This is a disadvantage of being a unicellular organism.
If one cell dies, the whole organism dies
The lining up of the chromosomes along the equator of the spindle fibers
Metaphase
Human arm and leg, dog leg and paw, bird wing, and whale flipper have all this in common.
Homologous structures
Mitochondria
the demand for resources, such as food, water, and shelter, in short supply in a community
competition
All ______ things are made of cells.
What is living?
Genetic Material in cells contained in a molecule
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
This is how well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment.
Survival of the Fittest
these are the waste products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, energy
A close, long-term relationship between two species that usually involves an exchange of food or energy
Symbiosis
This type of cell contains one large vacuole versus many smaller vacuoles
What is Plant?
the phase in which the nuclear membrane disappears and the spindle fibers begin to grow grabbing onto the chromosomes
These are structures that form but no longer serve a purpose to the individual
Vestigial Structures
These types of cells have lots of mitochondria because they are constantly working
Muscle cells
All the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time
Population
What is the order of cellular organization from smallest to biggest
Cell-Tissue-Organ-Organ System-Organism
What are the percentages for phenotypes AND genotypes of this cross?
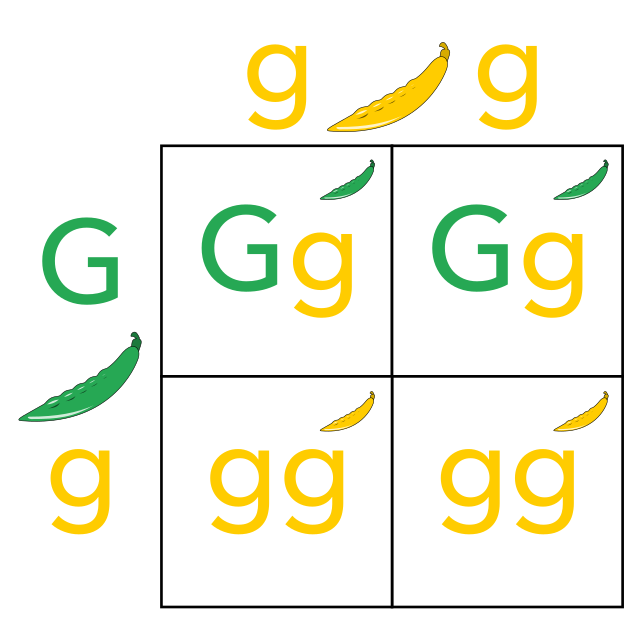
Phenotypes: 50% yellow, 50% green
Genotypes: 50% Gg, 50% gg
This difference was observed by Darwin's finches on the Galapagos Islands
Beak types
these are the reactants for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide, water, and Light
A symbiotic relationship that benefits one species and doesn't harm or benefit the other.
Commensalism
This is the function of the nervous system
It acts as an internal communication system
Meiosis divides a 2nd time without replication of DNA. This creates a cell called this, meaning to have one of each chromosome
Haploid
1. Chordata
2. Mollusca
3. Cnidaria
4. Arthropoda
Name the producers
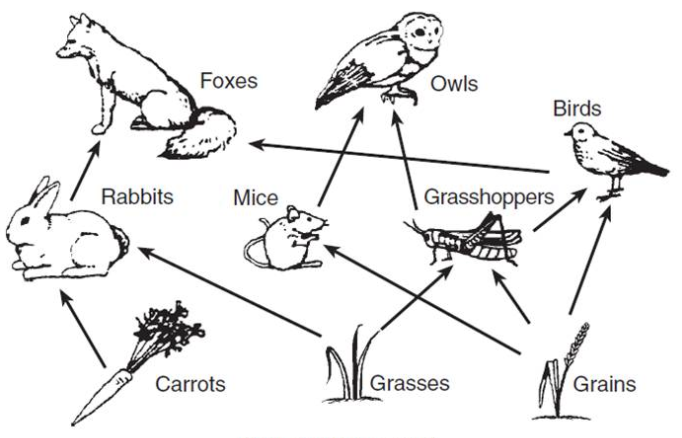
Grass, grain, carrot
Examples of limiting factors
shelter, water, food
Name the 3 principles of cell theory
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells
Complete the punnett square.

Domain Archaea
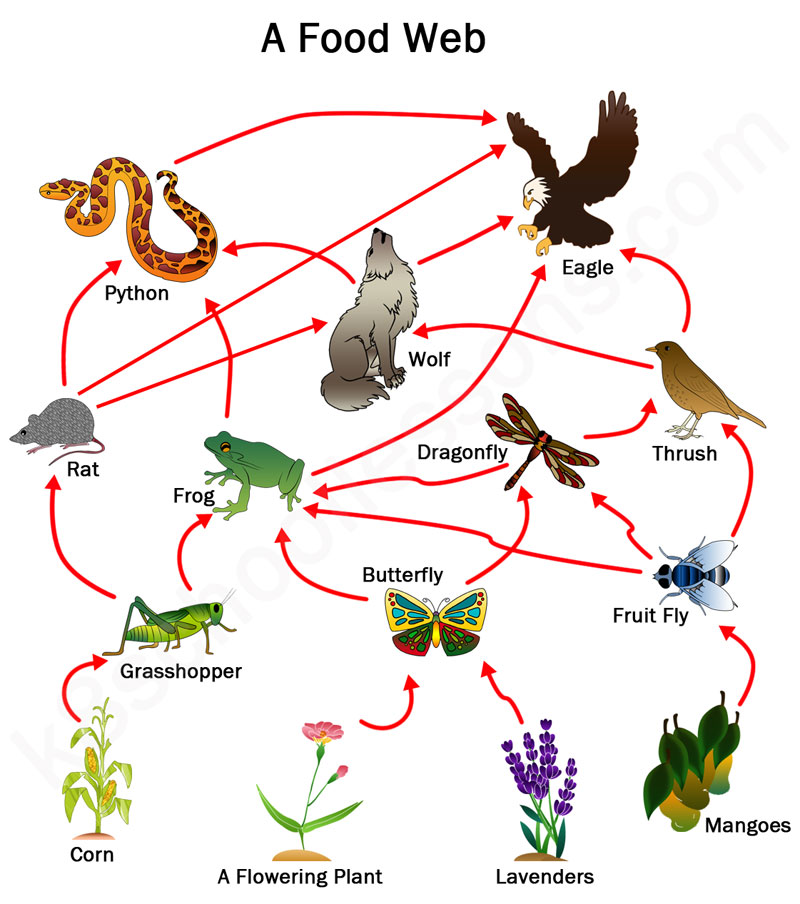
Name at least 2 tertiary consumers.
Wolf, frog, python, thrush
All living things and nonliving things in a given area
ecosystem
What is the net movement of particles (Water)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-112706652-5a0dac79ec2f640036c5cabc.jpg)
Left to right
Changes in the number, type, or order of bases on a piece of DNA
Mutations
This is the main difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms
Angiosperms are flowering plants and gymnosperms are not.
Top consumers of an energy pyramid have this amount of energy
0.1%
This species does not have a natural predator
Invasive species
Describe 3 main differences between plant and animal cells
plant cell has cell wall, large vacuole, chloroplasts; animal cell has lysosomes and small vacuoles
The phase in which the nuclear membrane reappears and the process in which the cytoplasm divides evenly into two new daughter cells
Telophase and Cytokinesis
Describes any alteration to the structure, function, or behavior of an organism resulting from Natural Selection
Adaptation
This is how cellular respiration and photosynthesis are related
They are exact opposites
Tropisms mean this
to grow towards a stimulus