Contractions that help the mother's body prepare for true labor; do not indicate that labor has begun.
What is Braxton-Hicks contractions?
Method of assessing the fetal heart rate that requires the use of gel
What is Doppler?
method involving ultrasonic transmission of fetal heart rates; it requires use of a gel.
Epidurals and Spinals cannot be given when a patient's lab results show _________________, which can be seen in cases of PIH and HELLP.
What are low platelets?
A patient complains of a headache and seeing blurry spots. The nurse knows these are symptoms of what complication?
What is preeclampsia
Simple things a nurse can do to help during labor
Lighting and temperature
◦ Cleanliness and mouth care
◦ Bladder
◦ Positioning
◦ Water
◦ Providing encouragement
◦ Pharmacologic pain relief
Effacement of the cervix
What is the thinning and shortening of the cervix to allow for easier passage of the fetal head during the first stage of labor?
What is a biophysical profile or BPP.
Use of ultrasound to look for fetal breathing, tone, movement, and amniotic fluid volume.
A form of anesthesia that is administered to mothers in labor both for vaginal and cesarean births which numbs the pain of labor without affecting the mother's ability to push.
What is an epidural?
A small cut that prevents tearing during delivery
What is an episiotomy?
Nursing jobs during labor and delivery
What is care and assessment of the newborn and administration of medication such as oxytocin to
contract the uterus and control blood loss?
A patient in preterm labor is receiving betamethasone, what is the indication for this
What is to enhance fetal lung maturity
1)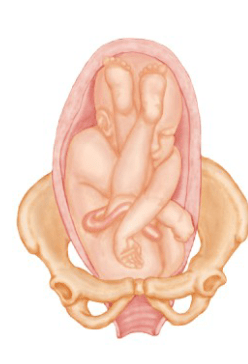 2)
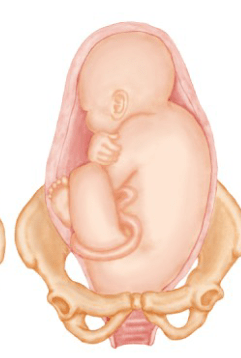
2)
3)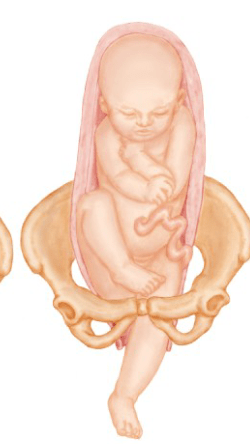
what presentations are these?
1)Frank breach
2) Full breach
3) single footed breach
Use of a fetal monitor to evaluate fetal well-being where you want to see 2 accelerations in 20 minutes and moderate variability.
What is a non-stress test or NST.
Breathing pattern used during contractions
What is pattern-paced breathing?
A patient is presenting with ruptured membranes, what tests will be performed to confirm rupure?
What is a speculum exam to look for pooling, nitrazine swab, ferning on a slide
.
There are three phases within the first stage of labor
What is latent, active, and transition?
Name at least 2 nursing considerations and care for the patient with an epidural.
What is continuous fetal heart rate monitoring, BP, pulse ox., foley cath, can NOT get out of bed.
What are: respiratory depression, N/V from decreased gastric emptying, sedation, tachycardia, hypotension, decrease variability of fetal heart rate.
Major side effect of opioid analgesics
What is respiratory depression?
Cardinal mechanisms of labor
List 7 of them
• Engagement: The baby’s head enters the pelvic inlet.
• Descent: The baby’s head descends further into the pelvic cavity. This occurs throughout labor, aided by uterine contractions, amniotic fluid pressure, and maternal pushing.
• Flexion: As the baby’s head descends and encounters resistance from the pelvic bones and soft tissues, it naturally tucks its chin toward its chest, presenting the smallest head diameter to the birth canal.
• Internal rotation: The baby’s head rotates about 90 degrees to align with the long axis of the body as it moves down the pelvis, typically from an orientation where the baby is facing sideways to facing the mother’s back.
• Extension: As the baby’s head passes under the pubic bone, it extends backwards, with the chin leaving the chest, so that the head can fully emerge.
• External rotation: After the head is delivered, it rotates again so that the baby’s face is turned towards one of the mother’s inner thighs, allowing the shoulders to align with the pelvic outlet.
• Expulsion: Following delivery of the head and shoulders, the rest of the baby’s body is delivered relatively easily and quickly.
Observations to look for in fetal heart monitoring
(VEAL CHOP)
What is variable deceleration, cord compression, early deceleration, head compression, acceleration, oxygenation, late deceleration, and placental insufficiency?
Four components of Bishop's scoring system
What are dilation, effacement, fetal station, and cervical consistency?