What do we call the highest point of a transverse wave?
The crest.
What is the line drawn perpendicular to a surface called in a reflection diagram?
The normal line.
Which type of electromagnetic wave has the longest wavelength?
Radio waves
What do we call the bottom point of a wave?
Trough
Draw and label a diagram of a transverse wave, including the crest, trough, rest position, amplitude, and wavelength.

Which term describes how tall a wave is from the rest position to a crest?
Amplitude
What unit is frequency measured in?
Hertz (Hz), or waves/second
What does the Law of Reflection state?
The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection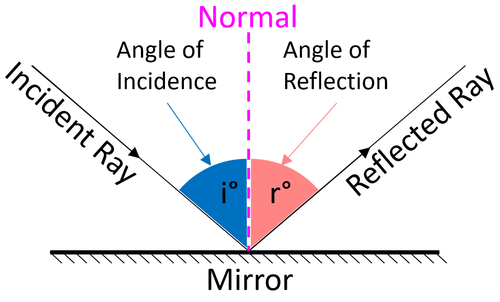
Which EM wave can cause sunburns?
Ultraviolet (UV) rays.
What is the distance from one trough to the next trough called?
Wavelength
Label a diagram of reflection (there should be five terms labeled)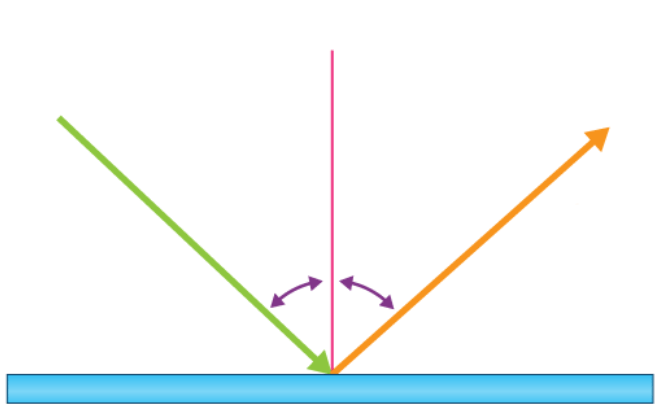
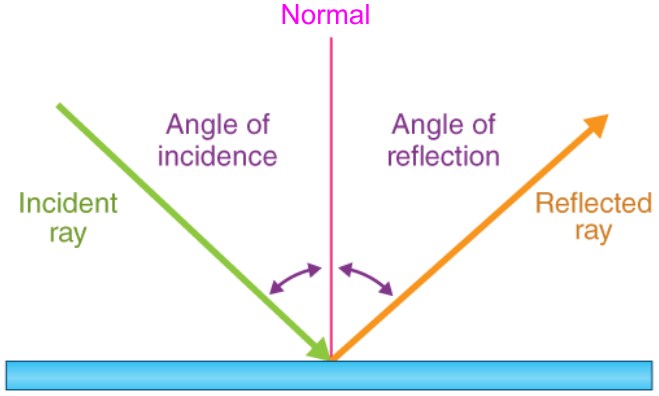
What type of wave has particles moving perpendicular to the wave direction?
Transverse
If a wave’s frequency increases, what happens to its wavelength?
The wavelength decreases.
Why does a red shirt appear red under white light?
It reflects red wavelengths and absorbs all other colours.
List the EM waves from lowest to highest energy.
Radio → Microwave → Infrared → Visible → Ultraviolet → X-ray → Gamma.
What do we call the number of wave cycles that pass a point each second?
Frequency
What is the angle of reflection for the following diagram?
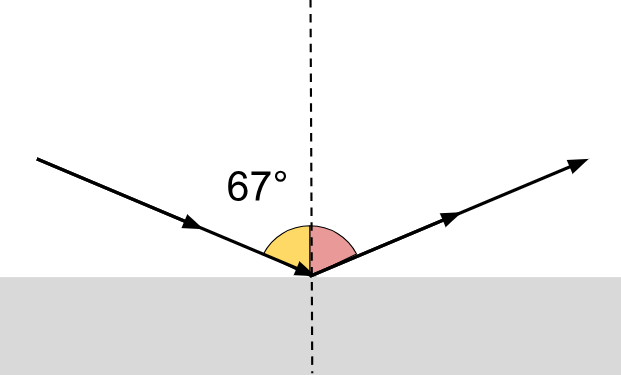
67
Define a medium in terms of waves.
The material through which a wave travels.
A wave has an amplitude of 2 cm. If you double the amplitude, what happens to the energy?
The energy increases (greater amplitude = more energy)
Describe the difference between reflection and refraction, and give an example of refraction happening.
Reflection = bouncing off a surface; refraction = bending when entering a new medium.
Example: a pencil appearing bent in water.
Explain why gamma rays have more energy than visible light.
Gamma rays have higher frequency, which gives them much more energy.
Define a compression wave.
The type of wave that moves with particles pushing parallel to the direction of the wave.
Predict which way the ray of light bend when it passes from air (a fast medium) into water (a slow medium)
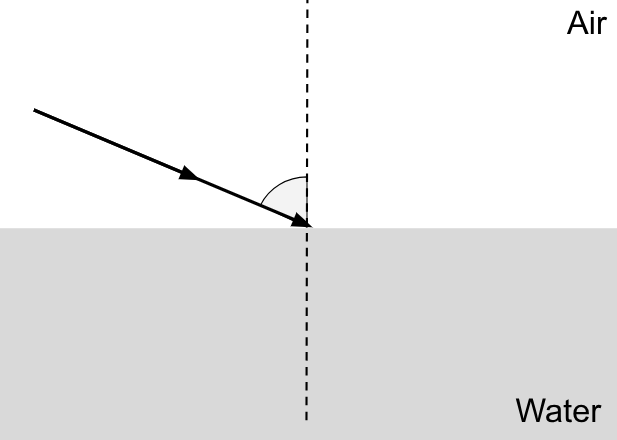
Towards the normal
What kind of radiation vibrates both electrical and magnetic fields?
Electromagnetic radiation
What is the frequency of waves passing under a dock if there are 21 waves in 7 seconds?
3 Hz / 3 Hertz
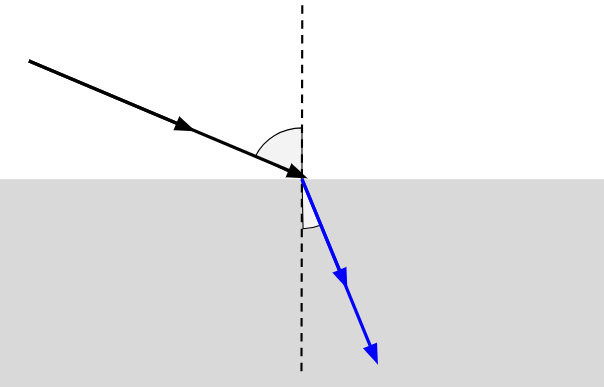
Light travels from air (fast medium) into water (slow medium). Will it bend toward or away from the normal?
* You may draw a diagram
Toward the normal.
Describe one technological application of radio waves.
Radio, television, wifi, MRI machines
Define absorption in the context of light behaviour.
When light energy is taken in by a material and not reflected or transmitted.
What is the wavelength and the amplitude of the following graph? (include units)
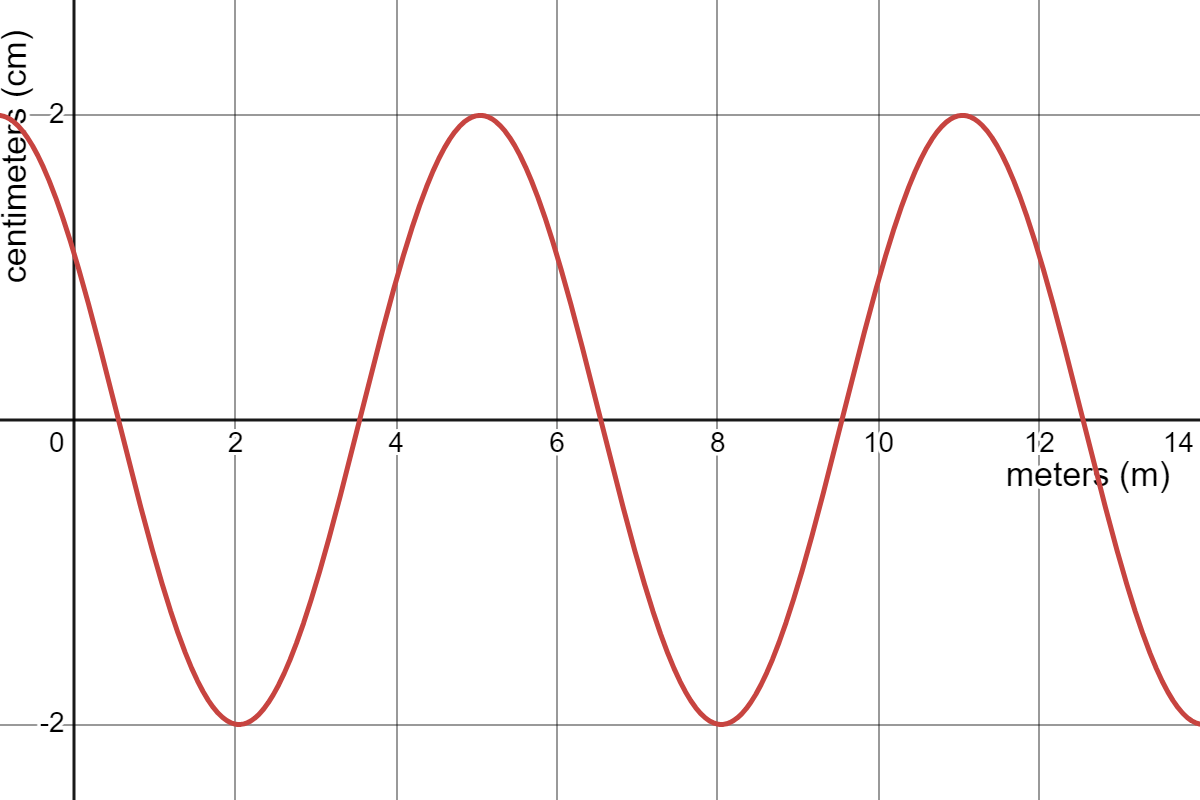
Wavelength = 6 m
Amplitude = 2 cm
What is the name of energy that radiates as electromagnetic waves, including visible and invisible radiation?
Radiant energy