a dense core of neutrons that remains after a Supernovae
What is Luminosity
the true brightness of an object
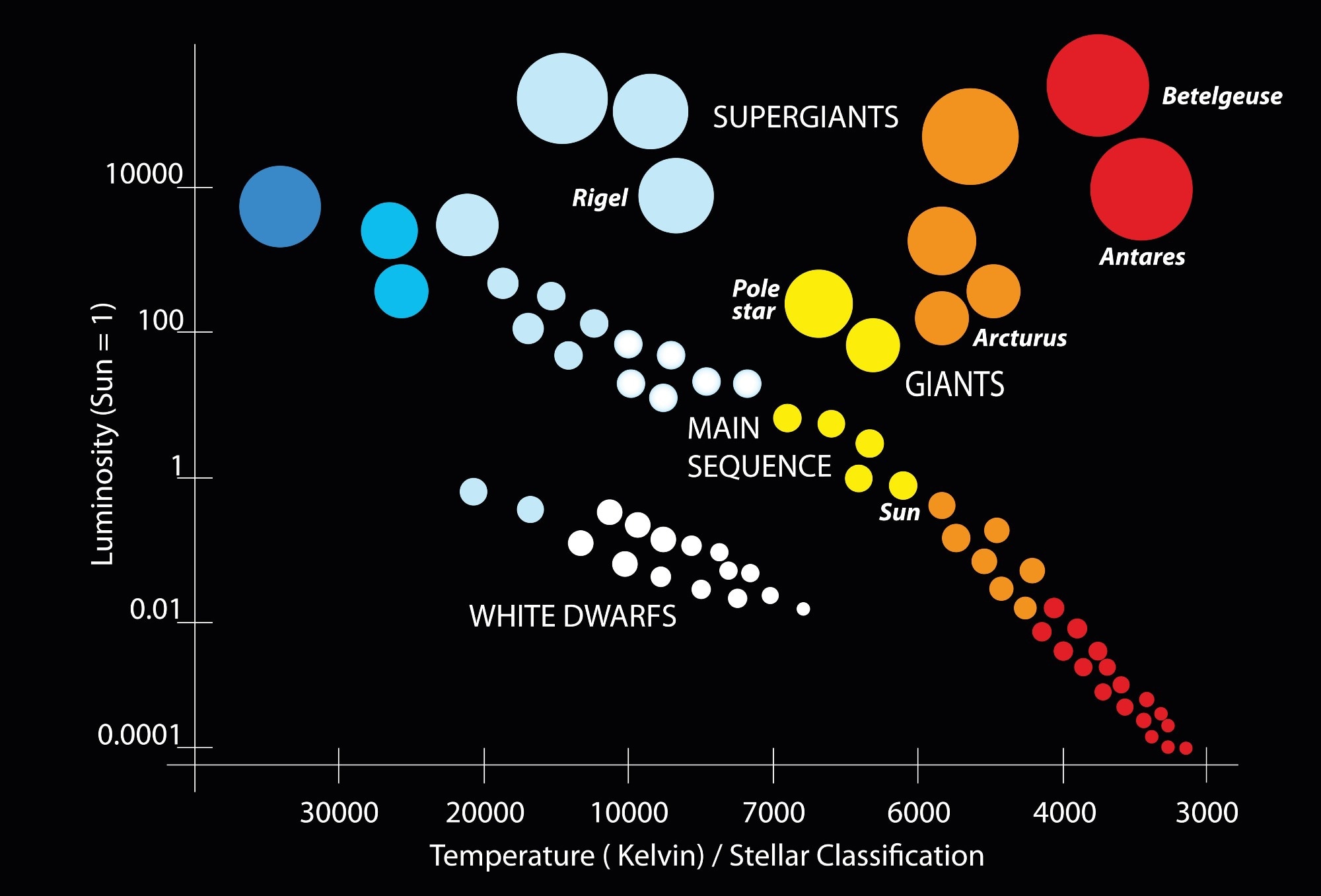 What does the x-axis on a H-R diagram display?
What does the x-axis on a H-R diagram display?
decreasing temperature
During a star's life cycle, it can be a white dwarf, black hole or a neutron star. What determines what the star will become?
The star's mass at birth
Where do stars first form? How do they form?
They form deep inside clouds of gas and dust (nebulae).
Gravity causes the densest parts to collapse, forming regions called protostars.
What is a black hole?
an object whose gravity is so great that no light can escape
What is a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram?
a graph that plots the luminosity versus the temperature of stars
 What does the Y-axis of the H-R diagram display?
What does the Y-axis of the H-R diagram display?
Increasing luminosity (light)
What is the coolest red star according to the diagram?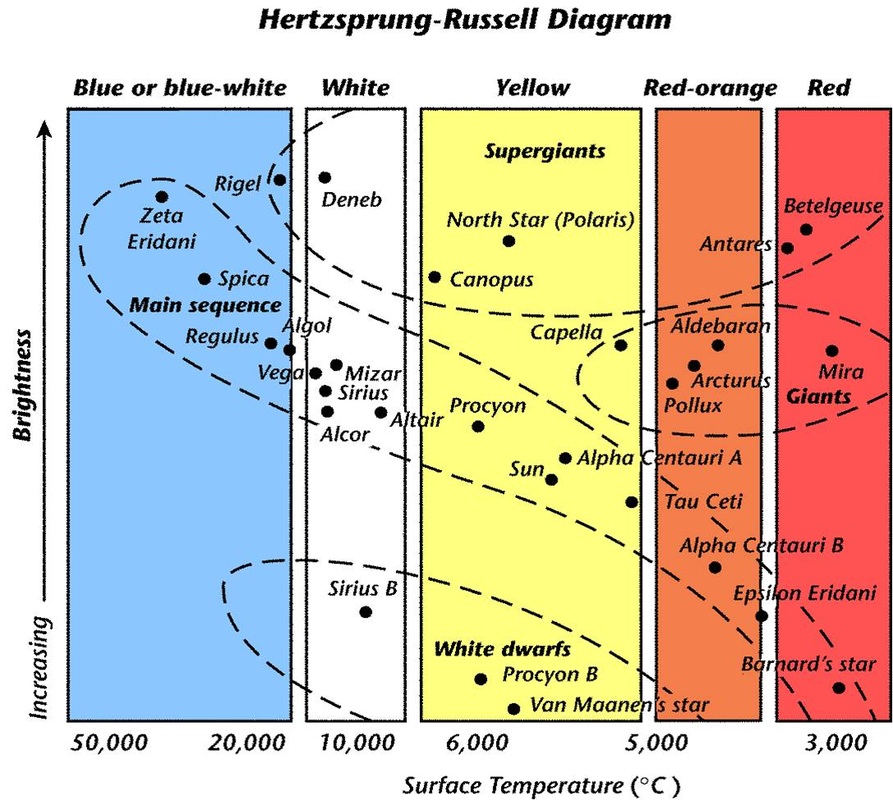
What happens at the protostar stage?
The protostars continue to contract, pulling in surrounding gas until their cores are hot and dense enough for nuclear fusion to take place.
What is a White Dwarf?
a hot, dense, slowly cooling sphere of carbon
What are the layers of a star in order from outermost layer to innermost layer?
Corona, Chromosphere, Photosphere, Convection zone, Radiative zone, and core
 What colors represent are the coolest v. the hottest stars on an H-R chart?
What colors represent are the coolest v. the hottest stars on an H-R chart?
Cooler stars (like red giants) are red in color.
The hottest stars are blue.
Stars that are in the middle can be either white or yellow.
The ________ of star determines it's fate at the end of its life cycle.
Mass
When does a star become a Main-Sequence Star?
when the star begins to fuse hydrogen into helium in it's core
What is a Supernovae?
an enormous explosion that destroys a star.
What is a red giant?
a dying star that has expanded and cooled to a red color
What is the hottest Blue star on the diagram below?
Zeta Eridani
What will be the final stage of our sun's life cycle?
the sun will become a white dwarf
When does a star leave the Main-Sequence Star category on an H-R Diagram?
when the star's hydrogen supply is nearly gone. It then moves into the next phase.
What is a (planetary) nebula?
A cloud of gas and dust created by a dying, average-sized star
What is nuclear fusion?
atoms collide and nuclei stick together
What is the brightest yellow star on the H-R diagram below?
North Star (Polaris)
How would the life cycle of the Sun be different if it were more massive?
it would explode instead of becoming a white dwarf
What are the THREE possible ways a star can end it's life cycle? [explain what happens to stars with a larger mass (massive stars) and stars with a smaller mass (average star)]
Massive stars experience a supernova, and either become a black hole or a neutron star.
Average stars become a white dwarf after all of the helium in their core is gone. They DO NOT experience a supernova.