What are things that are not alive?
Nonliving
All living things are composed of cells. Multi-cellular organisms consist of ______________ and one example of a multi-cellular organism is?
multiple cells
Animals
Plants
Fungi
Algae
Which organelle is responsible for generating most of the cell's energy through cellular respiration?
The mitochondria
A blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
the artery
What carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart from the rest of the body?
The veins
Which cell type has chloroplasts?
Eukaryotic cells such as the plant cell
Is grass living or nonliving explain your answer.
living
Grass grows and reproduces, and it can also die
List the organization of living things from smallest to largest
Cells
Tissues
organ
organ systems
organisms
A function of the kidneys?
Filters blood and removes waste products as urine
The two structures found in plant cells that are absent in animal cells
Chloroplasts and cell wall
Name something in the soil that helps plants grow
Nutrients
Photosynthesis is the process by which
Light energy is converted into the chemical energy of simple sugars
What are ribosomes
Organelles that make proteins with the help of RNA
Name the part of the digestive system where the absorption of food takes place
The small intestine
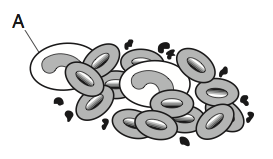
The diagram below represents a microscopic view of blood. Cell A protects the body by producing specific chemicals in response to pathogens. Cell A is
The white blood cell
What is diffusion?
Movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached
(Share at least 4)
1 Nutrition. Living things take in materials from their surroundings that they use for growth or to provide energy.
2. Respiration.
3 Movement.
4 Excretion
5 Growth
6 Reproduction
7 Sensitivity.
What is the main function of a cell membrane
A semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell through various transport mechanisms
What is an organ system?
organs working together and with other organ systems to make an organism
A characteristic common to both diffusion and active transport is that
the movement of molecules occurs
What is the nickname for the mitochondria?
powerhouse of the cell
What are the differences between biotic and abiotic factors in the ecosystems?
Biotic factors are living things within an ecosystem such as plants, animals, and bacteria
Abiotic are non-living components, such as water, soil, and atmosphere
Define active transport and state what it requires...
The movement of molecules from concentrations of where it is low to high concentration.
an input of energy called ATP
The nervous system plays an important role in everything we do. The 3 parts of the nervous system are....
brain
spinal cord
nerve cells
Plant cells can synthesize energy-rich organic molecules, and later break them down to extract that energy for performing life processes. These activities require direct interaction between the which 2 organelles in found in plant cells?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria