what happens to your field of view
decreases
What makes up the cell theory (3)
All living things are made of cells
All cells come from pre-existing cells
Cells are the basic unit of life
Which organelles are included in the process of protein synthesis?
Nucleus, Ribosomes, RER, Golgi Apparatus
What are the 6 steps of the scientific method in order?
Observe-Question-Hypothesis-Experiment-Results-Conclusion
Name 4 Life Characteristics
Evolution, cells, metabolism, homeostasis, stimuli response, growth & development, reproduction, heredity