A term that describes organisms that make their own food.
Autotrophs
What term describes differences among individuals in a species?
Variation
What process results in two identical daughter cells and is used for growth and repair?
Bonus 100: What biotechnology takes advantage of this process?
Mitosis
Bonus: Cloning
What organic compound is involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Glucose
Define the term niche.
An organism's role in an ecosystem.
Define metabolism.
All of the chemical reactions that occur in an organism.
In the “Beaks of Finches” lab, what did different beak tools represent?
Different adaptations for feeding.
What are the monomers of proteins and where does synthesis occur?
Bonus 400: What are the two stages of protein synthesis, their given locations, and goals.
Amino acids; at the ribosome
Bonus:
1. Transcription
Location: Nucleus
Goal: DNA to RNA
2. Translation
Location: Cytoplasm/ribosome
Goal: RNA to protein
What is the function of a lipid in comparison to a carbohydrate?
Long-term energy storage vs. short-term energy
What is biodiversity?
Variety of life on Earth.
What is the difference between an independent variable and dependent variable?
Bonus 200: How many variables should be tested in an experiment? (think: how many should be changed?)
Independent Variable = I control
Dependent Variable = Depends on the Independent Variable
Bonus: 1
Why do species with similar DNA often have similar proteins?
Bonus 300: Give the amino acid sequence for the following DNA sequence: TAC-GCC
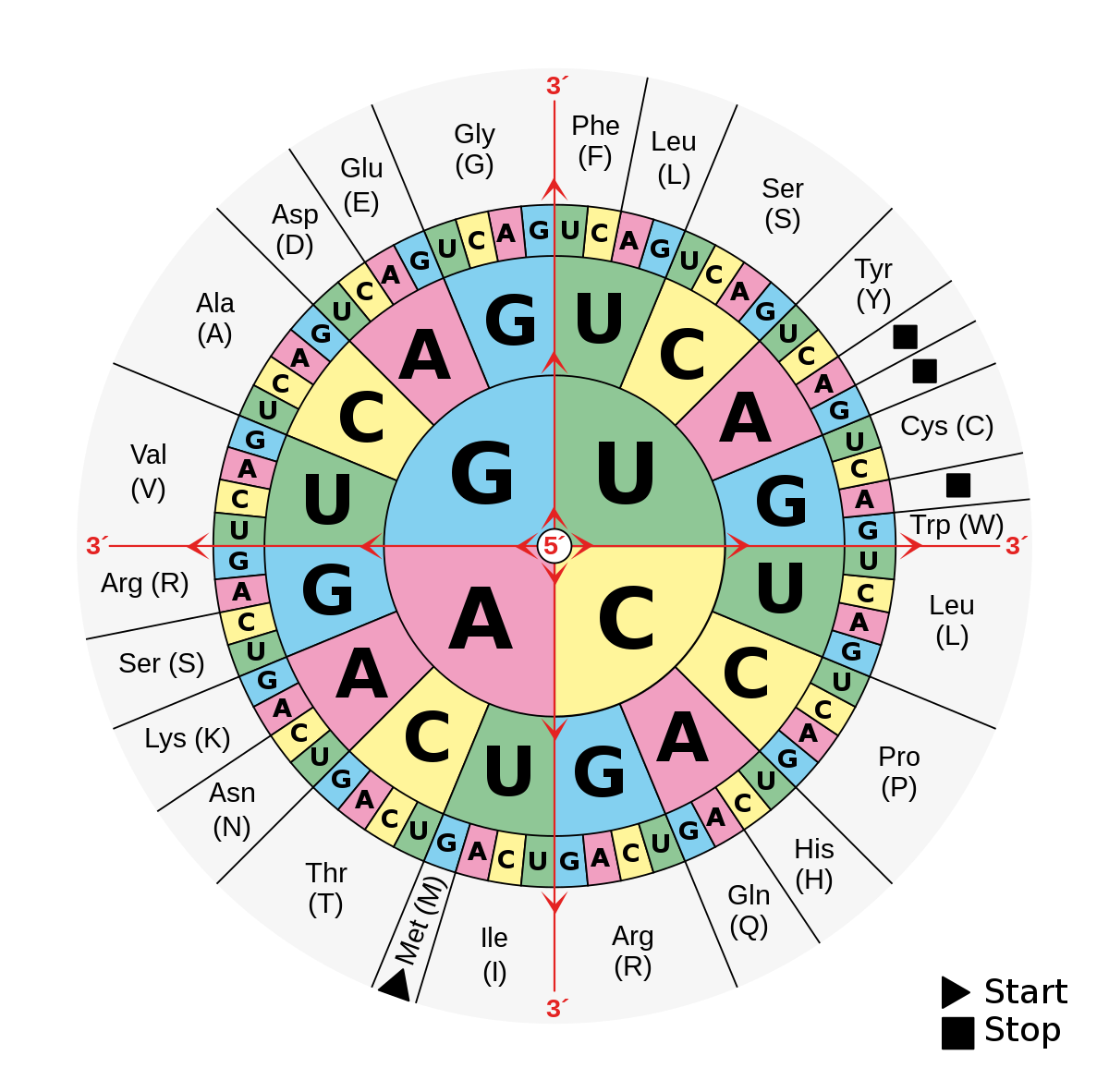
They likely share a common ancestor.
Bonus: mRNA: AUG-CGG
Amino Acids: Start (Met)-Arg
What is the role of the placenta in pregnancy?
Bonus 200: Where does fertilization occur?
It exchanges nutrients and wastes between mother and fetus.
Bonus: Oviduct/Fallopian Tube
What is the difference between active transport and diffusion? Describe in terms of energy and concentration gradients.
Active transport is low to high concentrations and requires ATP (energy)
Diffusion is high to low concentrations and does not require ATP (energy).
Identify an event that could disrupt a stable ecosystem.
Identify the process that would occur over time in that area following a disrupted event.
Ex. Wild fire
Ecological succession
What is a control group?
A group of subjects in an experiment that do not receive the variable being tested.
How do feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis?
Bonus 400: What two body systems work carry out a feedback system? Why do they?
By detecting changes and triggering a response to restore balance.
Bonus: The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to carry out a feedback system because they help the body maintain homeostasis.
The nervous system detects changes in the internal or external environment (stimuli) and sends fast electrical signals to organs and muscles to respond.
The endocrine system uses hormones (chemical messengers) to send slower, longer-lasting signals to regulate body functions like blood sugar, temperature, and water balance.
Why might identical twins raised in different environments show different traits?
Environmental factors affect gene expression.
What type of cells in the human body would contain a large surplus of mitochondria and why?
Muscle cells aid in carrying out cellular respiration to make ATP. ATP is in high demand to help these cells carry out their necessary functions/metabolic processes.
Which level of an energy pyramid has the most energy? What type of organisms are found here?
Bonus 200: What happens to the energy as we to the next trophic level?
The first level and producers (e.g., plants)
Bonus: It is lost as heat (about 90%)! Only 10% is passed on!
How are unicellular and multicellular organisms able to maintain homeostasis and carry out necessary life functions (think what do they each contain?)
Unicellular have organelles that help carry out life functions
Multicellular organisms have specialized cells to help carry out life functions.
In the “Relationships and Biodiversity” lab, what evidence supports evolutionary relationships?
Molecular similarities like enzyme activity and DNA banding.
We also studied the physical similarities, but the molecular evidence is more reliable!
What is selective breeding in comparison to genetic engineering?
Selective breeding: Choosing parents with desirable traits to breed offspring.
Genetic Engineering: To insert genes from one organism into another.
Explain why only certain molecules can pass through the plasma membrane. Name an example of a molecule that can pass through and one that cannot.
Semi-permeable
Can pass: Small, nonpolar molecules (e.g., monosaccharides)
Cannot pass: Large, polar molecules (e.g., polysaccharides)
Name an example of how humans are attempting to reduce their carbon footprint on Earth.
Driving electric cars, carpooling, recycling, etc.