Somatic
True or False. If false, correct the statement
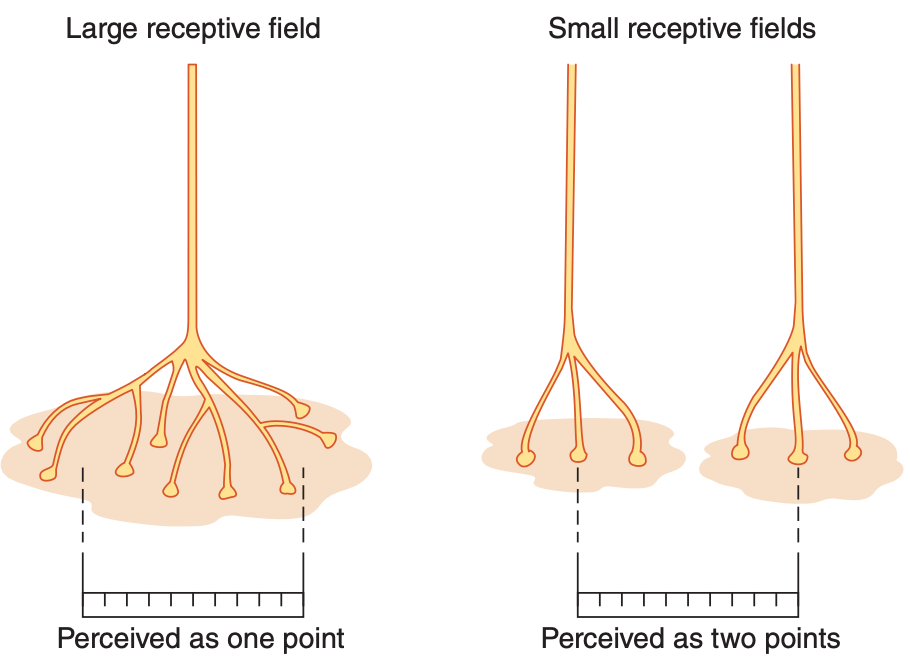
The larger the receptive fields, the greater the ability to discriminate two points, and the greater the tactile acuity.
FALSE
The corrected statement: The smaller the receptive fields, the greater the ability to discriminate two points, and the greater the tactile acuity.
What two special senses are associated with chemoreception? What are the receptors associated with each of these?
Olfaction (smell) and gustation (taste)
What region of the spinal cord do sympathetic preganglionic neurons originate?
The lateral horn, a region of gray matter between T1-L2
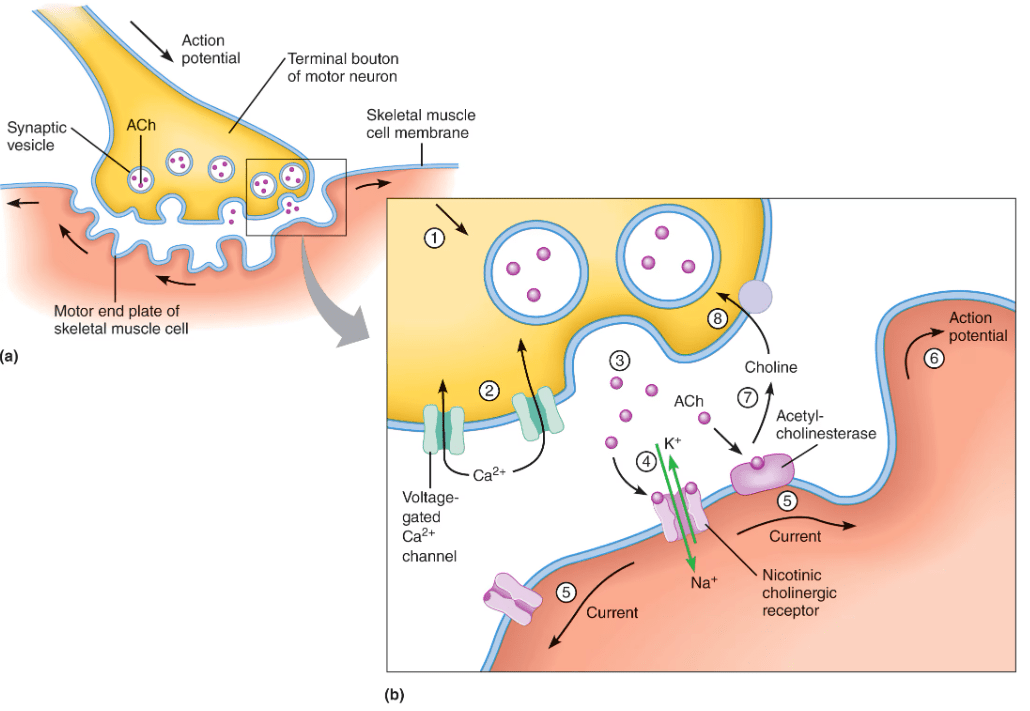
What is the synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle cell?
Neuromuscular junction
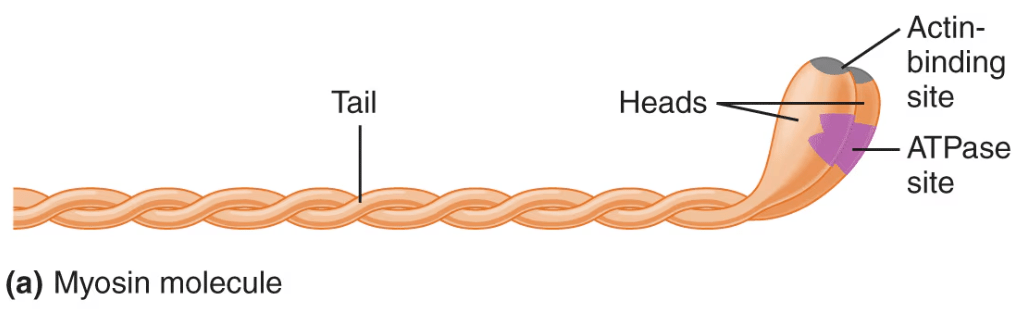
Myosin heads contain two important sites that facilitate cross-bridging. What are those sites?
Actin-binding site and the ATPase site
According to the anatomical definition, an artery is a blood vessel that __________.
a) transports blood toward the heart
b) transports oxygenated blood
c) transports blood away from the heart
d) none of the above
According to the anatomical definition, an artery is a blood vessel that __________.
c) transports blood away from the heart
The closing of the ______ valves is associated with heart sound 2 (dub)
The closure of the ______ valves is associated with heart sound 1 (lubb).
Which heart sound is the louder of the two?
Bonus for 100 points - what causes heart sound S3 and S4?
The closing of the semilunar valves is associated with heart sound 2 (dub)
The closure of the atrioventricular valves is associated with heart sound 1 (lubb)
Heart sound S1 is the louder, as the atrioventricular valves are larger than the SL valves and close with a greater force due to the high pressure developed as result of ventricular systole.
Bonus -
S3 - passive filling of ventricles with blood flow form vena cavae, pulmonary veins, and atria into ventricles
S4 - final filling of ventricles
What cranial nerve is responsible for conducting an impulse from the cochlea to the auditory cortex?
Cranial nerve VIII - the vestibulocochlear nerve (specifically the cochlear branch)
What is the area over which an adequate stimulus can produce a response (which can be either excitatory or inhibitory) in the afferent neuron
The receptive field is the area over which an adequate stimulus can produce a response (which can be either excitatory or inhibitory) in the afferent neuron
____ provide the ability to see in black and white during relatively low light conditions, such as the light provided by the moon at night.
____ provide us with color vision, but they are active only in relatively bright light, such as the sunlight during the day.
The ____ is the region of the retina with the highest visual acuity
Rods provide the ability to see in black and white during relatively low light conditions, such as the light provided by the moon at night.
Cones provide us with color vision, but they are active only in relatively bright light, such as the sunlight during the day.
The fovea is the region of the retina with the highest visual acuity
True or false. If false, correct the statement.
The sympathetic nervous system innervates the bronchioles and causes bronchodilation. The parasympathetic nervous system innervates the bronchioles as well and causes bronchoconstriction.
True.
What is a motor unit?
A motor neuron plus all the muscle fibers it innervates
The binding of _____ to troponin triggers muscle contraction by causing troponin to move tropomyosin aside, thereby exposing the myosin-binding sites on the actin molecules.
The binding of calcium to troponin triggers muscle contraction by causing troponin to move tropomyosin aside, thereby exposing the myosin-binding sites on the actin molecules.
What is the site of gas exchange between blood and interstitial fluid?
Bonus - why?
The capillaries are site of gas exchange between blood and interstitial fluid.
Surface area and the slow velocity at which blood flows through capillaries make them effective site of gas exchange
Intercalated discs consist of ___ and ____. Which of these structures helps the heart resist mechanical stress?
Intercalated discs consist of desmosomes and gap junctions. Desmosomes help the heart resist mechanical stress.
What muscle is antagonist to the biceps brachii while arm wrestling?
Pronator teres
The _______ states that a given sensory receptor is specific for a particular modality.
The law of specific nerve energies states that a given sensory receptor is specific for a particular modality.
What muscle in the eye controls the shape of the lens?
What happens to the shape of this muscle when it contracts? Is this better for seeing close objects or distant objects?
What happens to the shape of this muscle when it relaxes? Is this better for seeing close objects or distant objects?
The shape of the lens is controlled by the circularly arranged ciliary muscle through the tension it applies to the zonular fibers, which attach the ciliary muscle to the lens.
To achieve accommodation (the ability of the lens to increase its refractive power for viewing close objects), the ciliary muscle contracts, causing the lens to bulge and become rounder.
For viewing distant objects, the ciliary muscle relaxes, causing the lens to flatten
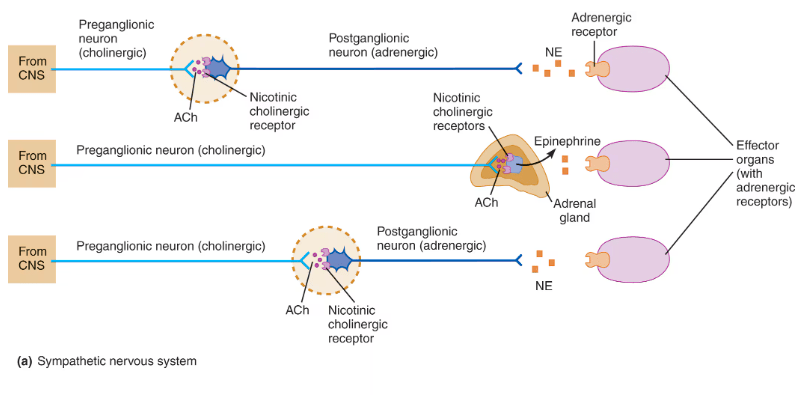
_____ is released by almost all sympathetic postganglionic neurons. Neurons that release this neurotransmitter are referred to as _______.
Norepinephrine is released by almost all sympathetic postganglionic neurons.
Neurons that release this neurotransmitter are referred to as adrenergic.
What is the sole neurotransmitter found in somatic nervous system?
Acetylcholine
When the myosin head is cocked, myosin is in a _____-energy configuration
When the myosin head is cocked, myosin is in a high-energy configuration
What separates the right and left atrium?
What separates the right and left ventricles?
The interatrial septum separates the right and left atrium
The interventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
Define autorhythmicity.
What are the autorhythmic cells of cardiac muscle?
Autorhythmicity refers to the ability of the heart to generate signals that trigger its contractions on a periodic basis—that is, to generate its own rhythm
Pacemaker cells and conduction fibers are the autorhythmic cells.
Autorhythmic cells generate little or no contractile force, but are critical to the heart’s pumping action because they coordinate and provide rhythm to the heartbeat.
_____ is due to defects in the tracts of the central nervous system associated with the auditory pathway or defects in the auditory cortex.
______ is a result of disruption of the cochlea, the hair cells specifically, or cranial nerve VIII.
Disruptions to the pathway of air conduction result in ______.
Central hearing loss is due to defects in the tracts of the central nervous system associated with the auditory pathway or defects in the auditory cortex.
Sensorineural hearing loss is a result of disruption of the cochlea, the hair cells specifically, or cranial nerve VIII.
Disruptions to the pathway of air conduction result in conductive hearing loss
The conversion of stimulus energy into a change in membrane potential is called ______________.
The energy form of a stimulus is called a _______________ (e.g., light waves, sound waves, pressure, temperature)
The form of energy to which a receptor responds is called its ___________.
The conversion of stimulus energy into a change in membrane potential is called transduction.
The energy form of a stimulus is called a modality (e.g., light waves, sound waves, pressure, temperature).
The form of energy to which a receptor responds best is called its adequate stimulus.
Identify the three layers of the retina. In which layer does phototransduction occur?
(1) an inner layer containing neurons called ganglion cells, whose axons make up CN II
(2) a middle layer containing neurons called bipolar cells
(3) an outer layer containing photoreceptors - rods and cones.
Photoreceptors transduce light energy into an electrical signal.
Which of the following is an incorrect pairing?
a. norepinephrine dilates the pupil
b. epinephrine increases blood pressure
c. acetylcholine decreases digestion
d. norepinephrine increases heart rate
c. acetylcholine decreases digestion
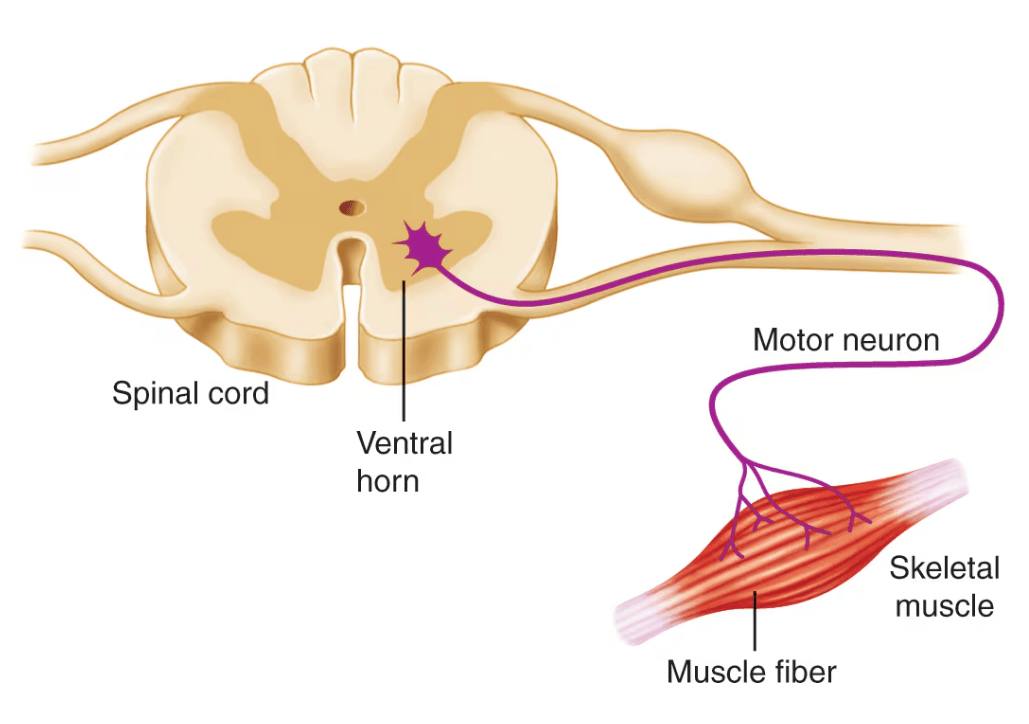
Where do motor neurons originate?
Motor neurons originate in the ventral horn of the spinal cord.
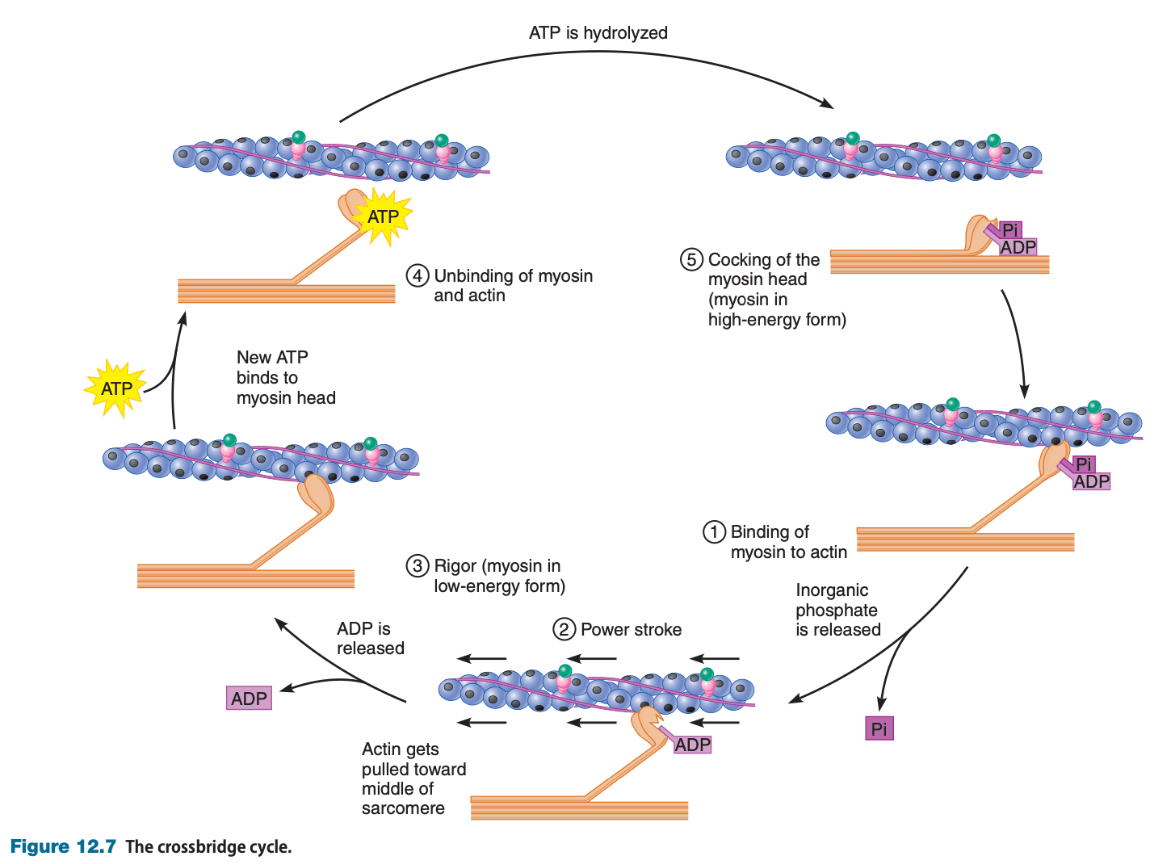
Put the events of the crossbridge cycle in the correct order, starting with the binding of myosin to actin:
a) binding of ATP
b) release of Pi
c) release of ADP
d) power stroke
1. b) release of Pi
2. d) power stroke
3. c) release of ADP
4. a) binding of ATP
What valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle? What valve separates the left atrium and the left ventricle?
What valve separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk? What valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta?
The tricuspid valve (or the right atrioventricular valve) separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. The bicuspid valve (or the mitral valve or the left atrioventricular valve) separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
The pulmonary semilunar valve separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk. The aortic semilunar valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta.
The pulmonary semilunar valve opens when __________.
a) left ventricular pressure > pulmonary vein pressure
b) left ventricular pressure > pulmonary artery pressure
c) right ventricular pressure > pulmonary artery pressure
d) right ventricle pressure > right pulmonary vein pressure
c) right ventricular pressure > pulmonary artery pressure
What is the ability to change the focal point of the eye from focusing on a distant object to focusing on a close object?
Accommodation is the ability to change the focal point of the eye from focusing on a distant object to focusing on a close object?
_______ is the phenomenon that increases the contrast between activated receptive fields and their inactive neighbors, thus facilitation identification of the location of a stimulus.
Lateral inhibition is the phenomenon that increases the contrast between activated receptive fields and their inactive neighbors, thus facilitation identification of the location of a stimulus.
The ____ of sound is coded by the degree of bending of the stereocilia, whereas the ____ of sound is coded for by the location of hair cells on the basilar membrane
The loudness of sound is coded by the degree of bending of the stereocilia, whereas the pitch of sound is coded for by the location of hair cells on the basilar membrane
_________ are axon swellings located at intervals of autonomic postganglionic neurons. Their function is the same as axon terminals with respect to synthesis of, storage and release of neurotransmitters in vesicles.
Varicosities are axon swellings located at intervals of autonomic postganglionic neurons. Their function is the same as axon terminals with respect to synthesis of, storage and release of neurotransmitters in vesicles.
Where is the motor end plate found in the neuromuscular junction - on the membrane of the the motor neuron or the muscle fiber?
The motor end plate is a specialized region of plasma membrane found on the muscle fiber.
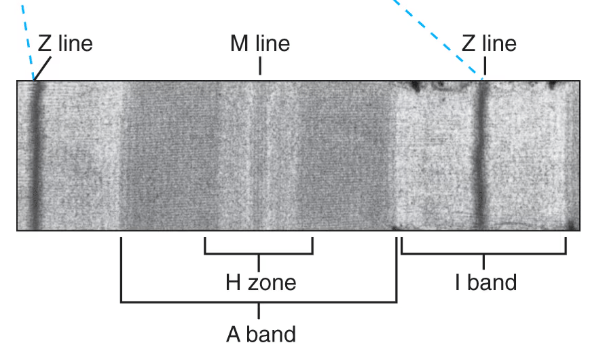
True or false. If false, correct the statement
The A band doesn't change length during contraction and it contains the entirety of I band and some of the myosin
False:
The first part of the statement was true - that the A band doesn't change length during contraction.
It is not true that the A band contains the entirety of the I band and some of the H zone. Rather, the A band contains all of the H zone and some of of the overlapping actin filaments, none of which would be considered part of the I band.
True or false: The apex of the heart is superior to the base.
If false, correct the statement.
FALSE: The apex of the heart is inferior to the base.
_____ detects the potential at the left arm minus that at the right arm;
_____ detects the potential at the left leg minus that at the right arm; _____ detects the potential at the left leg minus the left arm.
Lead I detects the potential at the left arm minus that at the right arm; lead II detects the potential at the left leg minus that at the right arm; lead III detects the potential at the left leg minus the left arm.
If a person is given the following prescription for eyeglasses: OD -1.25 and OS -1.75
Does this person have myopia or hyperopia?
Myopia
Distinguish between tonic receptors and phasic receptors. Provide an example of each.
Phasic receptors are rapidly adapting receptors that fire when they first receive a stimulus but cease firing if the strength of the stimulus remains constant.
Phasic receptors are attuned specifically to changes in a parameter. Once a stimulus reaches a steady intensity, phasic receptors adapt to the new steady state and turn off.
E.G. - Pacinian corpuscles & meissner's corpuscles (vibration receptors), hair follicle receptors, thermoreceptors
Tonic receptors are slowly adapting receptors that fire rapidly when first activated, then slow and maintain their firing as long as the stimulus is present.
Examples - Free nerve endings, merkel's discs (superficial pressure), Ruffini's ending (deep pressure)
The fluid in the scala media is called _____, which has a ____ potassium (K+) concentration and a ____ sodium (Na+) concentration.
The fluid in the scala media is called endolymph, which has a high potassium (K+) concentration and a low sodium (Na+) concentration.
True or false. If false, correct the statement.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for increasing the heart rate and vasodilation (i.e., dilation of the blood vessels). The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for decreasing the heart rate and vasoconstriction (i.e., narrowing of the blood vessels).
False:
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for increasing the heart rate and vasodilation (i.e., dilation of the blood vessels), but it is also responsible for vasoconstriction.
The parasympathetic nervous system is indeed responsible for helping to decrease the heart rate, but it does not innervate the vasculature.
What neurotransmitter will result in constriction of the pupil?
a. norepinephrine
b. acetylcholine
c. epinephrine
d. serotonin
b. acetylcholine
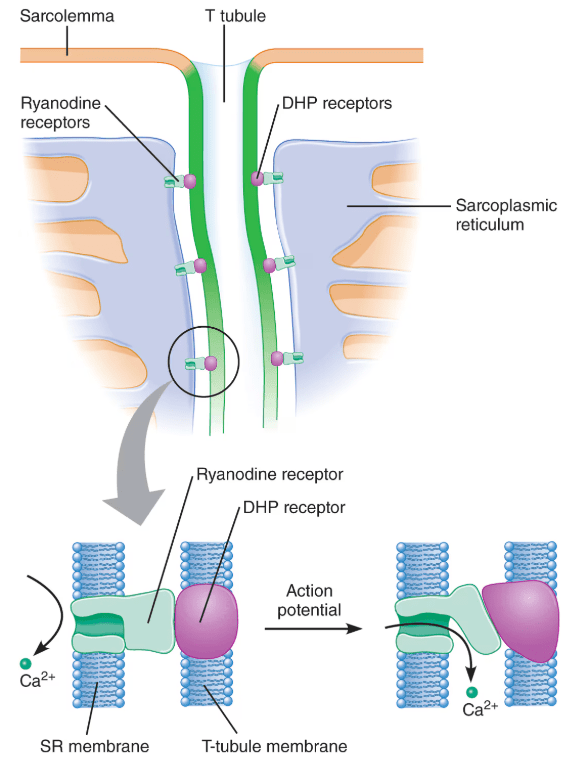
Where do you find the DHP receptor? Where do you find the ryanodine receptor? What are their functions?
DHP receptors are found in the T tubule membrane and function as voltage sensors.
Ryanodine receptors are found in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane and connected to the DHP receptor; they are also calcium channels.
Describe the electrical event associated with each wave of ECG. What is the mechanical event that these precede?
a. P wave
b. QRS complex
c. T wave
a. P wave - atrial depolarization
=> precedes atrial contraction
b. QRS complex - ventricular depolarization
=> precedes ventricular contraction
c. T wave - ventricular repolarization
=>precedes ventricular relaxation
The influx of which ion accounts for the plateau
phase?
a. sodium
b. potassium
c. chloride
d. calcium
d. calcium
______ is used to detect conductive hearing loss by comparing air conduction with bone conduction.
_____ uses the localization of hearing to detect either conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
Bonus for 100 points- what test is used to test the proper functioning of the vestibular apparatus? What is the direction of eye movement during post-rotational nystagmus after clockwise spinning?
Rinne's test is used to detect conductive hearing loss by comparing air conduction with bone conduction.
Weber's test uses the localization of hearing to detect either conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
Bonus - Barany's test and past pointing
Fast eye movements (in post-rotational nystagmus) will occur in opposite direction as the person was rotated, i.e. counterclockwise
Slow eye movements will occur in same direction as person was rotated, i.e., clockwise
The organ of Corti is found on the ______ membrane within the cochlea
The organ of Corti is found on the basilar membrane within the cochlea.
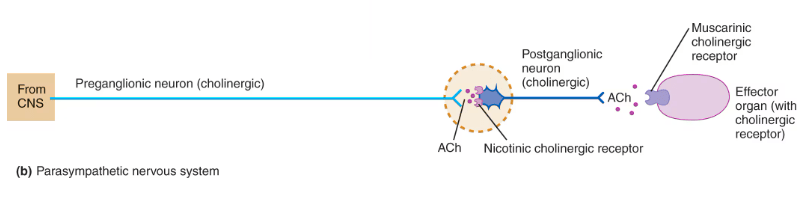
Go the board and draw out the parasympathetic pathway of preganglionic and postganglionic fibers and indicate the type of receptor found at each synapse.
What is another term for the axon terminals of motor neurons?
Terminal boutons
What is the mechanism that drives the sliding of thick and thin filaments past one another, i.e., what generates the force for contraction?
Crossbridge cycle
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium - outer connective tissue layer
Myocardium - middle muscular layer
Endothelium - layer of epithelial cells lining inner surface of walls of all blood vessels and heart
Ventricular relaxation immediately follows
________.
a. atrial depolarization
b. ventricular repolarization
c. ventricular depolarization
d. atrial repolarization
b. ventricular repolarization
The _____ of sound measures the pitch of sound, measured as number of cycles or oscillations per second.
The ______, or loudness of sound is determined by the amount of deformation of the hair cells.
The frequency of sound measures the pitch of sound, measured as number of cycles or oscillations per second.
The intensity, or loudness of sound is determined by the amount of deformation of the hair cells.
Identify the general receptor type associated with the following stimuli
-the smell of coffee
-smashing your thumb in your car door
-high blood pressure
-the smell of coffee - chemoreceptor
-smashing your thumb in your car door - nociceptor
-high blood pressure - baroreceptors
Which region of the ear is associated with the amplification of sound?
The middle ear
Go to the board and draw out the sympathetic pathway, indicating the length of the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers, and indicate the type of receptors found at each synapse.
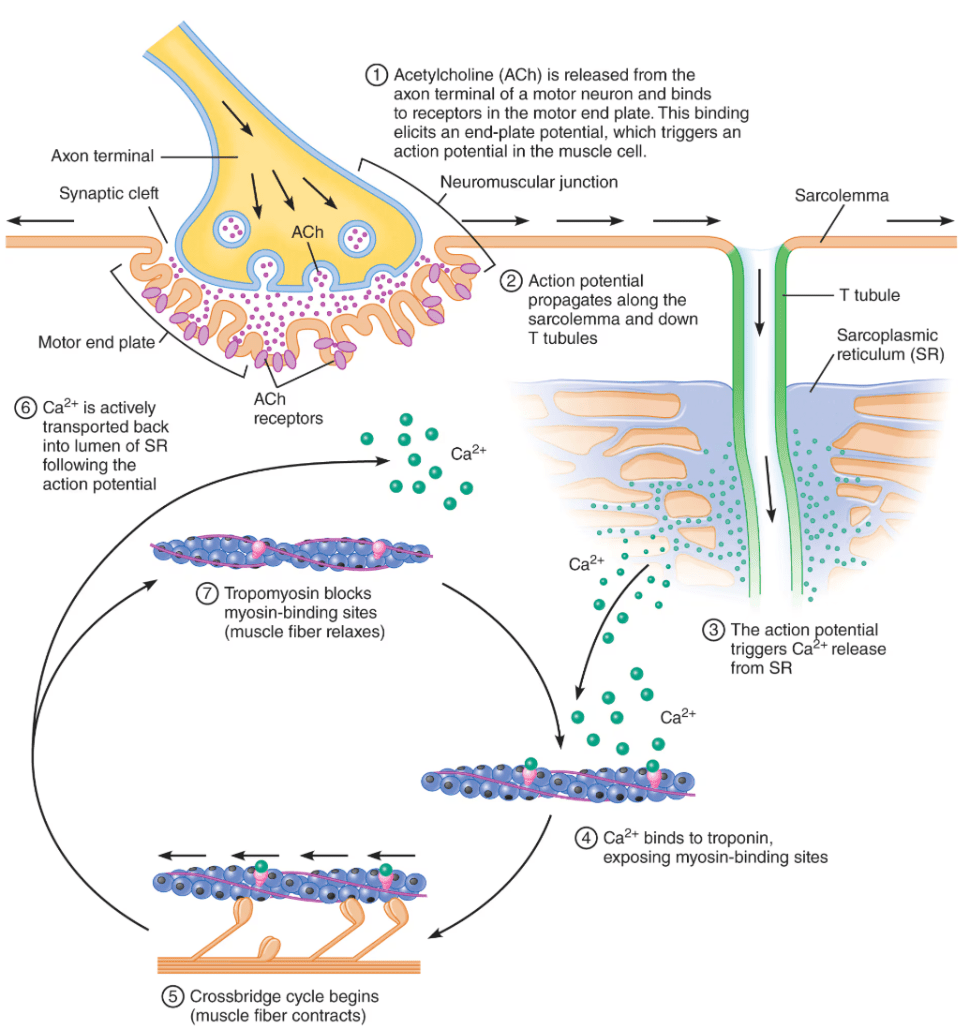
What is an end-plate potential (EPP)? What causes an EPP?
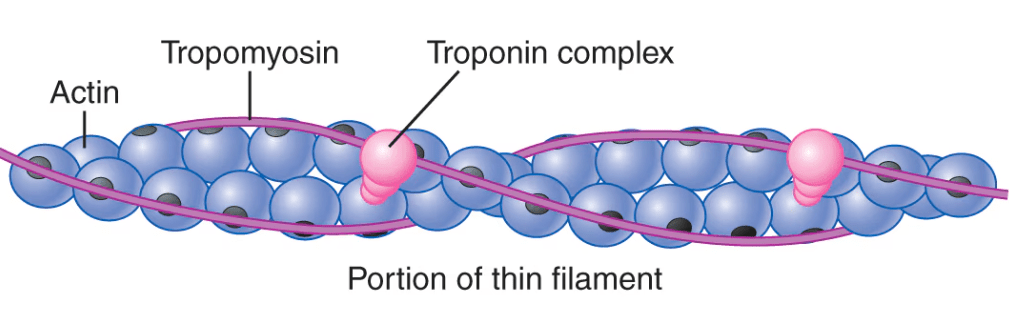
True or false. If false, correct the statement
Tropomyosin is a regulatory protein that blocks the actin-binding sites on myosin in muscles at rest.
False
Tropomyosin is a regulatory protein that blocks the myosin-binding sites on actin in muscles at rest.
True or false:
During isovolumetric relaxation in the cardiac cycle, all valves are closed and ventricular pressure is increasing.
False
During isovolumetric relaxation in the cardiac cycle, all valves are closed and ventricular pressure is decreasing.
What is the proper term for each of the following?
a. number of heart contractions per minute
b. volume of blood in the ventricle before the heart contracts
c. volume of blood left in ventricles after contraction
d. volume of blood that enters the aorta with each contraction
a. Heart rate
b. EDV
c. ESV
d. Stroke volume
Consider a person who is focusing on an object that is being moved further away from eyes. Describe what is occurring in the eye movement, the pupils, the ciliary muscles, and the lens
The eyes diverge
The pupils dilate
The ciliary muscles relax
The lenses thin
Identify two neurotransmitters released from primary afferent neurons and binds to receptors on second-order neurons in the pain pathway.
Substance P and glutamate
Define refraction and its importance in vision. What two structures of the eye are associated with refraction? Which one has higher refractive power?
Refraction refers to the bending of light waves as they pass through transparent materials of different densities.
Refraction is important in the focusing of light waves on the retina.
The cornea and the lens both refract light waves.
The cornea has three times the refractive power as the lens.
Identify the three major areas of the brain that regulate autonomic function.
Which one of these areas initiates the fight-or-flight response?
The major areas of the brain that regulate autonomic function include the hypothalamus, pons, and medulla oblongata.
The hypothalamus initiates the fight-or-flight response to elicit widespread activation of the sympathetic nervous system when a person is in danger or is otherwise excited.
Effector organs of the autonomic nervous system include all of the following except
a. Heart muscle.
b. Smooth muscle in the pupils of the eye.
c. Respiratory muscles.
d. Sweat glands.
e. Salivary glands.
C. Respiratory muscles
Those are innervated by the somatic nervous system.
When a muscle cell receives input from a motor neuron, the cell depolarizes and fires an action potential that then stimulates contraction. What do you call the sequence of events that link the action potential to the muscle contraction?
Excitation-contraction coupling
All valves open and close based on a ______ gradient
All valves open and close based on a pressure gradient
Describe the conduction system of the heart, starting with the pacemaker of the heart.
1. AP is initiated in pacemaker cells of SA node.
2. Impulse travels by way of internodal pathways to the AV node.
3. impulse travels to atrioventricular bundle, or bundle of His located in the interventricular septum
4. Signal splits into left and right bundle brances, which conduct impulse to left and right ventricles, respectively
5. Impulse travels through Purkinje fibers, which spread through ventricular myocardium from the apex toward the valves. Impulses travel through rest of myocardial cells.
Vision Tests
The _____ is used to test visual acuity, or the ability of focus incoming light on the retina.
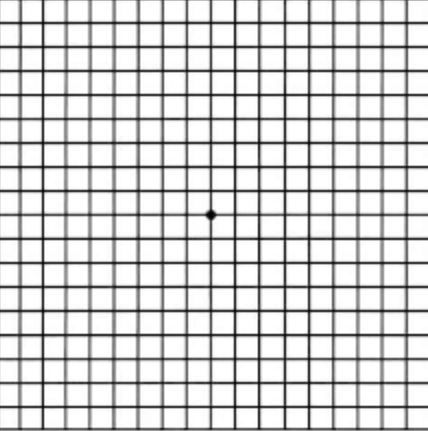
The ______ is used to detect changes in/damages to the retina and the neural pathway.
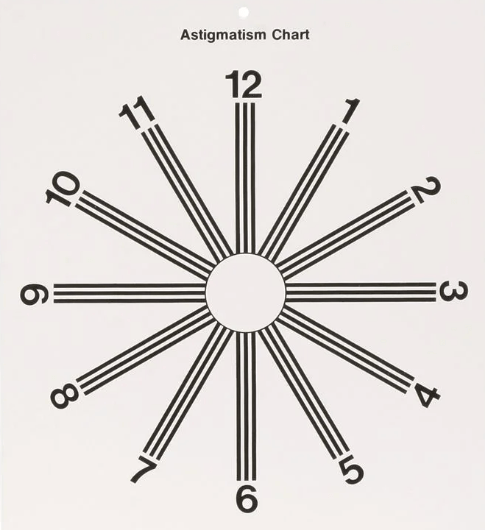
The _______ is used to test for astigmatism (uneven cornea thickness)
The Snellen chart is used to test visual acuity, or the ability of focus incoming light on the retina.
The Amsler grid is used to detect changes in the retina as well as in the optic nerve and pathway of visual information in the brain.
The Green's chart is used to test for astigmatism (uneven cornea thickness)
The _______ states that somatic signals of non-painful sources can inhibit signals of pain at the spinal level
The gate-control theory states that somatic signals of non-painful sources can inhibit signals of pain at the spinal level
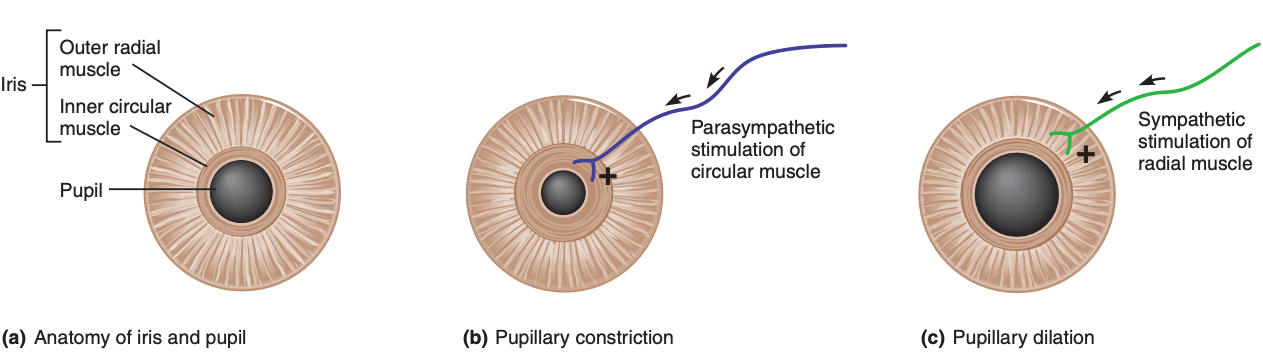
What muscle regulates the amount of light entering the eye?
Identify the two layers of this muscle. Which layer is associated with pupil dilation, and which layer is associated with pupil constriction?
The iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye by changing diameter of pupil
Inner circular layer is associated with pupil constriction
Outer radial layer is associated with pupil dilation.
Atropine acts on ________ receptors to treat vagal-induced fainting and gastric ulcers, as well as to induce pupillary dilation for purposes of viewing retina
Atropine acts on muscarinic cholinergic receptors
Somatic motor pathways
a. are excitatory or inhibitory?
b. are composed of a single neuron or a preganglionic and a post-ganglionic neuron?
c. synapse with glands or with smooth, cardiac, or skeletal muscle?
Somatic motor pathways are
a. excitatory
b. composed of a single neuron
c. synapse with skeletal muscle
What are the two functions of ATP within the muscle cell?
1. ATP supplies the energy for muscle contraction to take place. In addition to its direct role in the cross-bridge cycle,
2. ATP also provides the energy for the active-transport Ca++ pumps in the SR.
Distinguish between the two members of each of the following pairs:
a. end-systolic volume (ESV) and end-diastolic volume (EDV)
b. sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart rate
c. diastole and systole
d. systemic and pulmonary circulation
e. AV node and SA node
(a) ESV—volume of blood in ventricle at end of contraction; EDV—volume of blood in the ventricle at beginning of contraction
(b) sympathetic - increases HR; parasympathetic - decreases HR
(c) diastole - relaxation of ventricles (phases 1 & 4); systole - contraction of ventricles (phases 2 & 3)
(d) Pulmonary circulation goes to the lungs; systemic goes to rest of body
(e) SA node is the (atrial) pacemaker; AV node transmits signals from atria to ventricles
Define the cardiac cycle.
What are the four stages of the cardiac cycle?
Which of these events are associated with diastole, and which of these stages are associated with systole?
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of all the electrical and mechanical events associated with a single heartbeat.
1. Ventricular filling
2. Isovolumetric contraction
3. Ventricular ejection
4. Isvolumetric relaxation
Phases 1 and 4 are associated with diastole (relaxation of ventricles).
Phases 2 and 3 are associated with systole (contraction)