This difference between two atoms is often a good predictor of the type of bond that will form between them.
electronegativity
The unreactive series of elements in the periodic table due to their already full valence electrons.
Nobel Gases
A type of shorthand for representing bonding and non-bonding valence electrons in molecules and ions.
Lewis (dot) Structures
The outermost energy level of an atom, often considered full or stable with 8 electrons
Valence Shell
The charge separation produced by polar covalent bonds
dipole
The unit of measure for electronegativity
Pauling
The trend for electronegativity as you move from left to right on the periodic table
Increasing
What are the two dots above Nitrogen?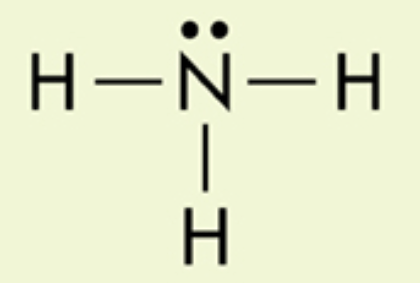
non-bonding pair of electrons
VSEPR
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule; often determines if a dipole exists when more than 2 atoms form a molecule
Molecular Geometry
An electronegativity difference of less than 0.4 between two atoms
non-polar covalent
the number of valence electrons is determined by this
group number
Moving from single to double to triple bonds, these increase and decrease respectively.
What is bond energy and bond length
180 degree bond angle (molecular)
linear
dipole-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding and London dispersion forces are examples of this
Intermolecular forces
The energy in a molecule is stored here
chemical bonds
the number of energy levels is determined by this
period
repulsion between this type of electron pair is strongest
non-bonding pairs
120 degree bond angles
trigonal planar
the weakest of the intermolecular forces
London dispersion forces
In this type of bonding, the shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative of the two atoms.
Polar Covalent
This series of elements has a greater attraction for electrons because their valence shell electrons are closer to a complete octet
non-metals
- A molecule can have polar bonds, but be non-polar because its dipoles are arranged in a way so that they ________ each other.
cancel
Although this molecule has polar bonds, the molecule itself is non-polar because _________
180 degree bond angle; force cancellation
the strongest of the intermolecular forces
hydrogen bonding