Shows the DIRECT interaction between organisms in an ecosystem
Food chain
The energy found in an energy pyramid/food web.
the sun
A clown fish lives in a sea anemone. The clown fish has a safe place to live and the sea anemone is clean from parasites. This is an example of ________
mutualism
the number of different species in an area is called this
biodiversity
an organism that eats both meat and plants
omnivore
The order of organisms in a food web or food chain
Producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer
The amount of energy that is passed between trophic levels
10%
two organisms competing for the same resources,habitat or mate and often both have to exert energy for survival
competition
a species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
keystone species
Relationship when an organism kills another for food
predation
The term for an organism that cannot make its own food and needs to consume others for food.
Heterotroph
As the trophic levels go up in the pyramid, the amount of organisms in each level...
decreases
Tapeworms eat food that are already digested so they live in the intestines of animals and take the nourishment from that animal. This causes the animals to become weaker and more vulnerable to diseases. This relationship is an example of _________.
parasitism
Difference between threatened and endangered species
Endangered Species - a species in danger of becoming extinct in the near future
Threatened species - a species that could become endangered in the near future
Advantages to sexual reproduction
selective breeding
genetic variation
The role of decomposers in an ecosystem.
breaks down dead & decaying matter to return it to the Earth & make soil
If a producer has 80,000 kcal of energy, then the tertiary consumer will get _______ kcal of energy.
80 kcal
Barnacles attach themselves to other organisms such as sharks and whales so they can move around and eat. This is an example of ________
commensalism
2 factors that affect biodiversity
climate, living space/size of an area, niche diversity, genetic diversity, extinction, human impact
The REACTANTS of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide and water
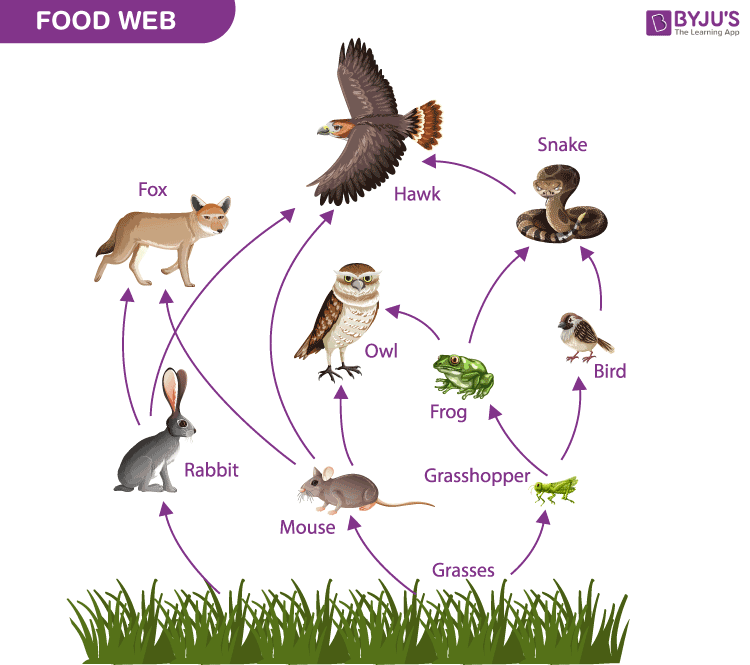 One of these organisms is BOTH a secondary and tertiary consumer.
One of these organisms is BOTH a secondary and tertiary consumer.
Owl
Excess energy in an ecosystem is loss as _______.
heat
True or false - parasites always kill the host
False
Two ways humans negatively impact biodiversity
habitat destruction, poaching
equation for cellular respiration
oxygen + glucose --> carbon dioxide + water + energy (ATP)