What is made out of cells?

Any organism.
What is a heterotroph and what is an autotroph?
An autotroph gets its own food and a heterotroph uses other organisms to get food or energy.

Define cell.
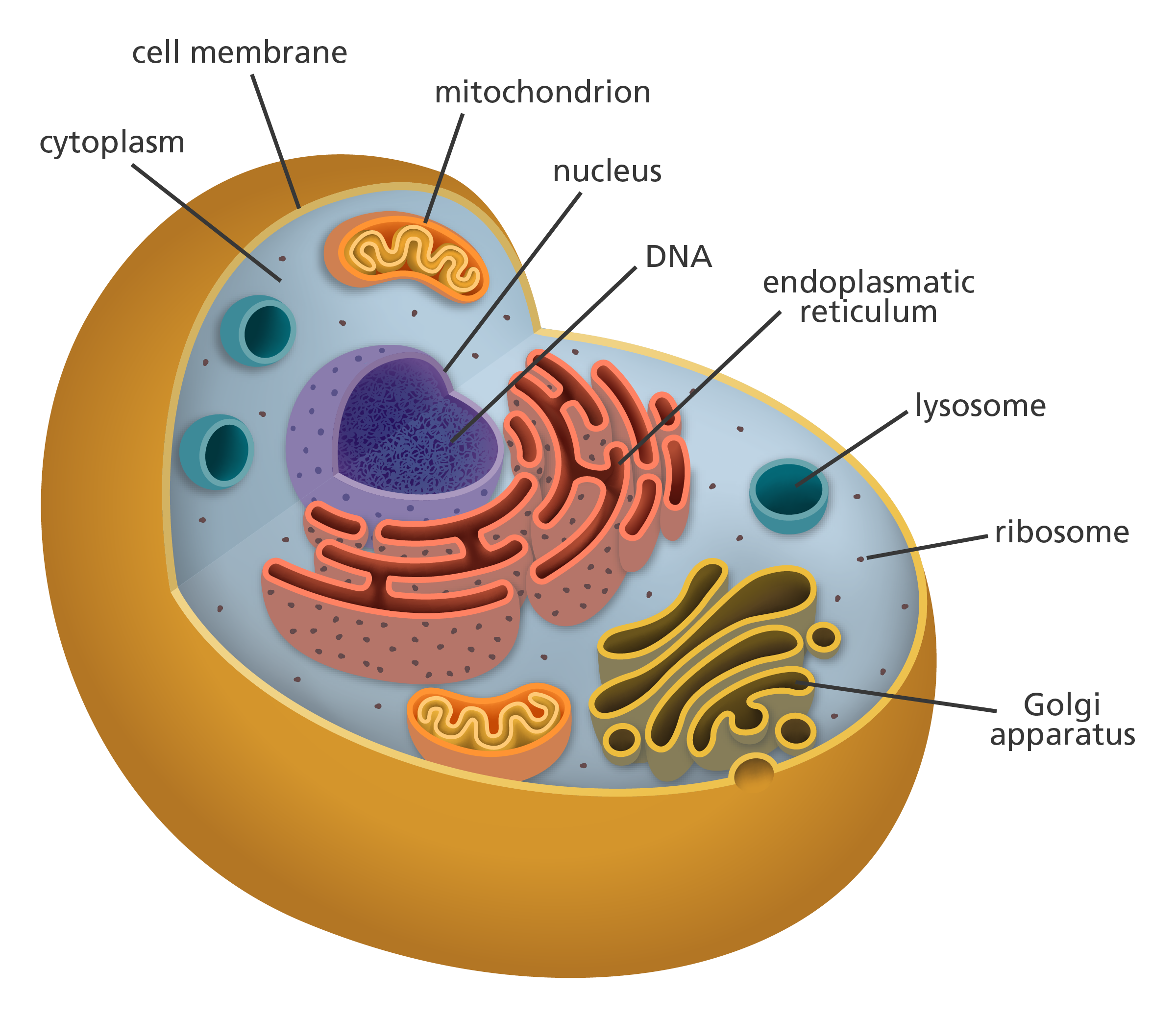
The basic unit of structure and function in living things
Define organism.
Any living thing.

Define classification.
The process of grouping things based on their similarities.

What are the three basic things organism need to survive?
Food, water, and space.

Is a tick a heterotroph or an autotroph?
It is a heterotroph.

Define unicellular.

A single celled organism.
Define multicellular.
An organism consisting of many cells.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/multicellularGE-57d812963df78c58333ff5c0.jpg)
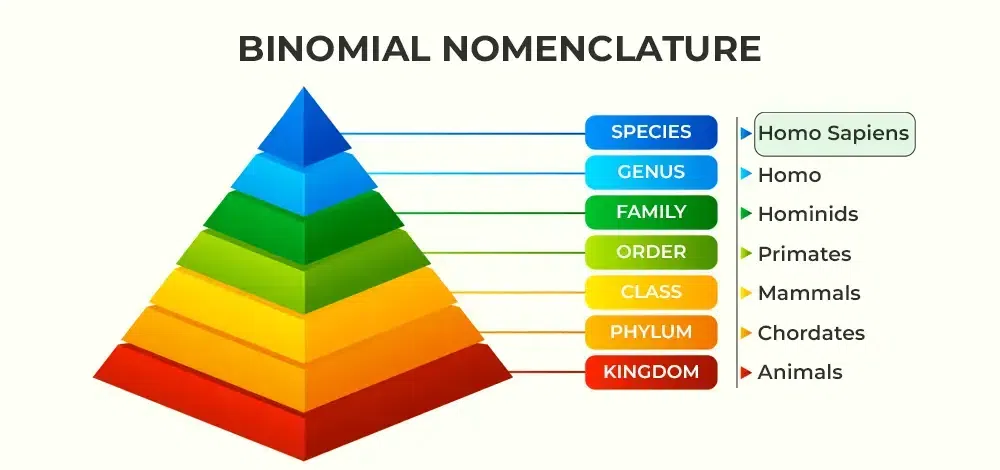
Define genus.
a group of similar, closely related organisms

True or False, all organisms contain very different chemicals.
False
Is a wolf a autotroph or a heterotroph?

It is a autotroph.
Define species.

A group of similar organisms that can mate with each other and produce offspring.
Define response.
An action or change in behavior when it reacts to a stimuli.
Define taxonomy.
The scientific study of how organisms are classified.
What does life produce?
More life.
Is a Zebra a hetertroph or an autotroph?

It is a hetertroph.
Define characteristics.

A feature that helps to identify something.
Define Spontaneous generation.
The mistaken idea that living things arise from nonliving sources.
Define Domain.
The broadest level of organization.

All organisms grow, develop, and ______

Reproduce
Is a human an autotroph or a heterotroph?
They are hetertroph's.

Define stimulus.
Any change or signal in the environment that can make an organism react in some way.

Define Homeostasis.
The maintenance of stable internal conditions.

Define binomial nomenclature.
When a species is given a name that indicates its genus and species.