Aluminum has this many valence electrons
What is 3
Resonance structures share the same:
What are formal charges
OR
What are arrangement of atoms
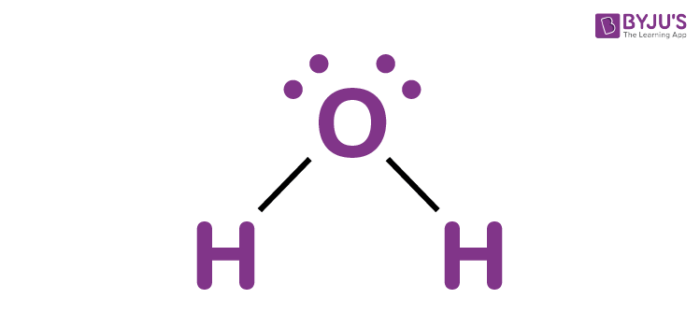 Molecular geometry for a water molecule
Molecular geometry for a water molecule
What is bent?
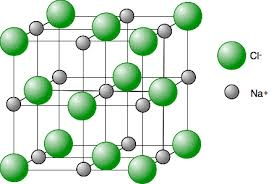 This is the force that holds together an ionic lattice
This is the force that holds together an ionic lattice
electrostatic force (between positive and negative ions)
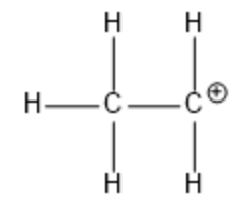
Where is the +1 formal charge?
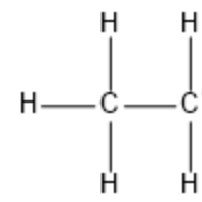
The molecule CH4 has a total of how many valence electrons
What is 8.
When writing resonance structures, what are two things you should always include.
brackets, double arrows, formal charges, electron pushing arrows
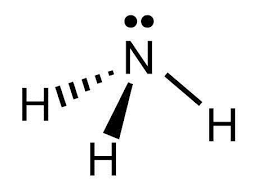 Molecular geometry for an ammonia molecule
Molecular geometry for an ammonia molecule
What is trigonal pyramidal?
What is one factor that determines the strength of an ionic bond?
atomic radius, charge
What is the overall charge on this molecule:

what is the overall charge on this?
H2SO4 - no charge
An example of an element that can have greater than an octet of electrons in Lewis structures
If a sulfur atom has two unpaired electrons around it, how many bonds must it have in order to have a formal charge of 0?
What is 4.
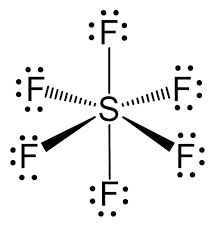 VSEPR shape of SF6
VSEPR shape of SF6
octahedral
NaF or NaI
NaF because F has the smaller atomic radii
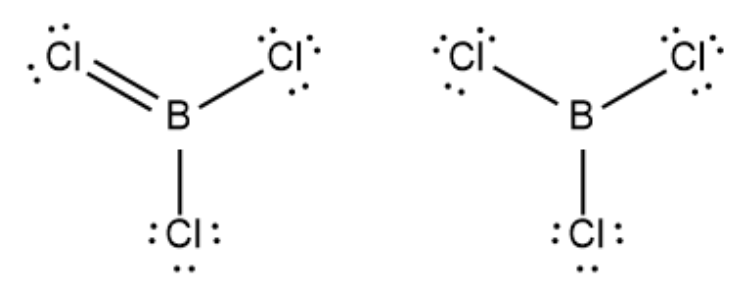
Which of these structures would be able to have resonance? Left or Right?
Left
If an ion has a negative charge, when determining the total number of valence electrons in the ion, one must:
add electrons equal to the charge.
The ozone molecule, O3, has this many resonance structures.
What is 2.
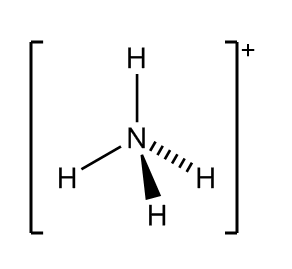 Molecular geometry for an ammonium molecule
Molecular geometry for an ammonium molecule
What is tetrahedral?
Higher melting point: NaF or H2O
NaF

Which is the most likely molecular structure for the nitrite (NO2−) ion?
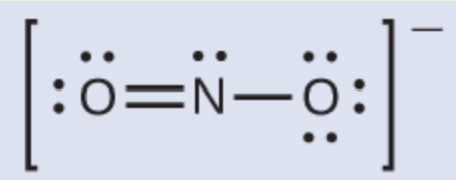
Name an element that, when in a molecule, can have less than 8 valence electrons associated with it.
What is H, He, B, or Be.
For a neutral molecule, the sum of formal charges is equal to:
0
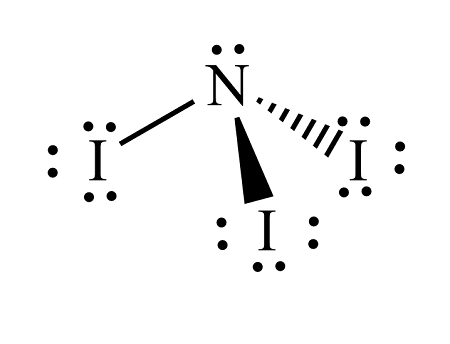 Nitrogen triiodide has this VSEPR Shape
Nitrogen triiodide has this VSEPR Shape
trigonal pyramidal
Higher melting point: CaCl2 or NaCl
Calcium chloride (CaCl₂) has a higher melting point than sodium chloride (NaCl) because the calcium ion (Ca²⁺) has a higher charge than the sodium ion (Na⁺), leading to stronger ionic bonds and a higher lattice energy.
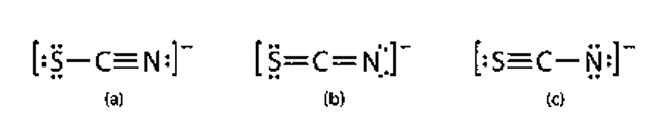
using formal charges, which is most likely to exist? (Hint: N is more electronegative than S)
(b) less formal charges than (c) & N is more electronegative than S