Nucleus
Directs cell activities and stores DNA which carries genetic instructions.

Genetic Engeering
Changing an organism’s DNA to give it new traits or abilities for the benefit of humans. 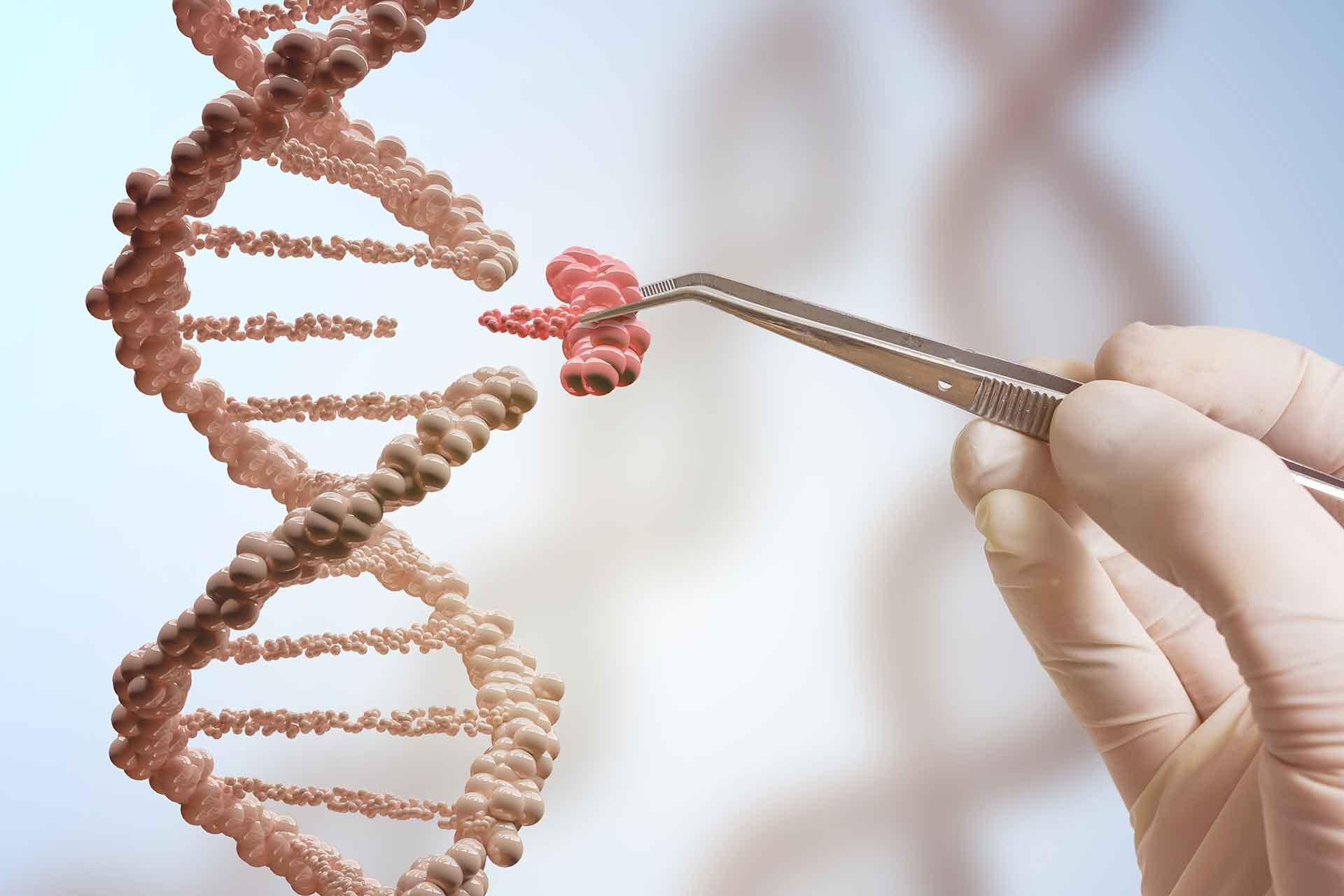
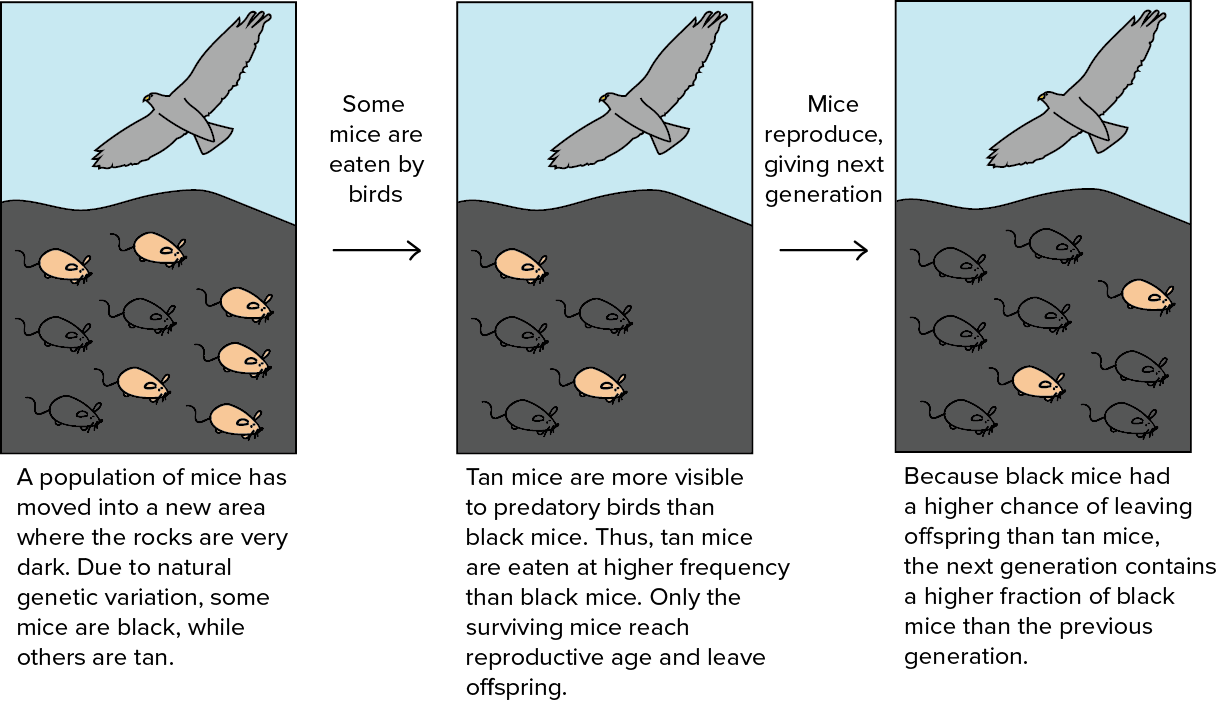
Natural Selection
Process where organisms with helpful traits survive and reproduce more successfully over time.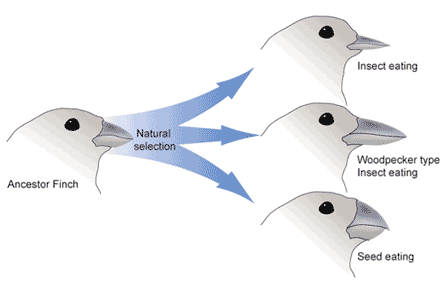
Pollution
Harmful substances released into air, water, or land by human activity.
Photosynthesis
Process where plants use sunlight to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water.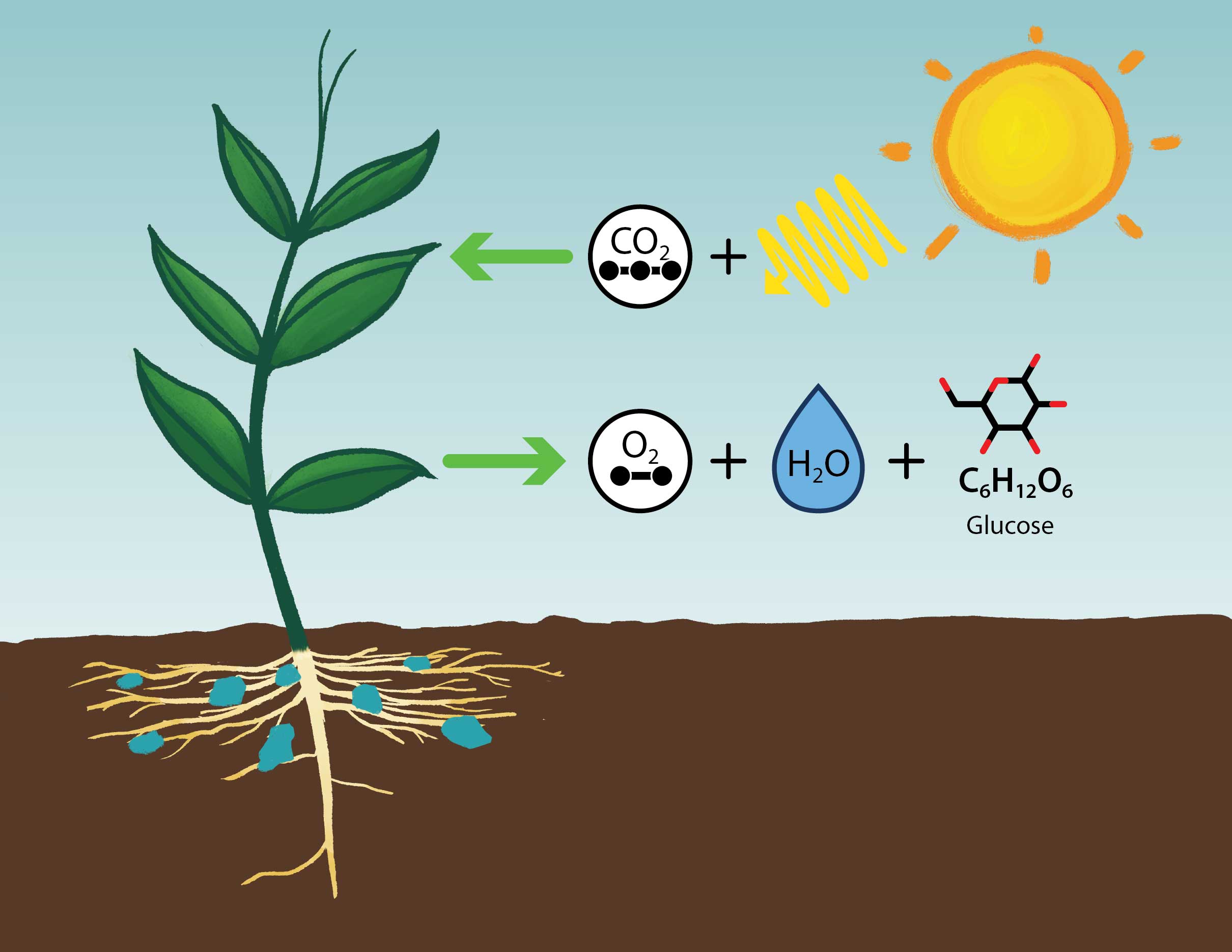
Mitochondria
Converts food into usable energy for the cell through cellular respiration.

Selective Breeding
Choosing organisms with desired traits to reproduce and pass them on.
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive better in its environment.
Deforestation
Large-scale removal of forests, often for farming, housing, or industry.
Cellular Respiration
Process where cells break down glucose to release ATP for life functions.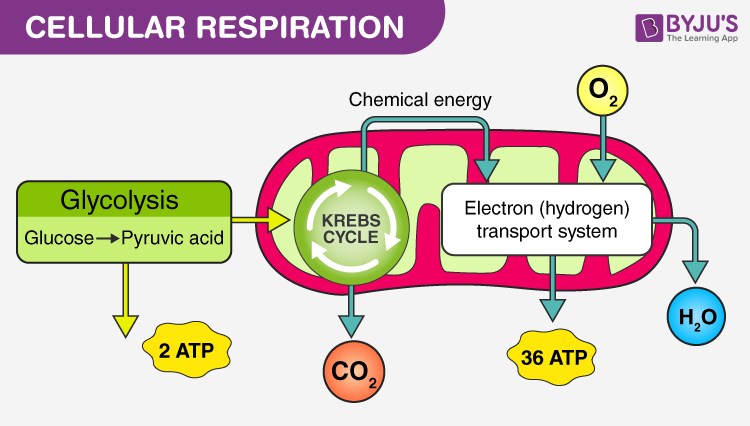
Ribosome
Builds proteins by assembling amino acids based on genetic code instructions.

Cloning
Making an exact genetic copy of an organism, cell, or gene.

Selecting Agent
Environmental factor that influences which traits help organisms survive and reproduce.
Global Warming
Rise in Earth’s temperature caused by greenhouse gases (CO2) from human actions.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration without using energy.
Receptors
Proteins on the surface of a cell that bind to specific hormones and facilitate a response.
Gel electrophoresis
Lab method that separates DNA fragments by size using electric current.

Fossil record
Collection of fossils showing how life has changed over time.

Nonrenewable resources
Natural materials that cannot be quickly replaced once they are used.
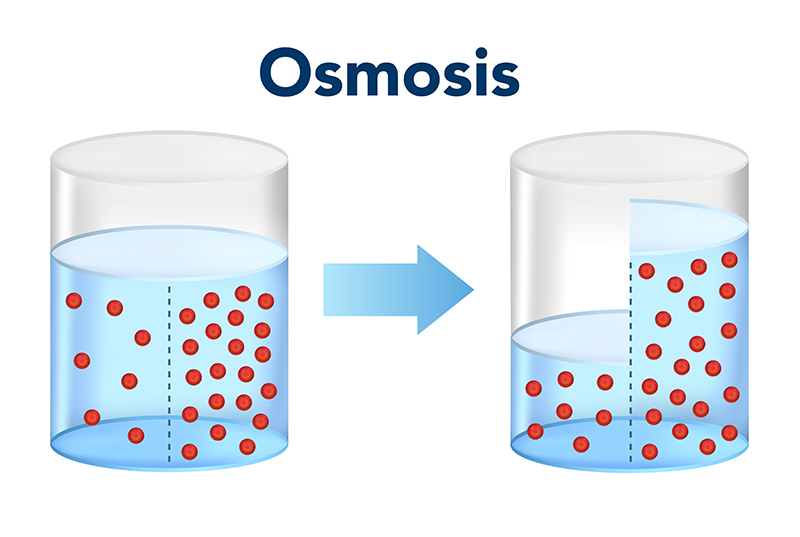
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane from high to low concentration.
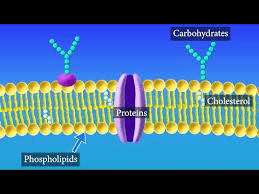
Cell Membrane
Outer boundary that controls movement of materials into and out of cell.
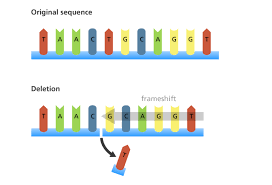
Mutation
A change in DNA that may affect how an organism looks or functions. Caused by UV radiation or chemicals.
Extinction
When an organism does not have sufficient adaptive characteristics within its environment and all members die off.

Renewable resources
Natural materials that can be replaced naturally and used again.

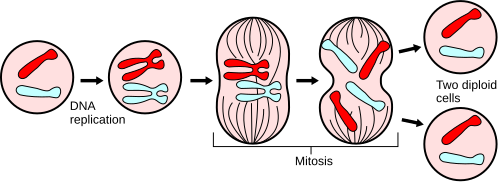
Mitosis
Cell division in body cells that produces two identical cells for growth or repair.