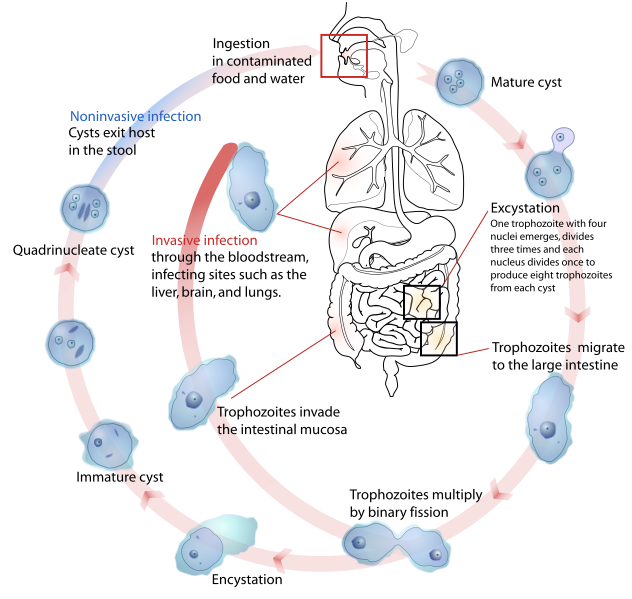
Diagnosis?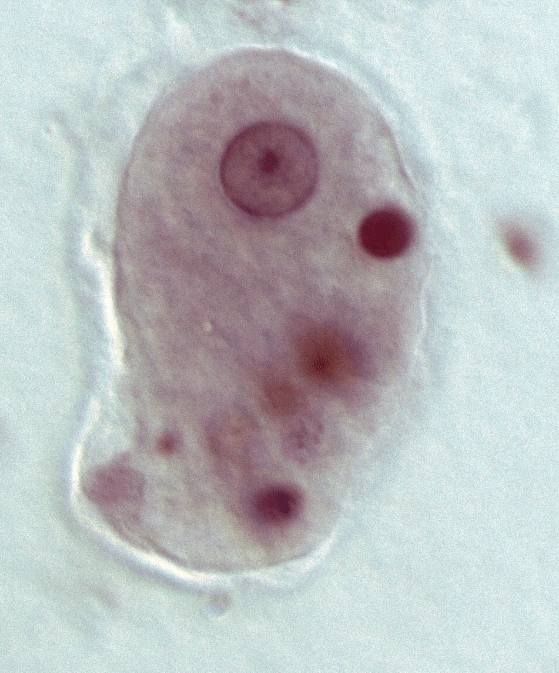
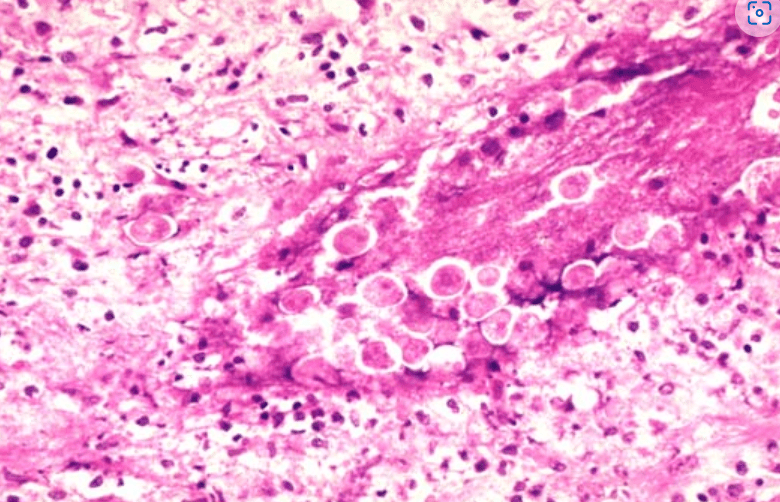
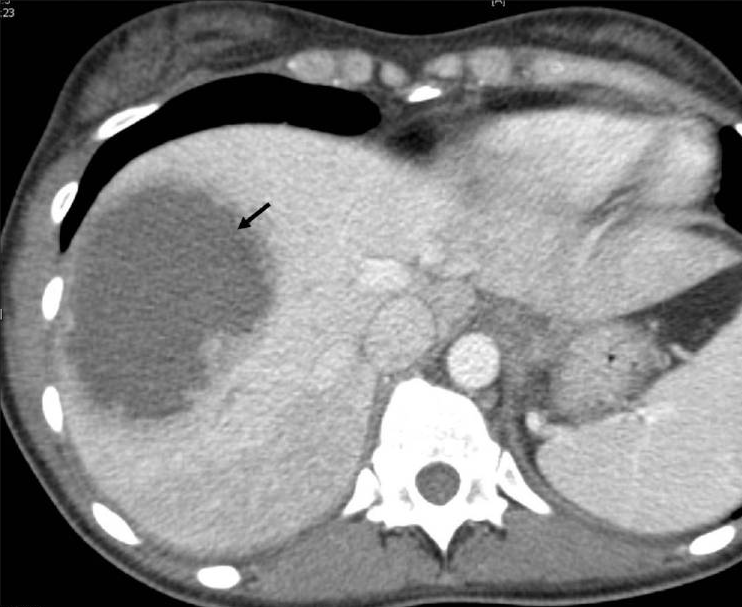
Entamoeba histolytica
Name the subtype/morphologic pattern of this HCC
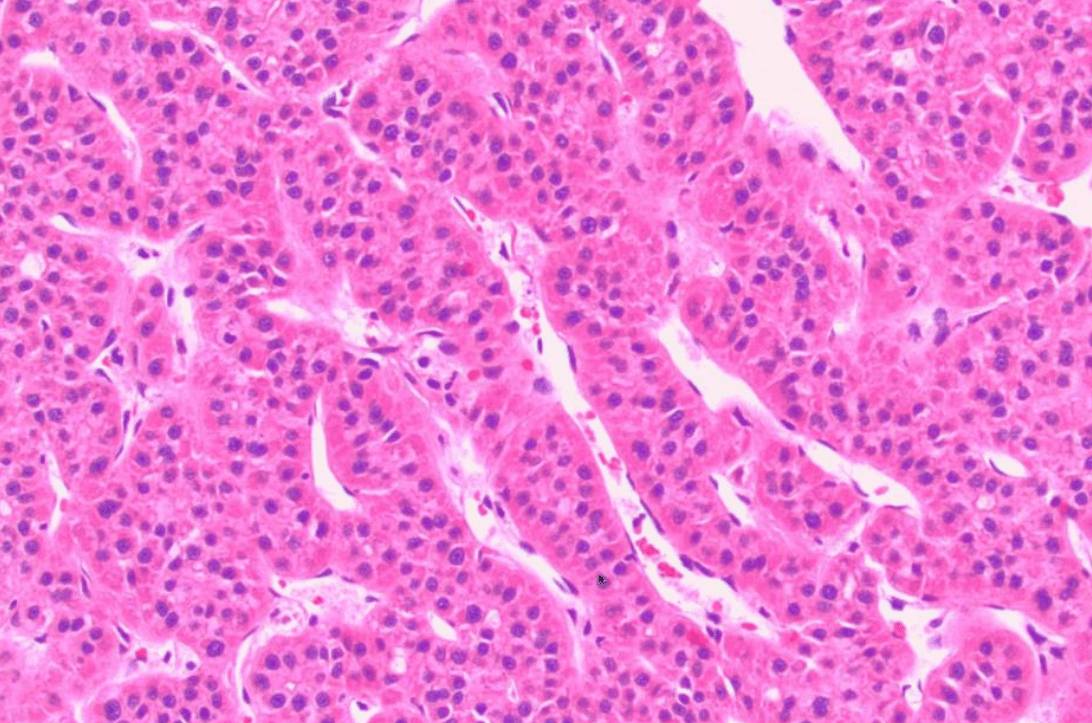
Trabecular
Bonus: Name the subtype/morphologic pattern of this HCC
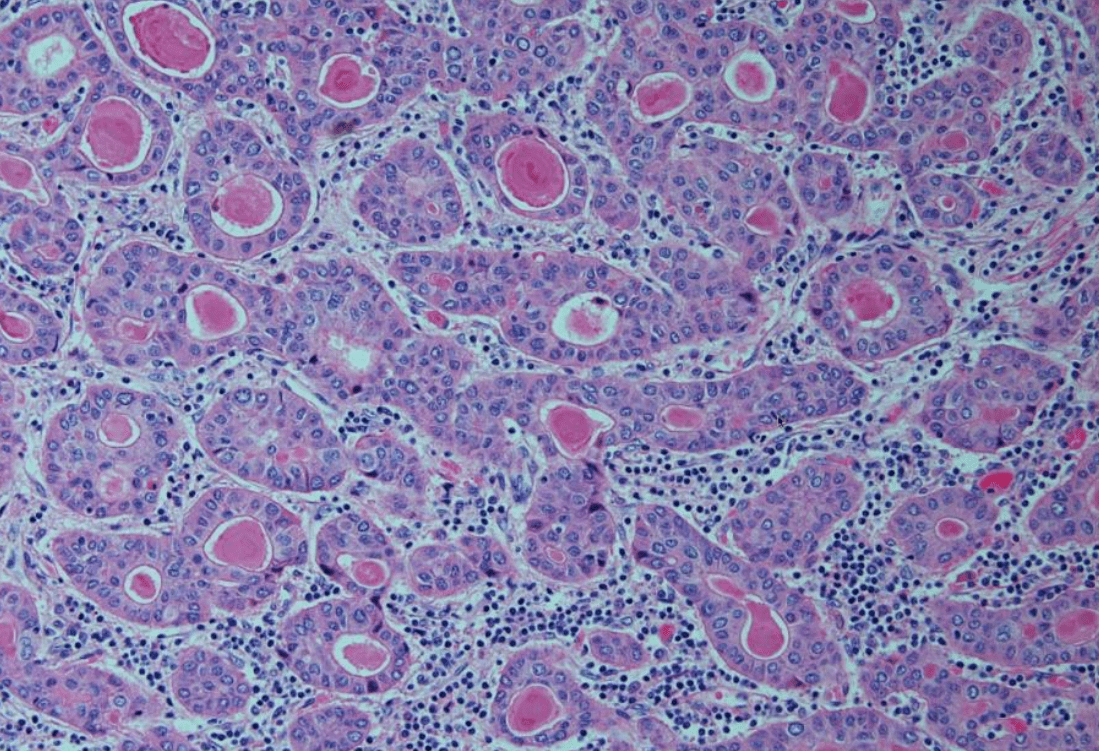
3 cm mass in a 55 F. No atypia is seen. Diagnosis?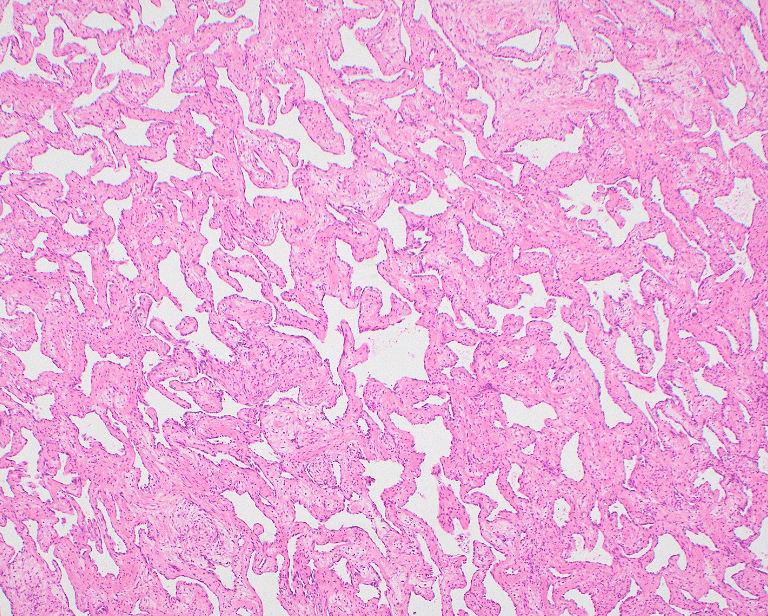
Cavernous Hemangioma
Histologic Description:
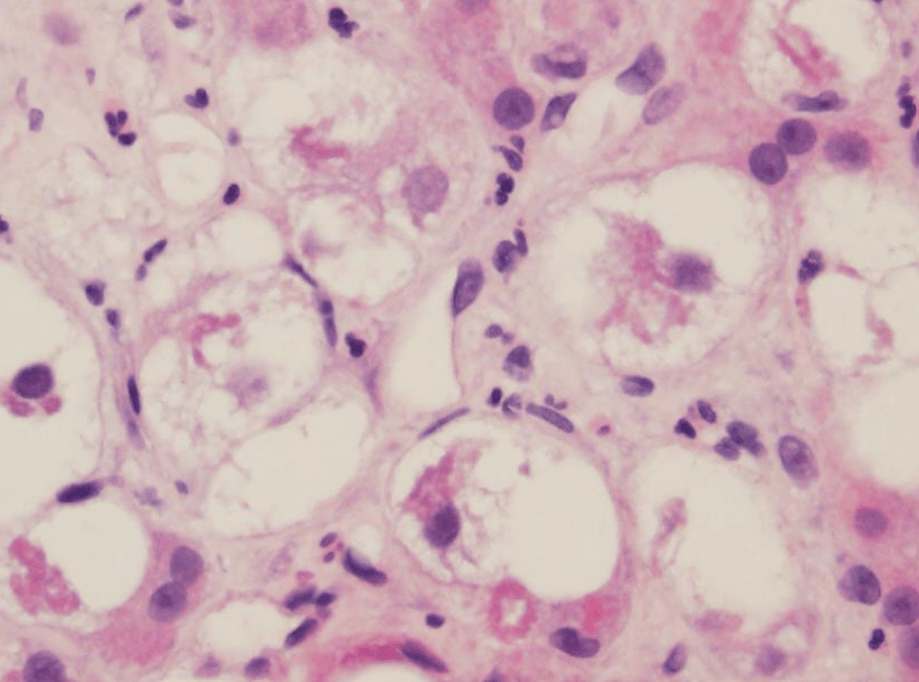
Ballooned Hepatocytes
You are paged for a donor evaluation. Grade the steatosis.
Mild, Moderate, Severe
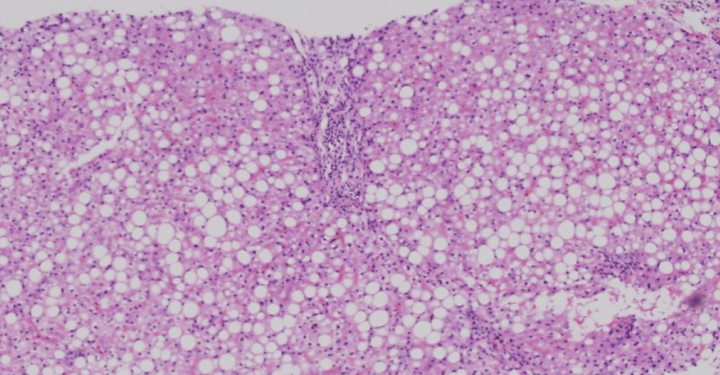
Severe
Histologic Description: 30 female, what do you favor clinically?
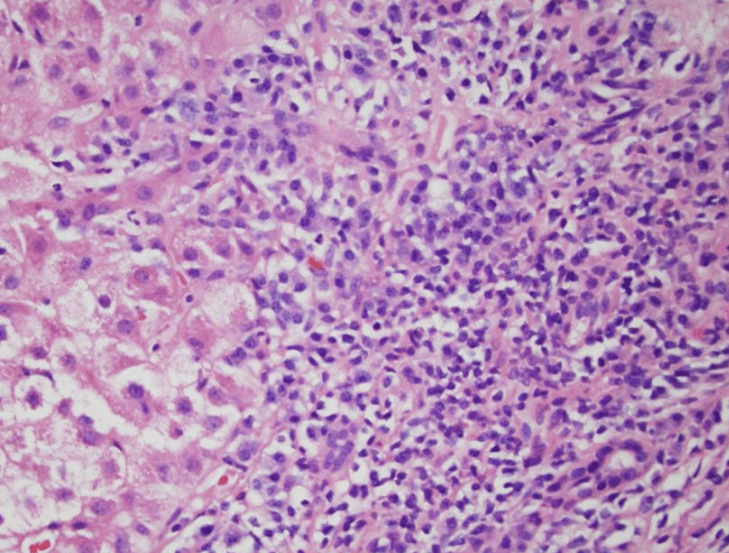
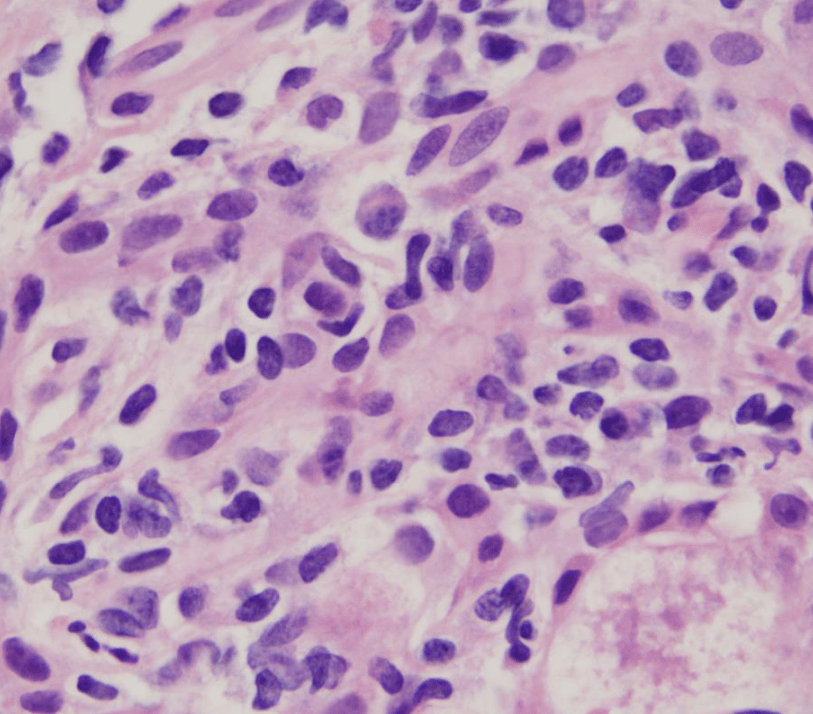
Interface Hepatitis
Autoimmune Hepatitis
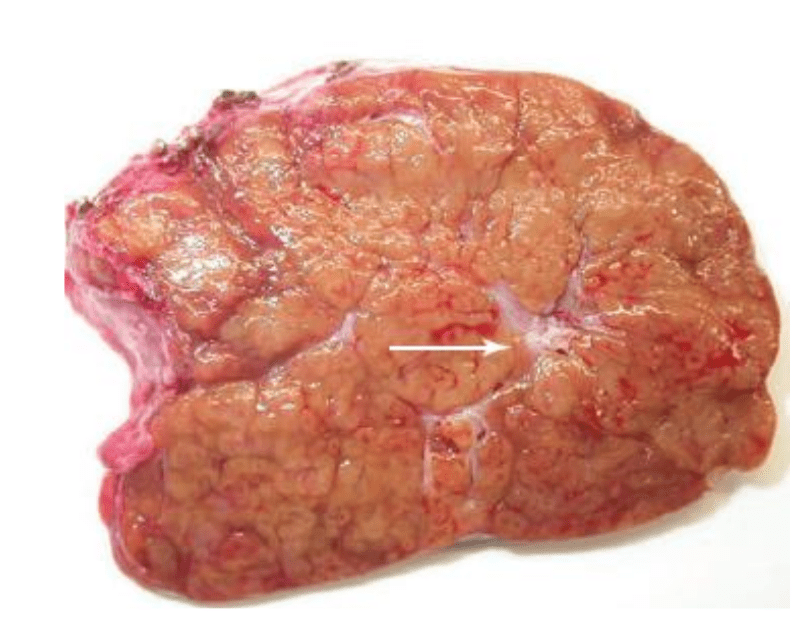
55 year old man with HCC was admitted for lobectomy. A small liver nodule was noted during surgery and sent for intraoperative consultation. Diagnosis?
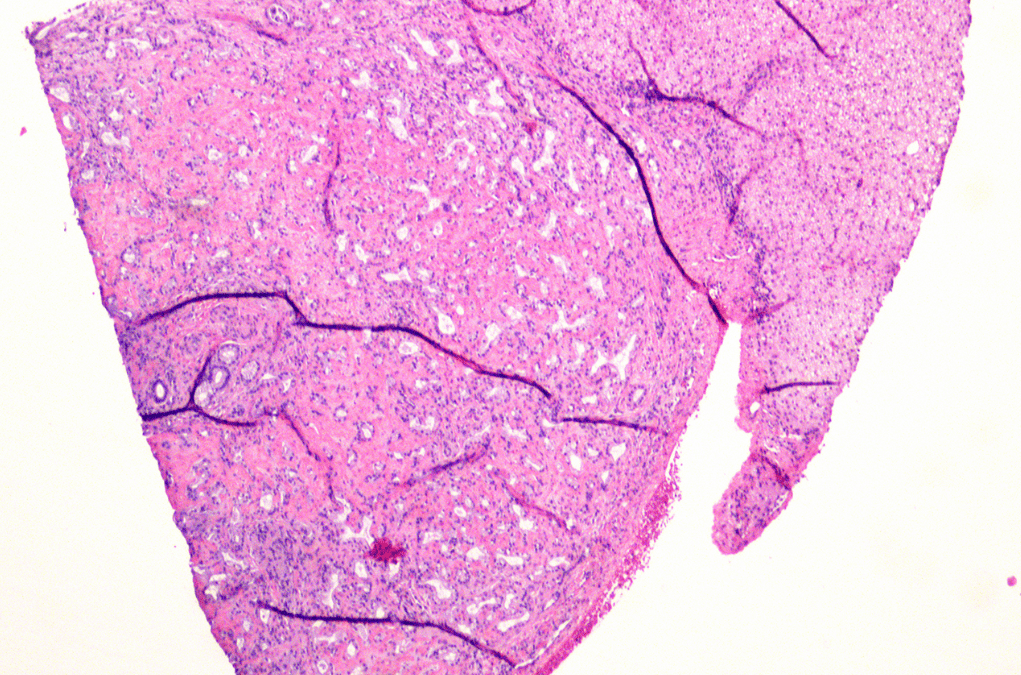
Bile duct adenoma
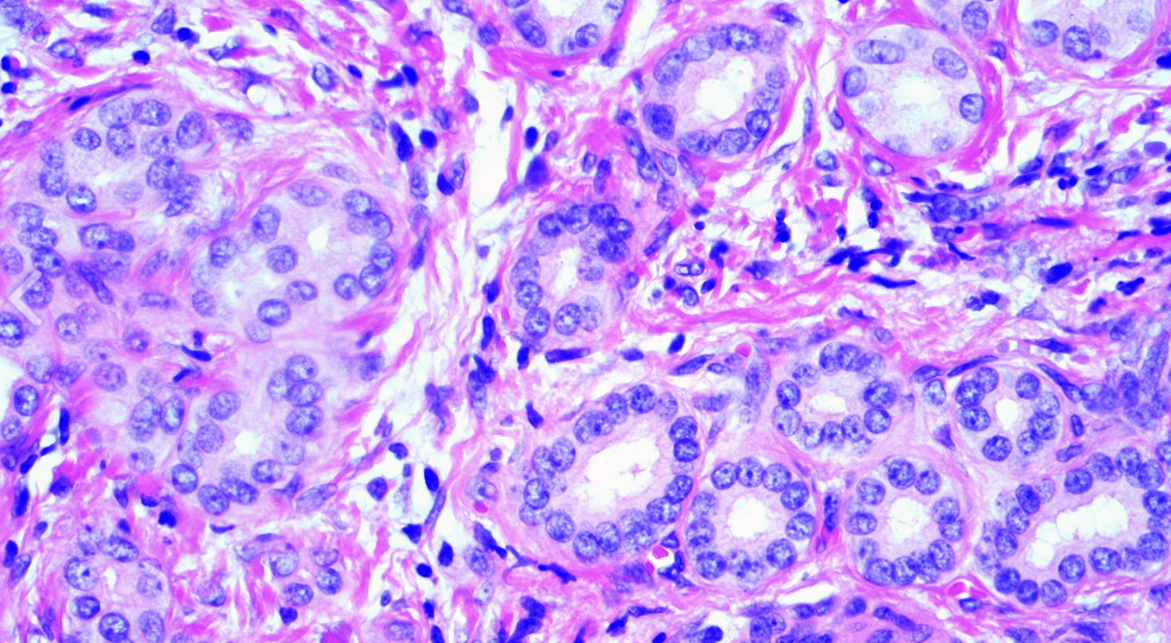
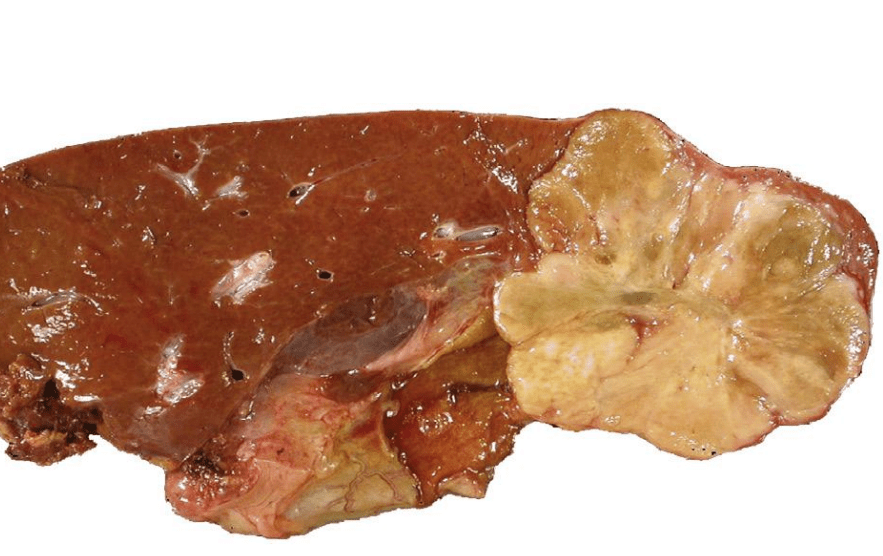
2 cm lesion is grossly shown. IHC shows a Map-like glutamine synthetase. Diagnosis?
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia (FNH)
What are the circled cells?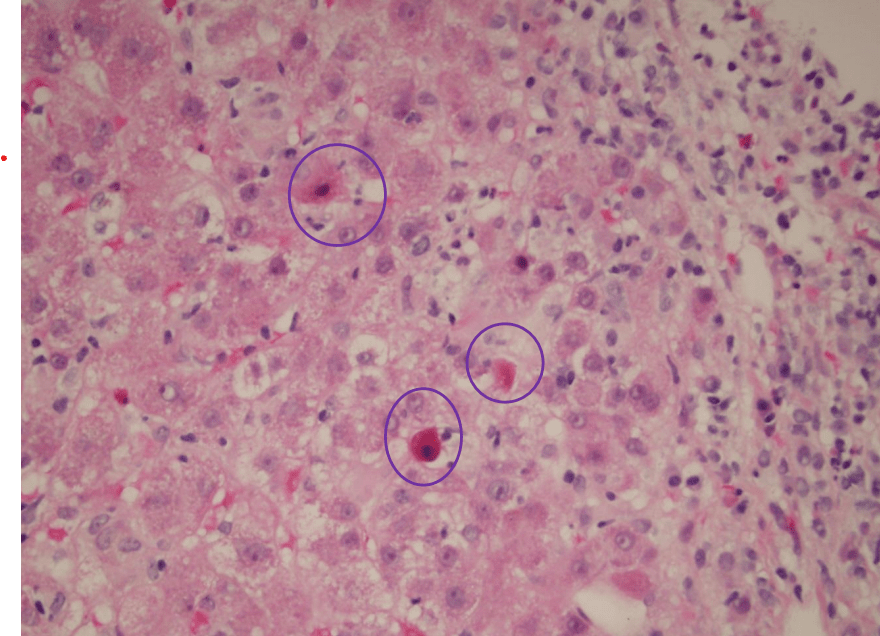
Councilman Body
Apoptotic Hepatocyte
You see the following in the transplant liver biopsy? 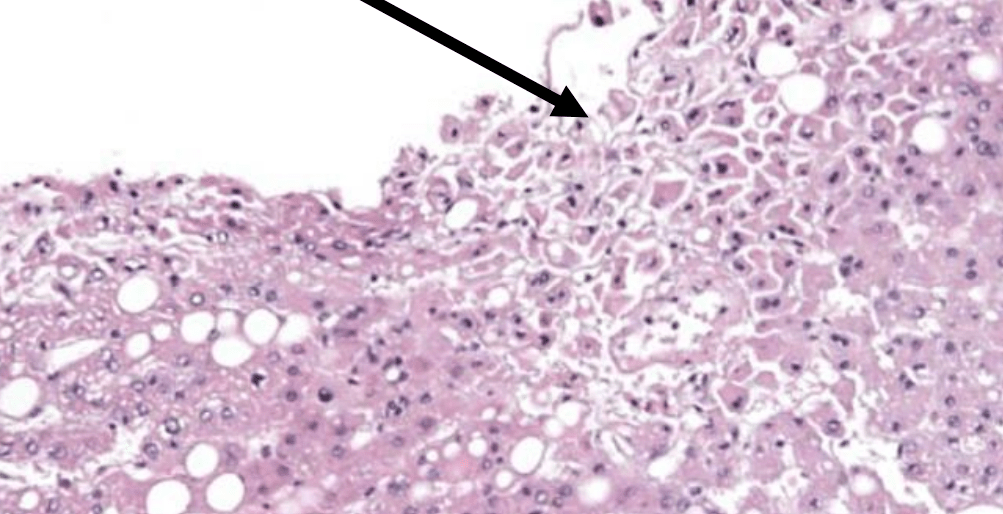
Saline artifact
Mallory-Denk body
MDBs stain positively using antibodies against _____ and _____, both proteins involved in degradation pathways, as well as with antibodies against cytokeratins ______and _______
Ill give you points for 3 of the 4
MDBs stain positively using antibodies against ubiquitin and p63, both proteins involved in degradation pathways, as well as with antibodies against cytokeratins 8 and 18
Name 3 IHC stains for hepatic differentiation:
Name 3 IHC stains for malignancy:
1. Arginase, HepPar1, pCEA/CD10, TTF-1, ISH for albumin mRNA
2. CD34, Glypican 3, Glutamine Synthetase, HSP70, AFP
20 month old Male with a large liver lesion and elevated AFP. Diagnosis? Morphologic pattern shown for double points.
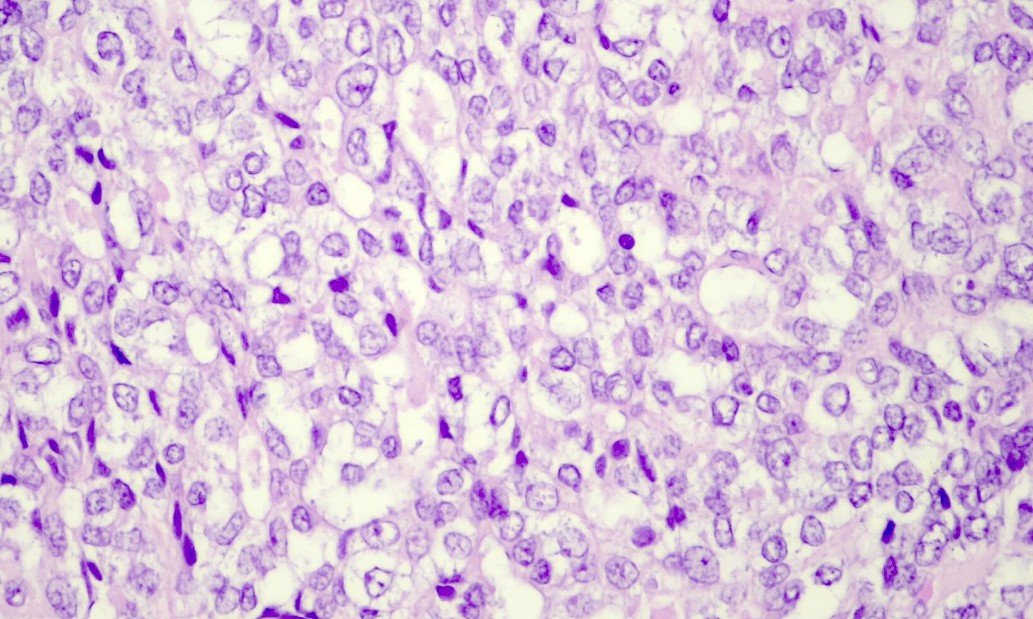
Hepatoblastoma
Fetal pattern.
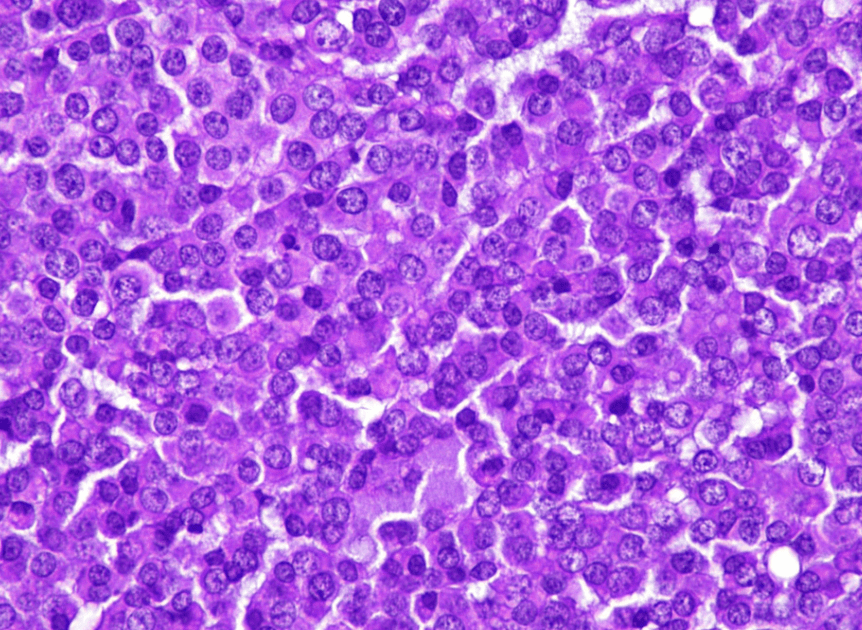
If INI-1 was lost, what kind of tumor would you favor this to be?
Patient with Polysubstance use disorder. Diagnosis?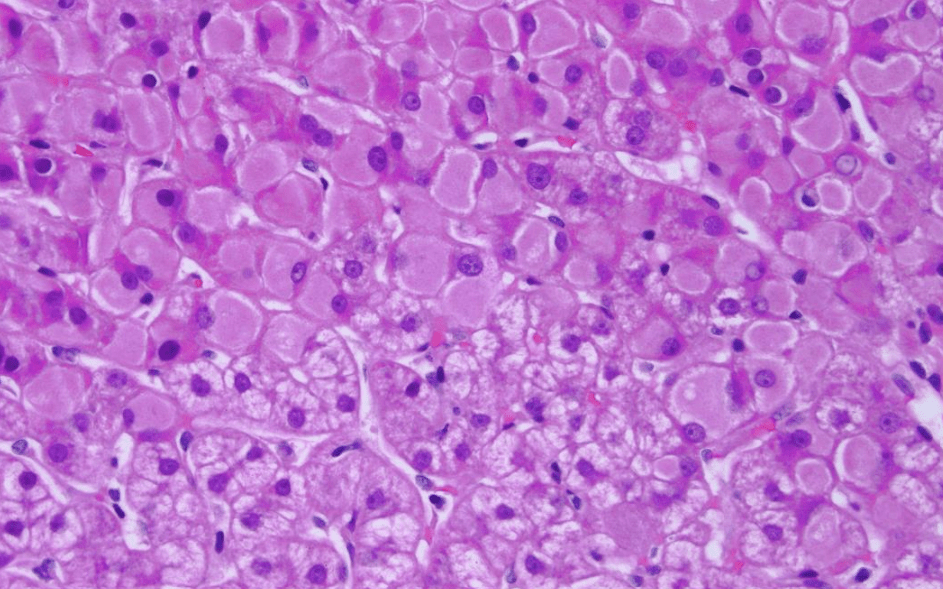
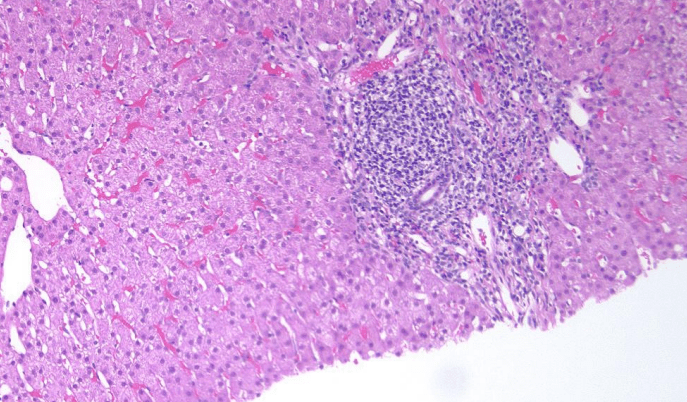
Viral Hepatitis
Most likely hepatitis B
Diagnosis?
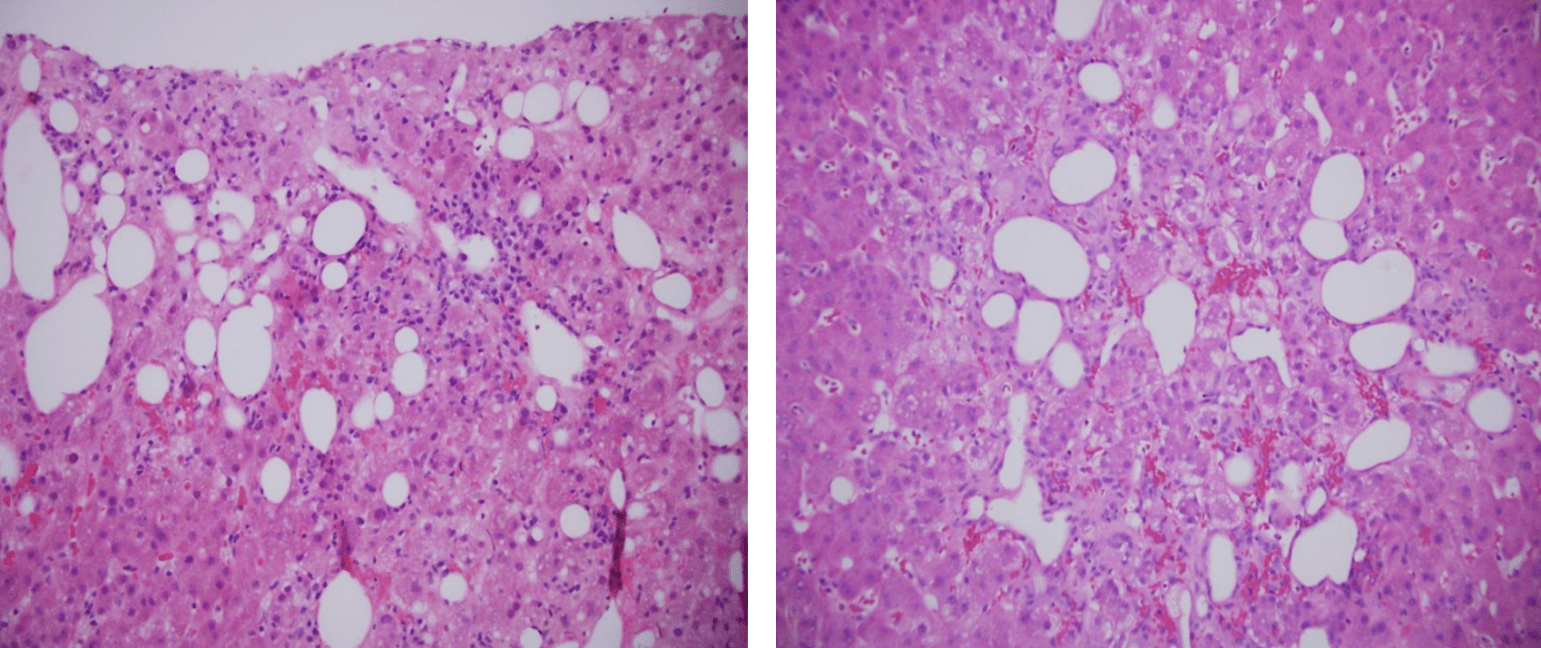
Lipopeliosis
Name 2 of the 3 causes for zone 3 necrosis
Acetaminophen toxicity
Venous outflow obstruction (congestive heart failure, Budd Chiari syndrome due to hepatic vein thrombosis)
Ischemic injury (hepatic artery/ portal vein hypoperfusion in shock-like states
25 M s/p liver explant for carcinoma on bx. Normal AFP. More specific diagnosis?

Fibrolamellar HCC
BONUS: Name the most common fusion.
32 G0 F with a 2.8 cm lesion. Name the 3 most common mutations. 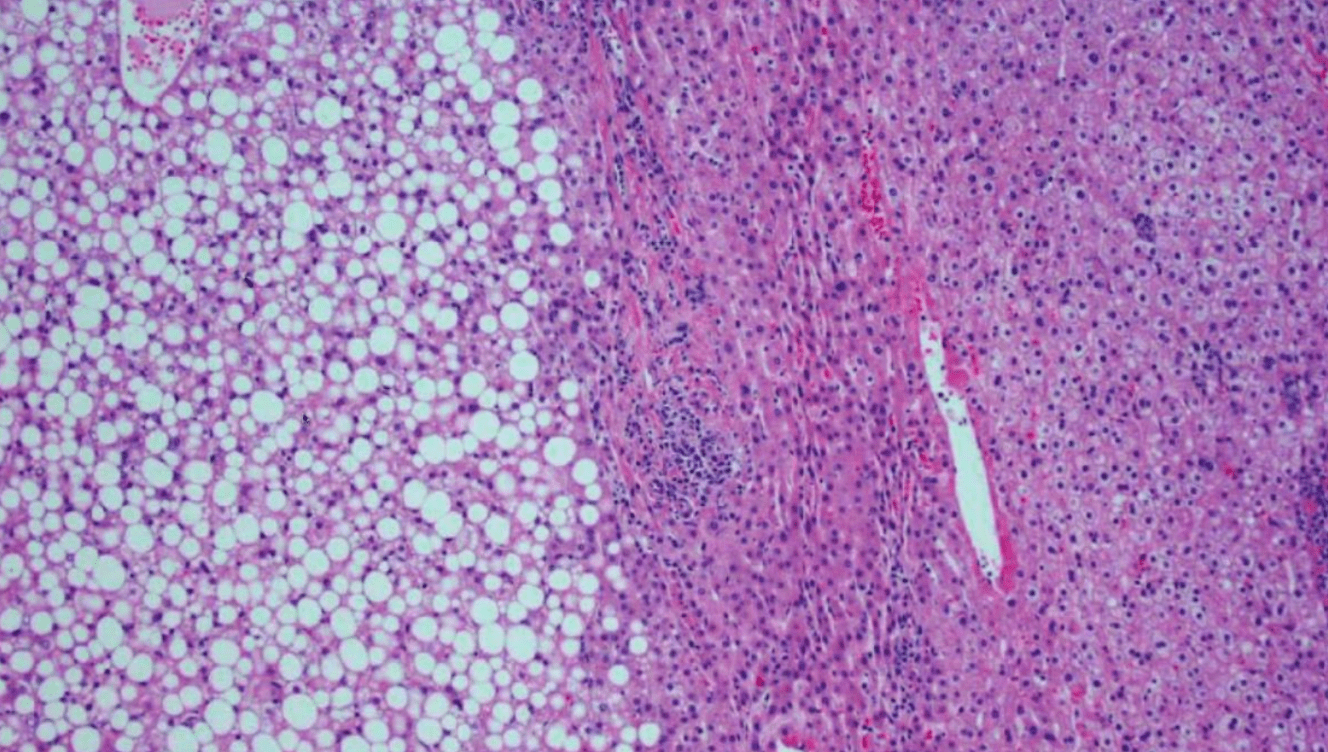
HNF1 alpha
Beta catenin/Wnt Pathway
IL6ST
Patient with DM1 and bronze skin. Name the mutated Gene.
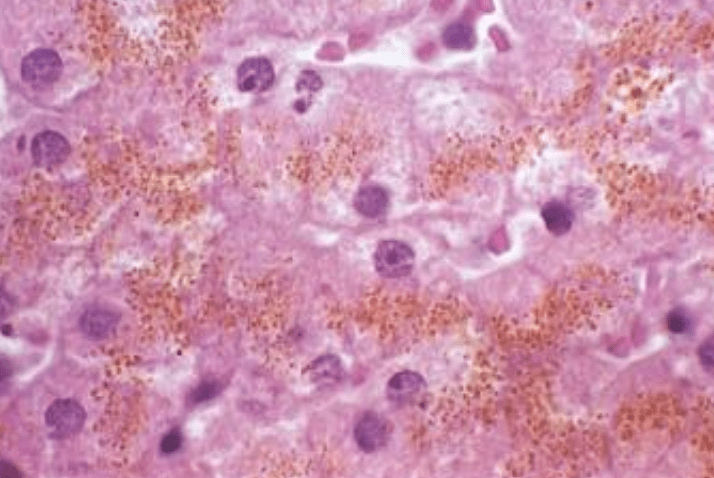
Most cases are caused by mutations in the HFE gene, particularly the C282Y and H63D mutations
Patient with a history of cardiac transplant now admitted for rejection. Found to have liver failure with the following:
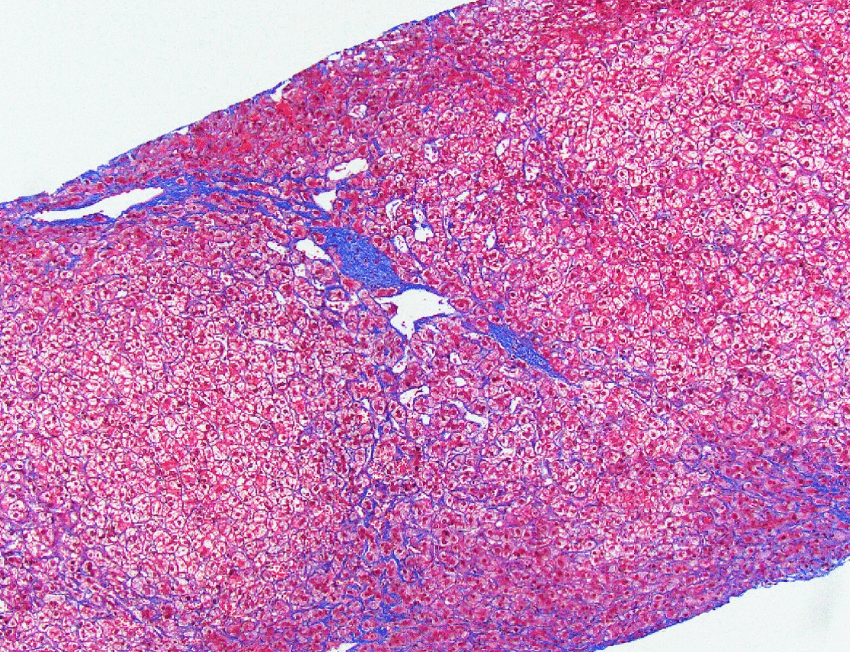
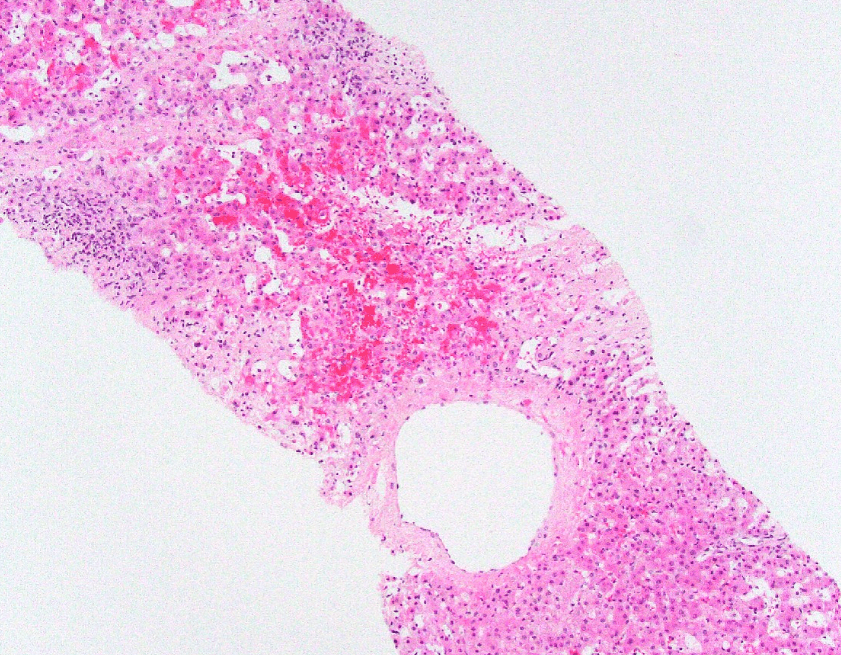
- Hepatic venous outflow obstruction
- Congestive Hepatopathy
- Cardiac (congestive) hepatopathy and Fontan associated liver disease
AAT encoded by _________ located on chromosome _______
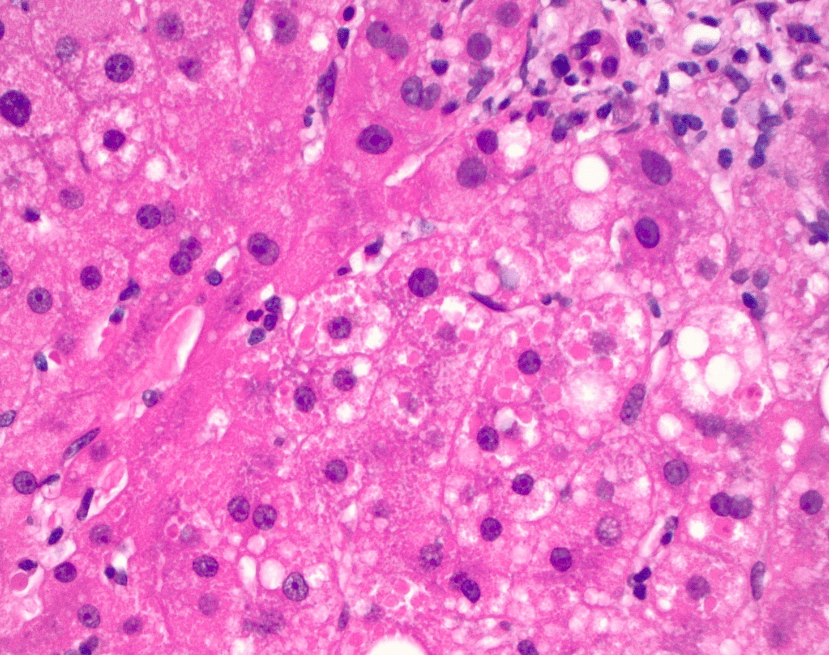
SERPINA1 gene located on chromosome 14
For this subtype of HCC with lots of fibrous stroma. Name the associated mutated genes.
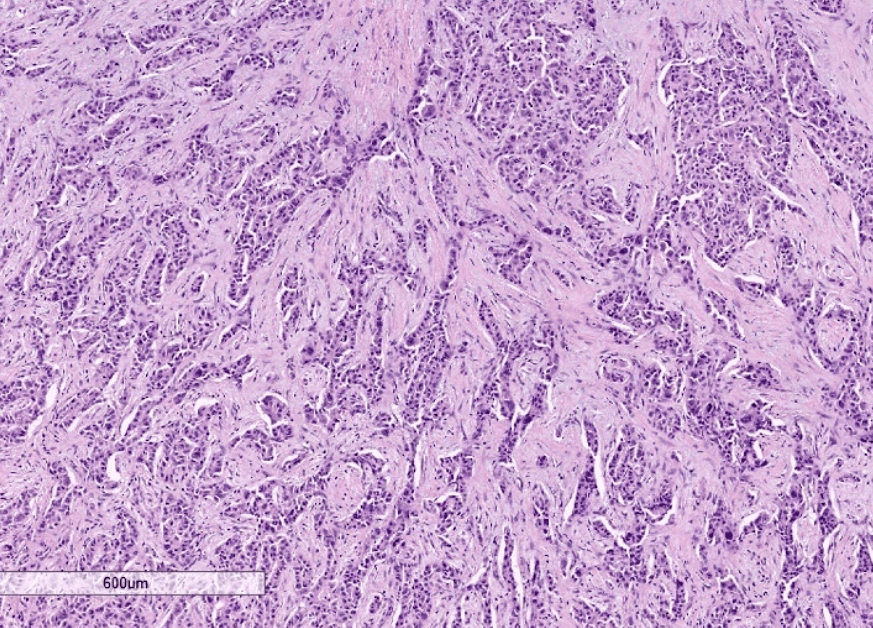
Scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma
TSC1 / TSC2
CD34 + and CAMTA1 +
Diagnosis? Can you name the fusion partner?
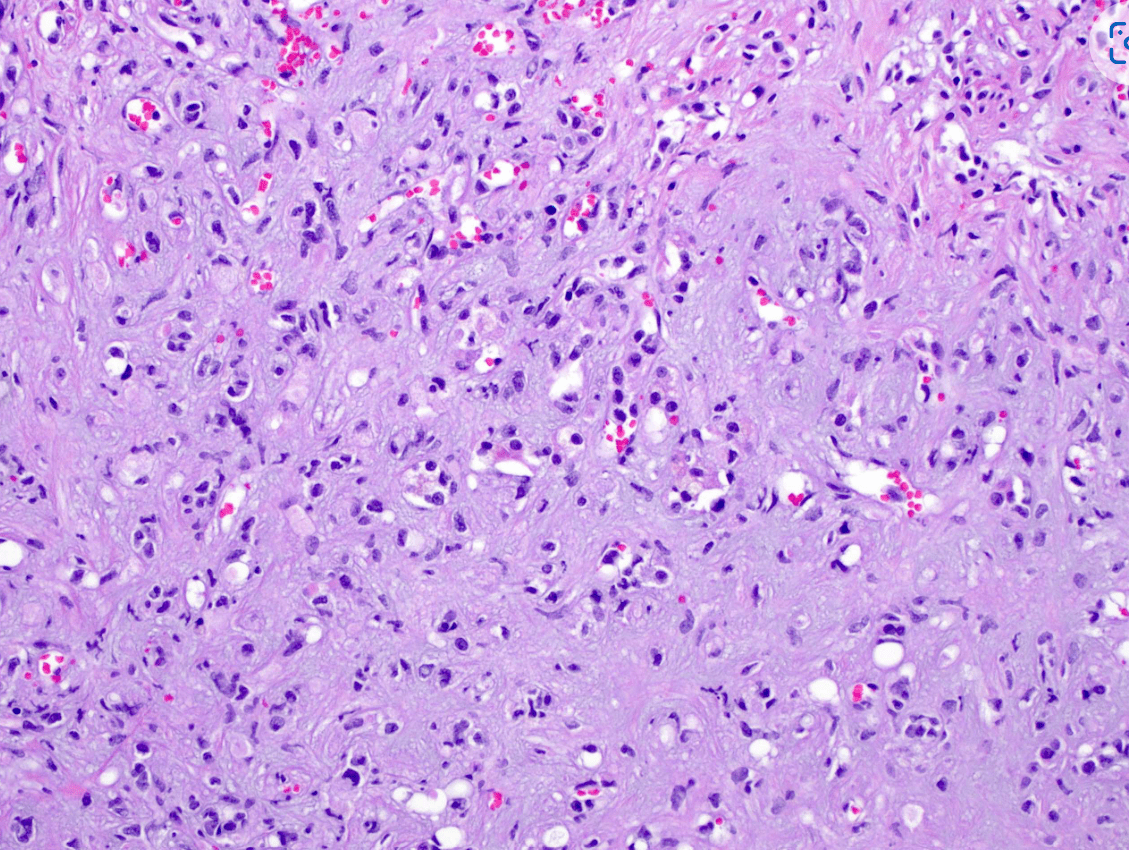
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion tumors: positive for CAMTA1
YAP1-TFE3 fusion tumors: nuclear expression of TFE3
Name the mutation and chromosome
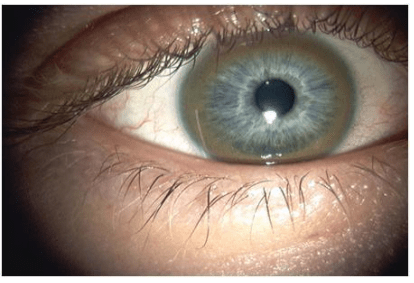
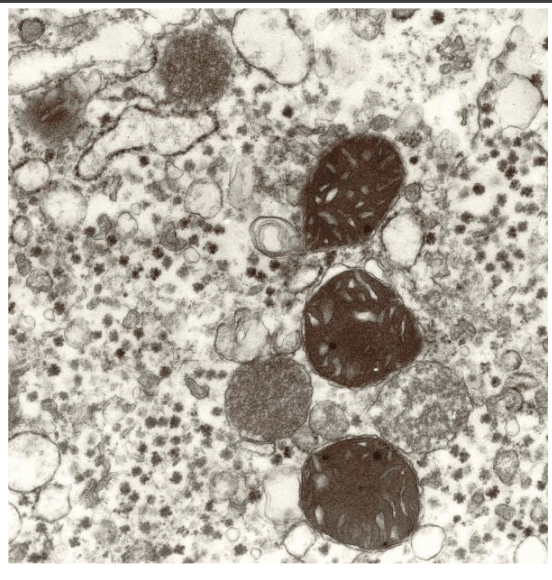
ATP7B mutation, Chr 13
In the context of liver transplantation, antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is characterized by the interaction of donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) with the graft, leading to the activation of the complement system. Name the initial complement component that binds to the immune complexes and the downstream effect it has, specifically describing how it ultimately contributes to graft injury through the membrane attack complex (MAC).
What is C1, and it binds to the immune complexes of DSAs and donor antigens, initiating the classical complement pathway. This activation leads to a cascade involving C4 and C2, producing C3 convertase that generates the anaphylatoxin C3a and opsonin C3b. Continued activation results in the formation of C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 to C5a and C5b, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex (C5b-9), causing direct lysis of graft endothelial cells and contributing to graft injury and dysfunction.
2 M with a large intra-abdominal mass (19 cm with solid and cystic areas).
What syndrome is most commonly associated with this tumor.
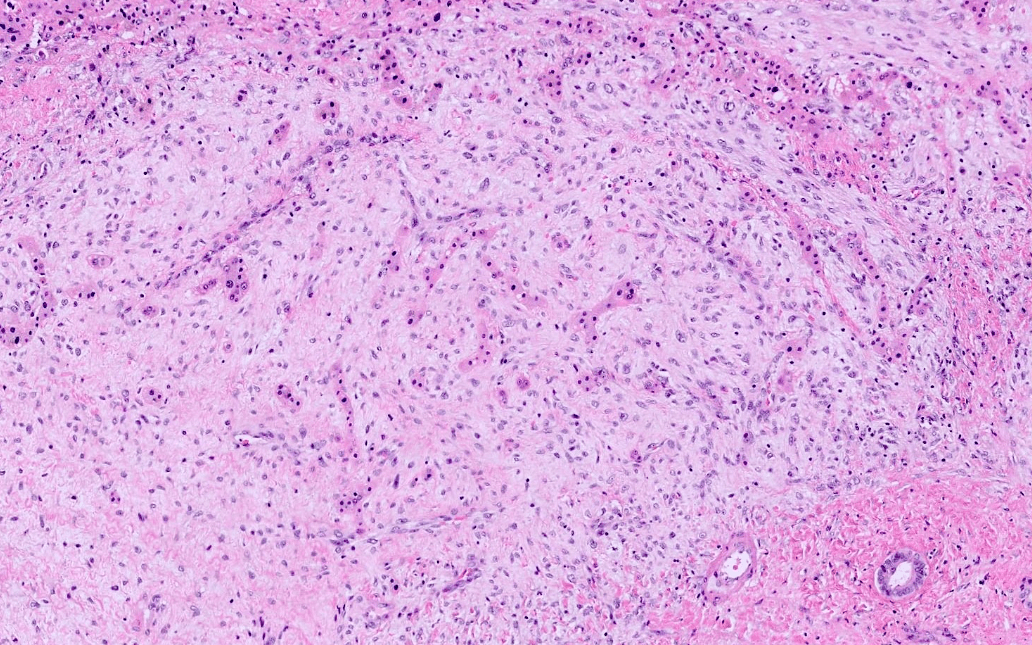
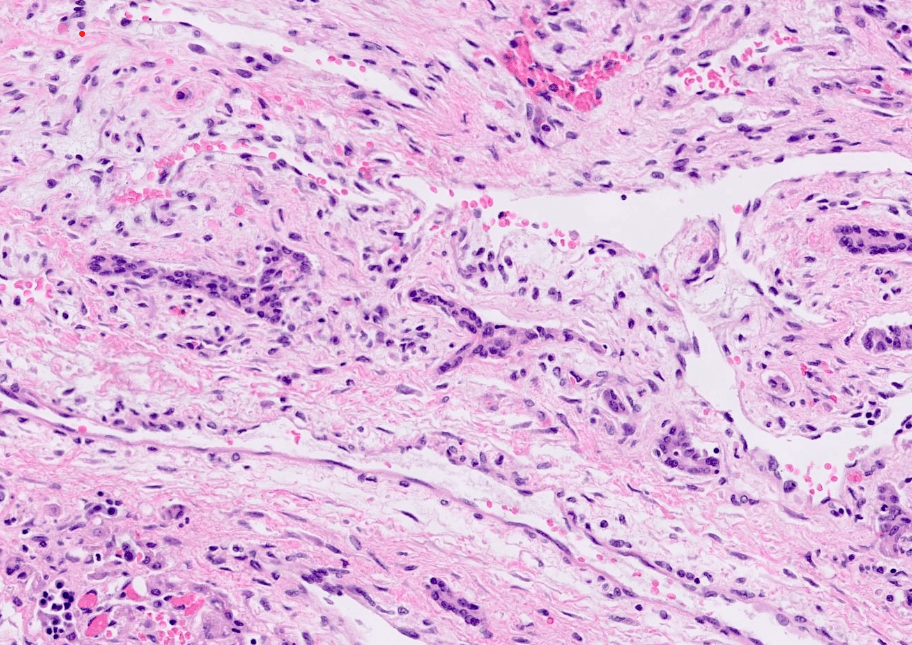
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome