In a patient with deranged LFTS, screening tests for HH
Iron, Ferritin and Transferrin
High serum ferritin (eg, >300 ng/mL in males or postmenopausal females; >200 ng/mL in premenopausal females)
High transferrin saturation (TSAT; eg, >45 percent)
Sources for ALP other than Liver? Any 3
Bone, Placenta, Intestine, Kidney
Person with Chronic Hepatitis B presents with post prandial pain and skin rash. Diagnosis
PAN
Medical treatment for HRS
Splanchnic vasoconstrictors
Albumin
The two most common organisms associated with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) are:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
Tests of hepatic synthetic function include
Serum albumin
Prothrombin time/international normalized ratio
Bilirubin
In those with ALT and/or AST levels >15X ULN, or massive elevation ALT of >10,000 IU/l, evaluation should also assess for:
2 most common causes
Acetaminophen toxicity and ischemic hepatopathy (shock liver)
Two medications known to reduce mortality in Variceal bleed patients with cirrhosis?
Octreotide and Antibiotics
Mechanism of action N- Acetyl Cytstein in Acetaminophen toxicity.
Reducing NAPQi by Glutathione replenishment
Two variants of HFE gene responsible for Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
C282Y and H63D
Patients with persistently elevated AST and ALT levels, especially patients <55 years of age, should undergo screening for Wilson’s disease with serum ceruloplasmin testing. In the setting of low ceruloplasmin, what is the confirmatory testing?
24-hour urinary copper and slit-lamp eye examination to identify pathognomonic Kayser–Fleischer rings should occur.
A patient who presents with AST>ALT, what is the quantity of alcohol (in grams) is considered a high risk for developing Alcoholic Liver disease?
Women consuming more than 140 g per week or men consuming more than 210 g per week. should be counseled for alcohol cessation
A 50-year-old man presents with jaundice, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, and vomiting. He has a history of chronic heavy alcohol consumption (8-10 drinks per day for the past 12 years). On examination, he has jaundice, hepatomegaly, and tenderness in the right upper quadrant. His MDF >32. Whats the next best step?
Prednisone 40 mg for 28 days.
Calculate Lille's score at 7 days to check for response
Last drink within the last 60 days.
A 32-year-old woman with a history of Wilson's disease diagnosed 5 years ago, and is currently on copper chelating treatment, presents with a 2-week history of fatigue, joint pain, Shortness of breath, and a new onset of rash. Labs reveal anti-histone antibodies. What's the most likely cause?
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus (DILE) due to Pencillamine
A 45-year-old female for referred to the office for evaluation of elevated LFTs. She reports a history of radiation therapy to the chest 10 years ago for breast cancer. Jugular venous distention, a pericardial knock, and pulsus paradoxes are noticed on examination. Echo shows thickened pericardium and impaired diastolic filling.
What is the diagnosis and the zone of the affected hepatic segment?
Zone 3 is typically the most affected in congestive hepatopathy (also known as nutmeg liver)
Liver injury can be classified into Hepaticellular, Mixed and Cholestatic patterns based on R ratio. How to calculate R ratio?
R value = (ALT ÷ ULN ALT) / (alkaline phosphatase ÷ ULN alkaline phosphatase)
Patient with rash, Flu-like symptoms, and confusion. Labs reveal AST and ALT in 300s, Thrombocytopenia, and Leukopenia.
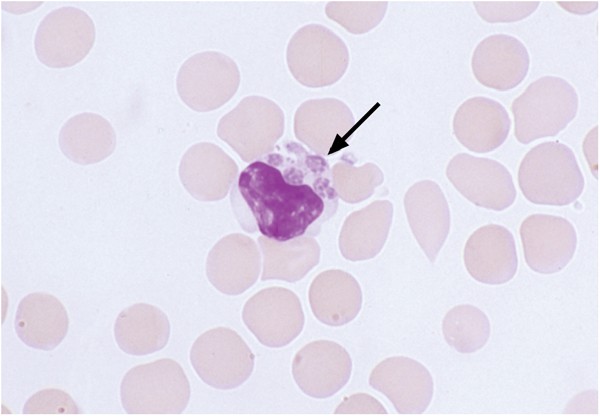
Ehrlichiosis
A patient presents with right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, and elevated liver enzymes. An abdominal ultrasound shows bile duct dilation without gallstones. The patient reports recent travel to Southeast Asia and consumption of freshwater fish. What is the most likely cause?
Opisthorchis sinensis (or Clonorchis sinensis, commonly known as the Chinese liver fluke)
monoclonal antibody medication primarily used to treat moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (eczema), asthma, and EOE
Dupilumab
Two scores based on biochemical tests for assessing Liver fibrosis
APRI and Fib-4 score
APRI Calculation:
APRI=(AST (U/L)/Upper limit of normal for AST)×(100/Platelet count )
Interpretation of APRI:
- APRI < 0.5: Low probability of significant liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- APRI 0.5 to 1.5: Intermediate probability of liver fibrosis (may require further assessment).
- APRI > 1.5: High probability of significant fibrosis or cirrhosis.
2. FIB-4 (Fibrosis-4 Index)
FIB-4 uses age, AST, ALT (alanine aminotransferase), and platelet count to estimate the degree of liver fibrosis.
FIB-4 Calculation:
Interpretation of FIB-4:
- FIB-4 < 1.45: Low likelihood of significant fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- FIB-4 1.45 to 3.25: Intermediate likelihood of fibrosis (may require further assessment).
- FIB-4 > 3.25: High likelihood of significant fibrosis or cirrhosis.
The half-life of Delta Bilirubin?
3 weeks


Tissue diagnosis and ERCP of the above images is consistent with?
PSC
Shock liver can be differentiated from alternative causing using ___to __ratio. What is the cut of value?
ALT to LDH Ratio in Shock Liver:
- A/LDH Ratio < 1.5: Suggests ischemic hepatitis (shock liver).
- A/LDH Ratio > 1.5: Suggests alternative causes of liver injury (e.g., viral hepatitis, acetaminophen toxicity).
selective thyroid hormone receptor beta (THR-β) agonist approved the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Resmetiron
Blood types associated with a transient increase in ALP after a fatty meal?
Blood Type O and B