What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane bound nucleus and other organelles, eukaryotes do.
Osmosis and diffusion are both example of what?
Passive Transport
What do all four biomoleucles have in common
- they are organic molecules
- Carbon and hydrogen
What organelle controls the flow of substances in and out of the cell.
Cell membrane
In a controled experiment how many variables are changed?
ONE
The life process by which organisms obtain and process food
Nutrition
Chloroplast & cell wall
What is the direction of the concentration gradient.
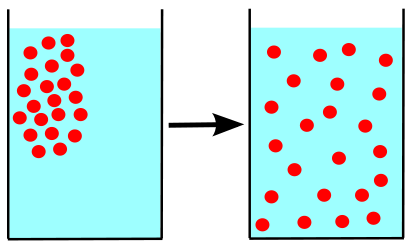
high concentration to low concentration
This biomolecule functions to provide short-term energy through saccharides.
Starch is an example
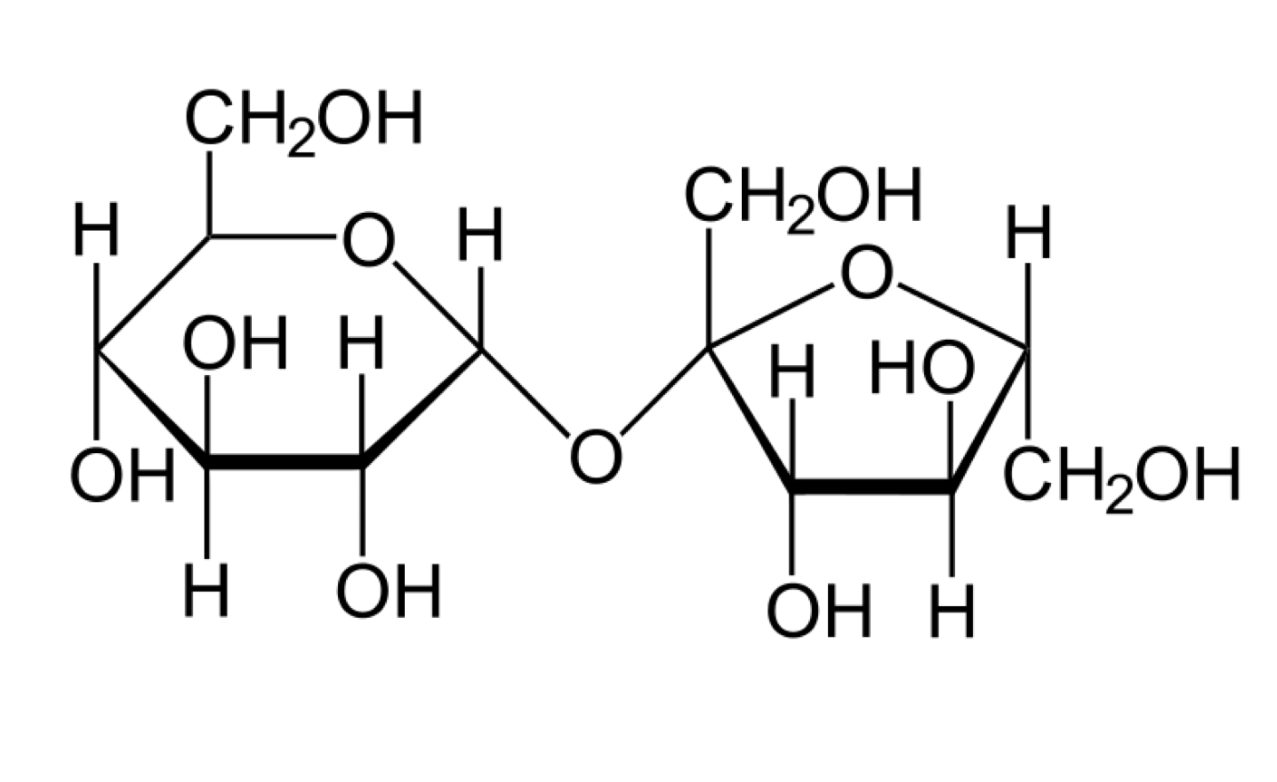
carbohydrates
Organelles
If you are looking to see how pH effects plant growth, What is the dependent variable?
Plant growth
The removal of harmful cellular waste
Excretion
What organelle creates ATP energy for the cell and all life processes
Mitochondria
This term is defined as the process of maintaining balance within a cell via self-regulation.
Homeostasis
DNA belongs to this family of biomolecules.
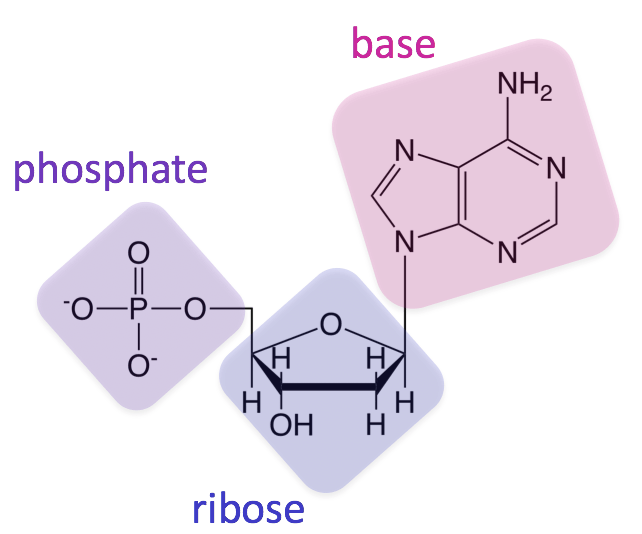
nucleic acid
A small lizard spends the morning hours laying in the sunlight until its body temperature rises. Later on in the day, the lizard rests in a shady area until its body temperature cools. This type of behavior is important to...
Maintain homeostasis
When does the enzyme start to denature?
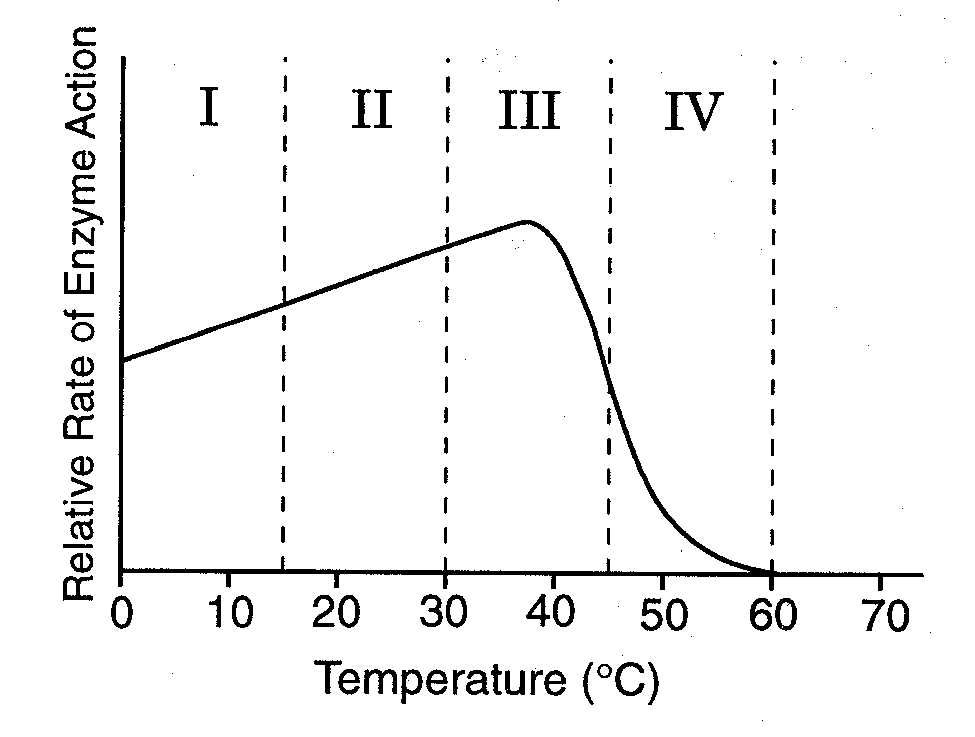
3 or III
The release of energy from food
Respiration
In what organelle can you find genetic material in the cell, and what does it look like.
The nucleus, it is a large circle in the middle of the cell.
What is the difference between passive transport and active transport?
Active requires energy; passive does not.
This biomolecule provides long-term energy and heat insulation.
Examples are oils, butter, fats ,waxes
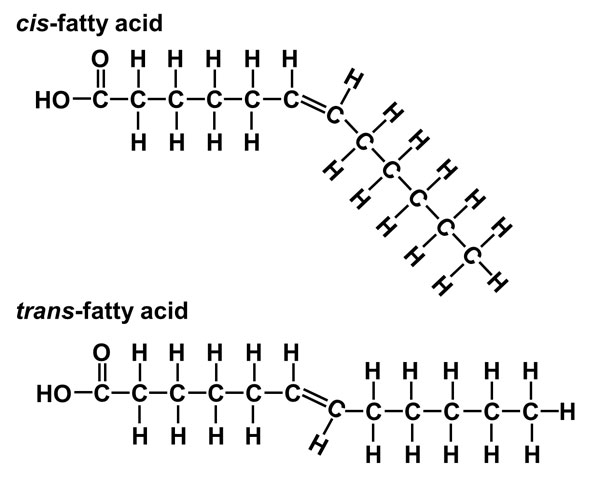
lipids
What was the approximate change in CO2 level from the year 1000 to the year 2000? 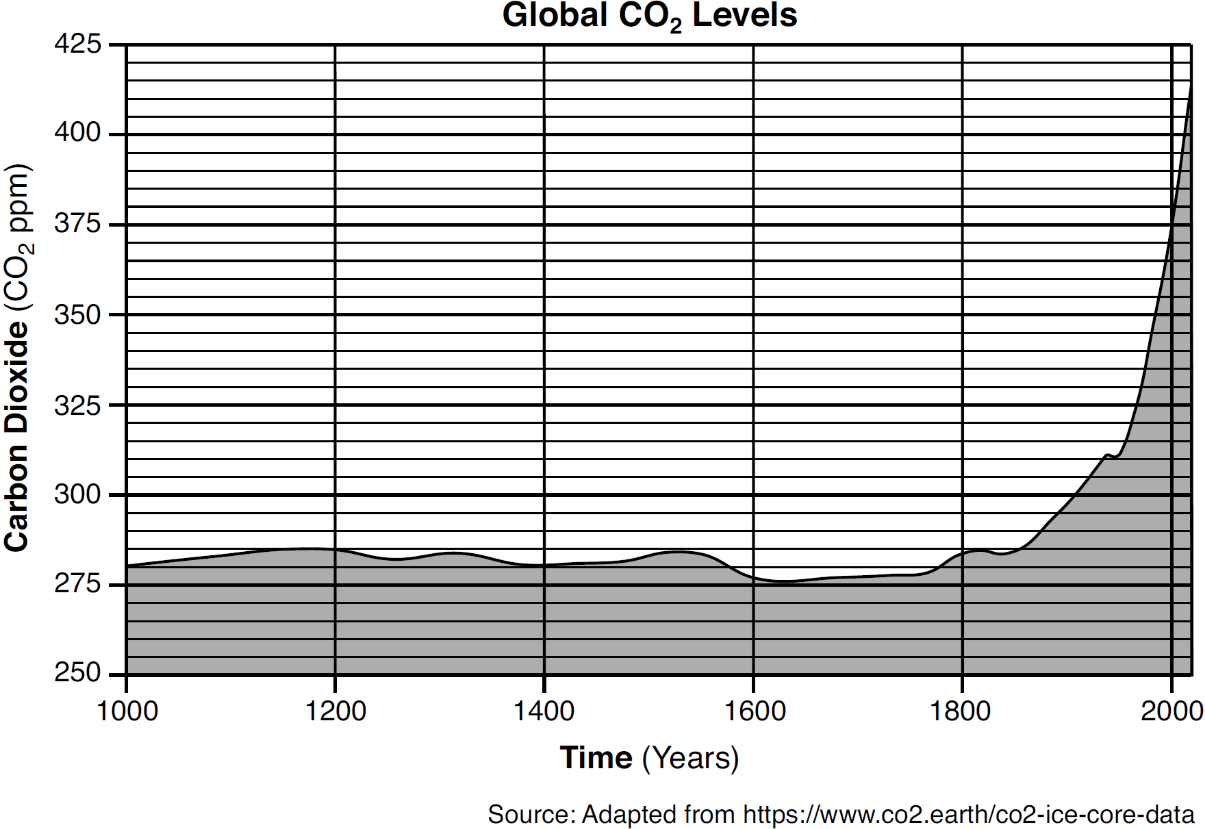
an increase of 95 ppm
What is a control group?
The control group is the group that does not get the experimental (independent) variable. They are "unaffected" and used to compare experimental finding back to.
What is the characteristic of living things that is NOT necessary for an individual organism to stay alive?
Reproduction
What are the levels of biological organization (starting with Organelle) from simplest to most complex.
Organelle -> cell -> tissue -> organ -> organ system -> organism
Analyze the date in this graph.
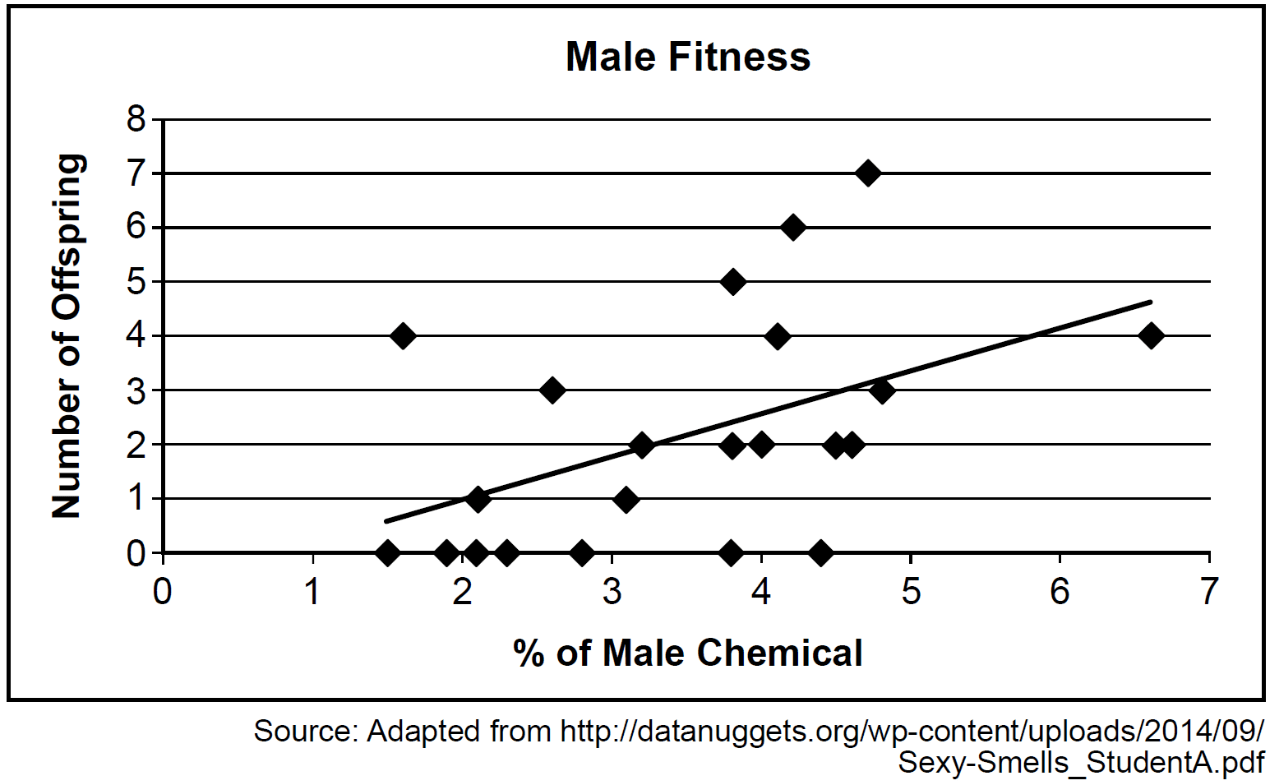
The higher the % of male chemical the higher the number of offspring . Males with more male chemical have high reproductive success.
What type of protein speeds up chemical reactions?
Enzymes
DAILY DOUBLE: Name something that could make an enzyme denature and not work and why.
What organelle makes enzymes?
Ribosomes
The graphs show the relative enzymatic activity of four different enzymes in acidic (below pH 7) and basic (above pH 7) environments. The activity of which enzyme decreases in both acidic and basic environments?
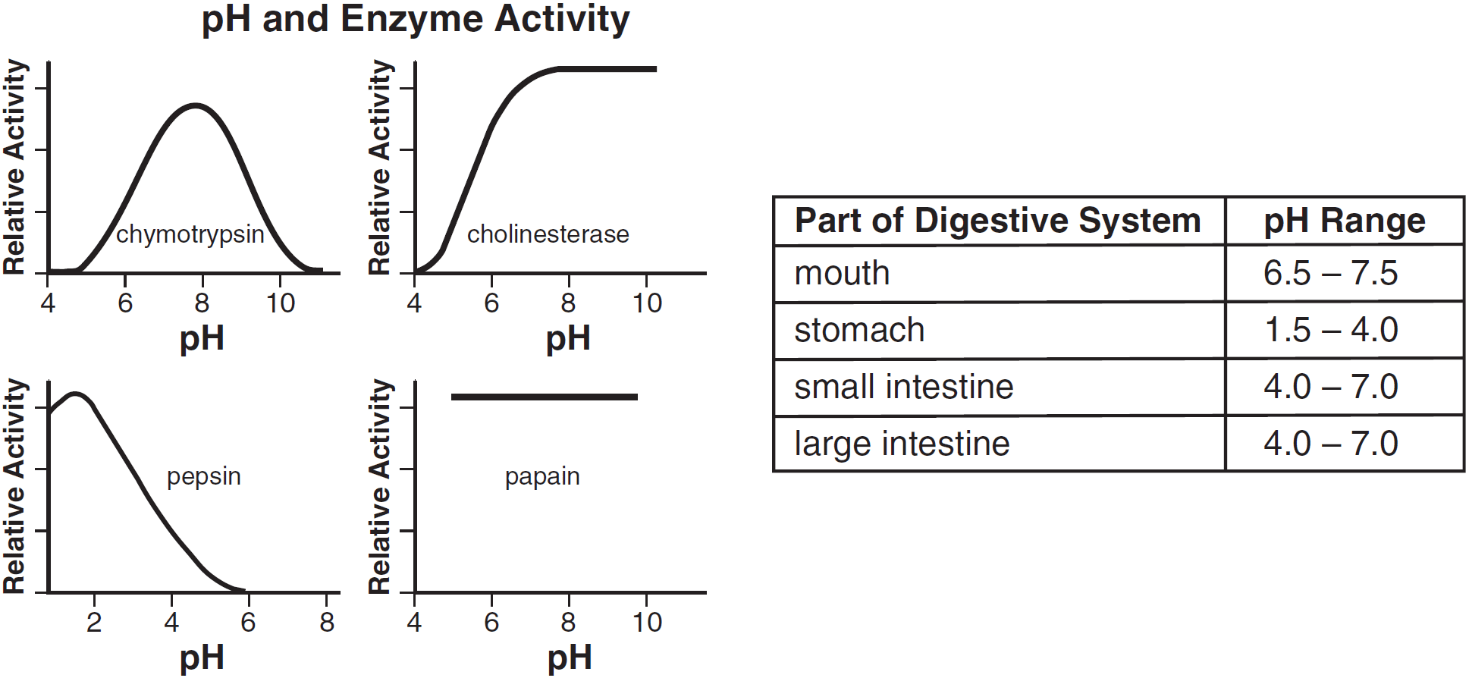
chymotrypsin
Cytoplasm in an amoeba and the circulatory system in rabbits are both examples of which life activity?
Transport
The diagram below is of a human cheek cell.
Select one of the lettered parts from the diagram and record the letter of the part chosen. Using or more complete sentences, state a function of the part.
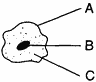
A. Cell membrane - It regulates the transport of materials into and out of the cell;
B. Nucleus - It controls the activities of the cell;
C. Cytoplasm - It provides a fluid like environment in which organelles are suspended and within which many biochemical processes occur.
Using information from the diagram, state one reason why the movement of molecules in method C represents active transport.
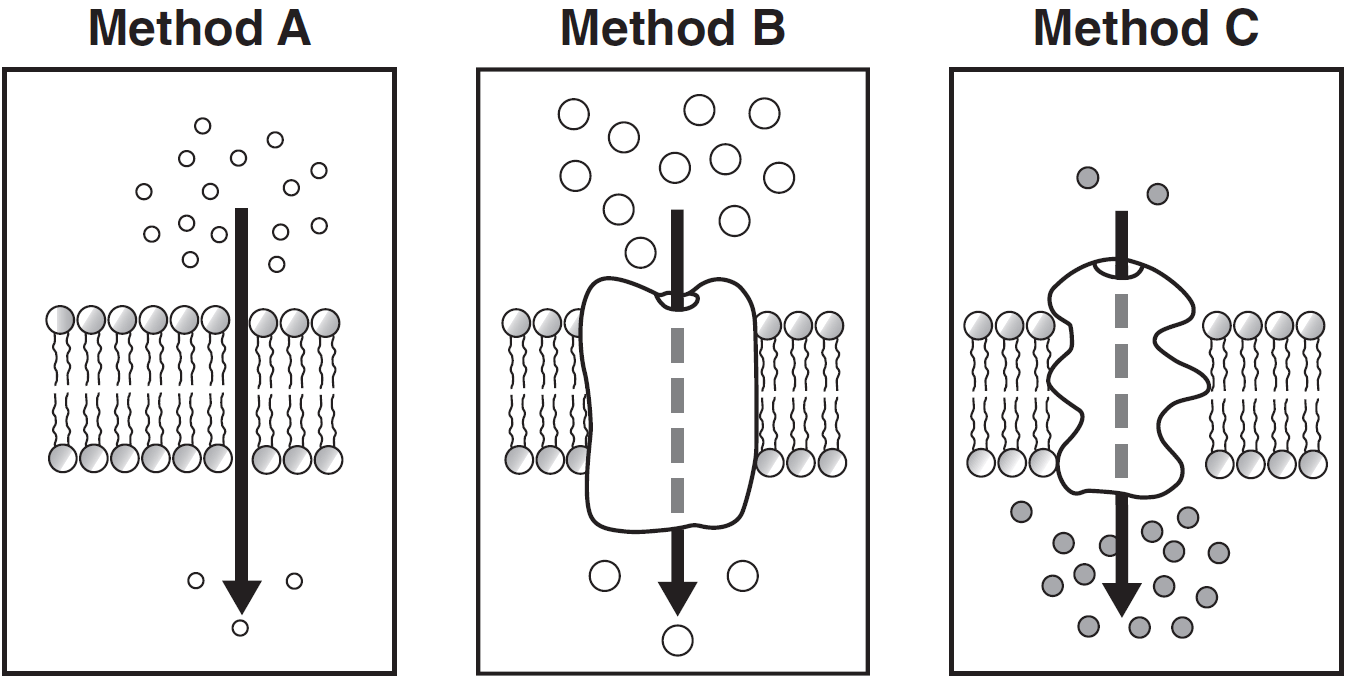
C shows the transport of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration. — The molecules are moving against the concentration gradient.
List the 4 major organic biomolecules and their building blocks or (monomers)
Proteins - Amino acids
Lipids - Fatty acid and glycerol
Carbohydrates - simple sugars (monosaccharides)
Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides
State which cell type would probably be most affected by mitochondrial diseases. Support your answer.
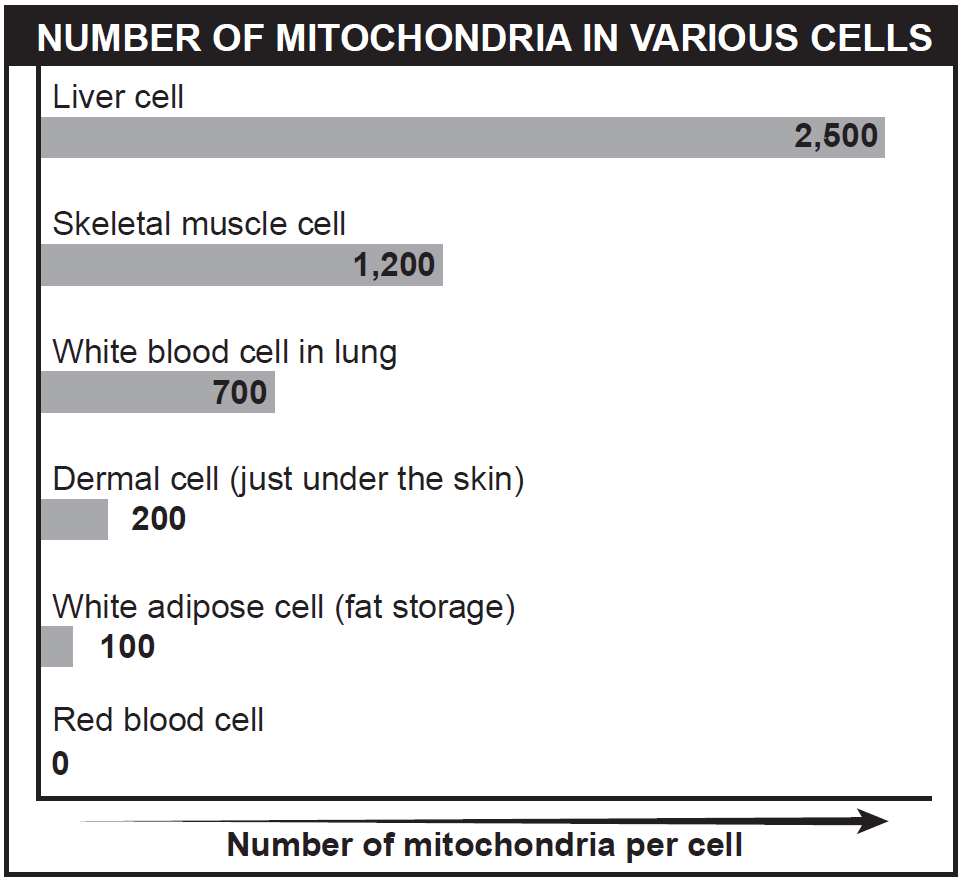
Liver cells may be most affected since they contain the most mitochondria.
Explain why putting stoppers in the test tubes could be dangerous.
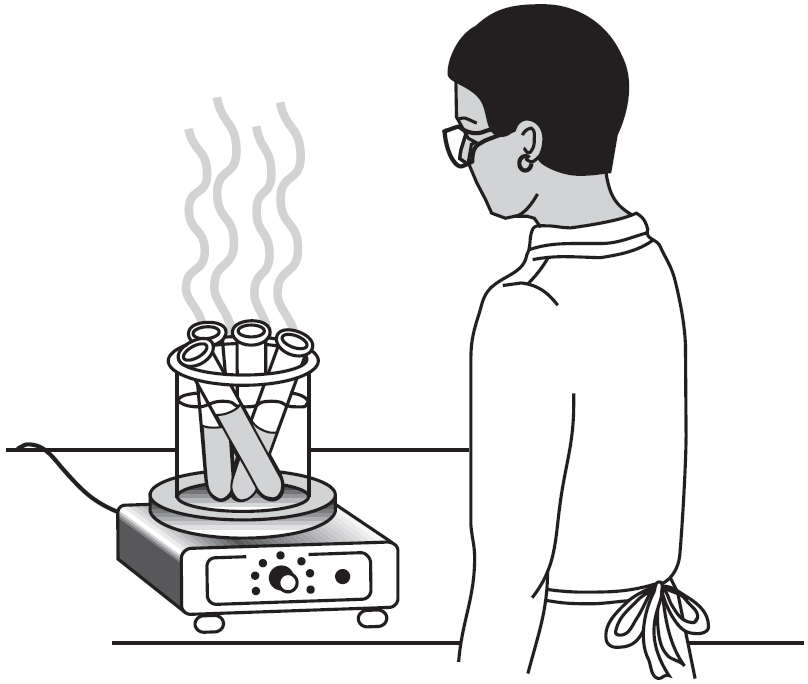
The stoppers would pop out of the heated tubes and possibly injure someone. — The test tubes may explode.
Two skin cells from the same animal were each placed in a different solution. The diagrams below represent the changes that occurred in each cell after 5 minutes in each solution. Which cell was placed in a solution containing a higher concentration of salt than the concentration of salt normally found in these skin cells? Support your answer.
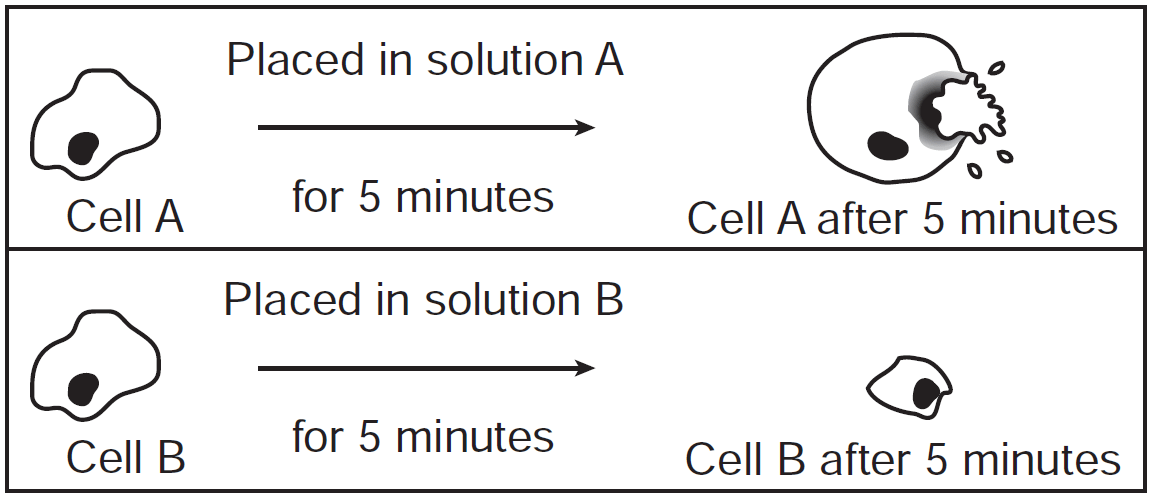
B - When cells are placed in a high salt concentration solution, they lose water and shrink.