This modal expresses an obligation imposed by an external rule or authority, as in, "You ______ wear a uniform at school.

Have to
This modal expresses a high degree of logical conclusion or certainty, as in, "The lights are off, so they ______ be home."
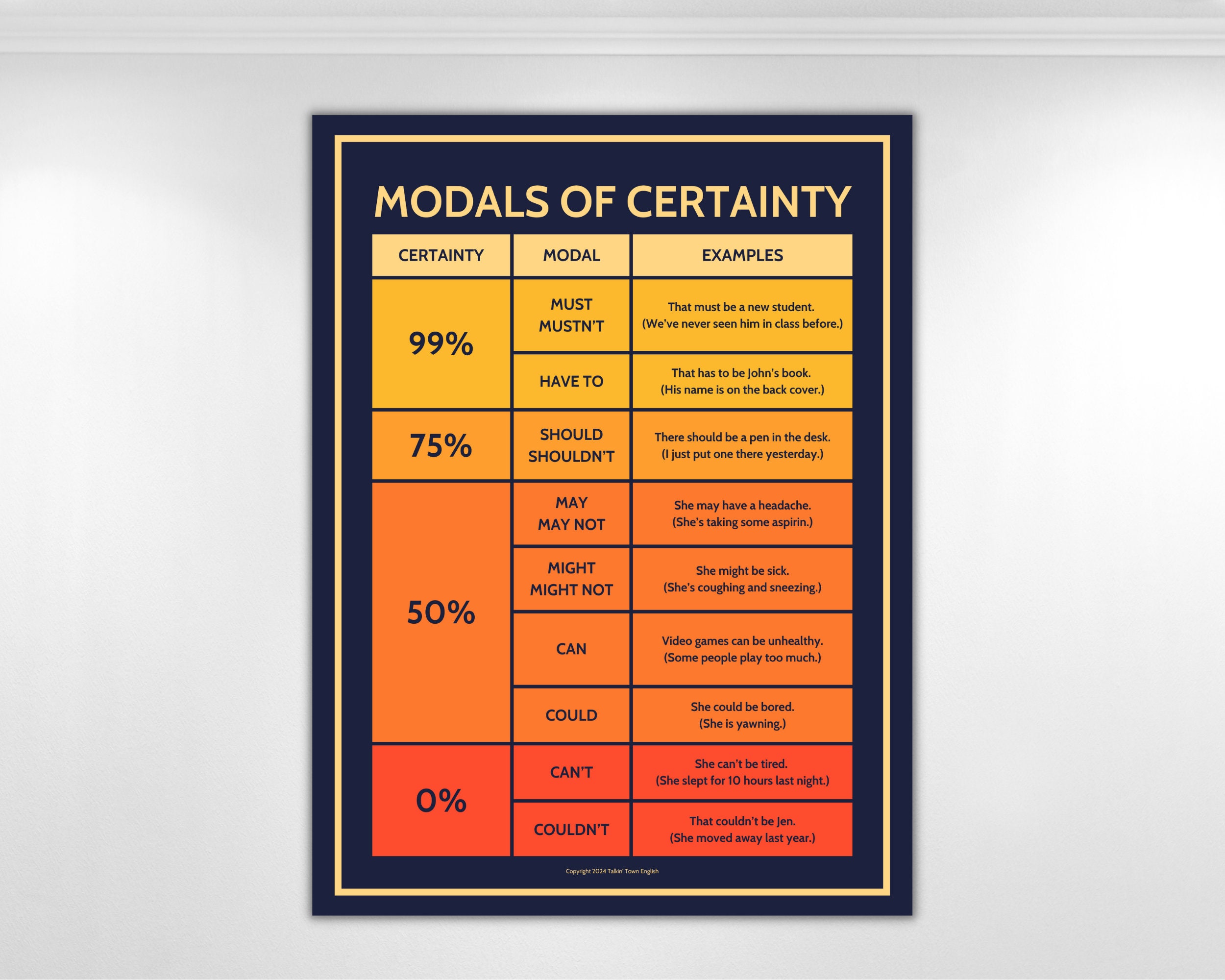
Must
The two essential components of every passive verb structure.
A form of 'be' and the Past Participle
This passive form is used to describe an action that is ongoing or temporary.

Progressive Passive
This passive structure describes the condition or result of a previous action, focusing on the state of the subject.
clue 
Stative Passive
This modal expresses a strong, often personal, necessity or duty, like "I ______ study harder to pass the exam."

Must
The modal used to express strong negative certainty, meaning you are sure something is not true, as in, "That story ______ be true."

Can't or Couldn't

WIN 200
This word is inserted between the conjugated form of 'be' and the past participle in a progressive passive structure.

Being
In this passive, the past participle is often described as functioning grammatically as this part of speech.
Adjective
This modal structure means something is not required or is optional, as in, "You ______ pay for parking on Sundays."

Don't have to
These two modal verbs express a moderate level of possibility or less definite certainty.
![]()
MAY OR MIGHT 67
Convert this active sentence to the simple passive voice: "The company designed the website."
The website was designed by the company.
Form the progressive passive for the Present Continuous tense: "The road ______ repaired right now."

Is being repaired

The past form of "have to," used for obligations that existed in the past, as in, "We ______ reschedule the meeting."

Had to
The full structure used to express moderate certainty about a past event, as in, "He ______ missed the bus."
Modal+...
Modal + Have + Past Participle
The main function of the passive voice when the performer of the action is unknown or unimportant.

To emphasize the action or the receiver of the action
Convert this active sentence to the progressive passive: "They were painting the mural all morning."
The mural was being painted all morning.
The verb often used instead of 'be' in the stative passive to show a transition or change to a new state, like "He ______ worried about the results.
Get
The difference between using "Must not" and "Don't have to".
Prohibition (Must not)
Lack of Necessity (Don't have to).
This modal expresses a firm expectation that something is true, often based on what is generally known, as in, "The repair ______ be finished by now."
Should
The correct passive structure for the Past Perfect tense, as in, "The contract ______ signed before the meeting."
Had been + Past Participle
The specific name of the passive structure that can only be used with continuous tenses
Progressive Passive
Use the stative passive to describe the current state of the subject in this sentence: "Someone broke the window last night.
The window is broken.