Name the suspected medical disorder when a chronic, dry, persistent cough changes and dyspnea develops.
What is lung cancer?
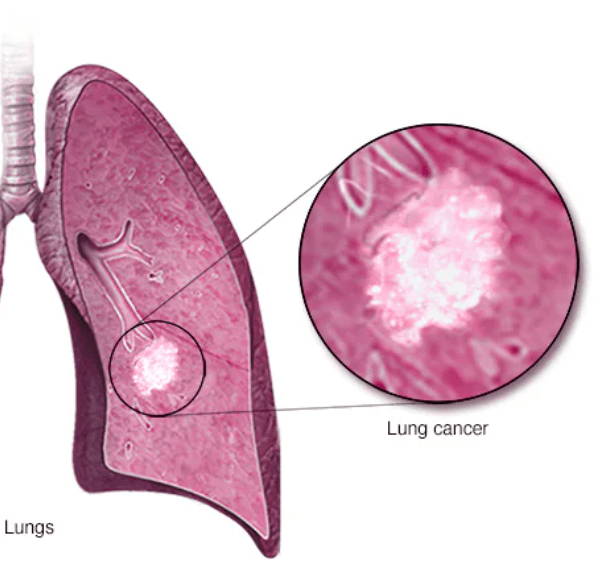
Name the suspected medical condition when crackles are auscultated in the lung bases.
What is pneumonia?
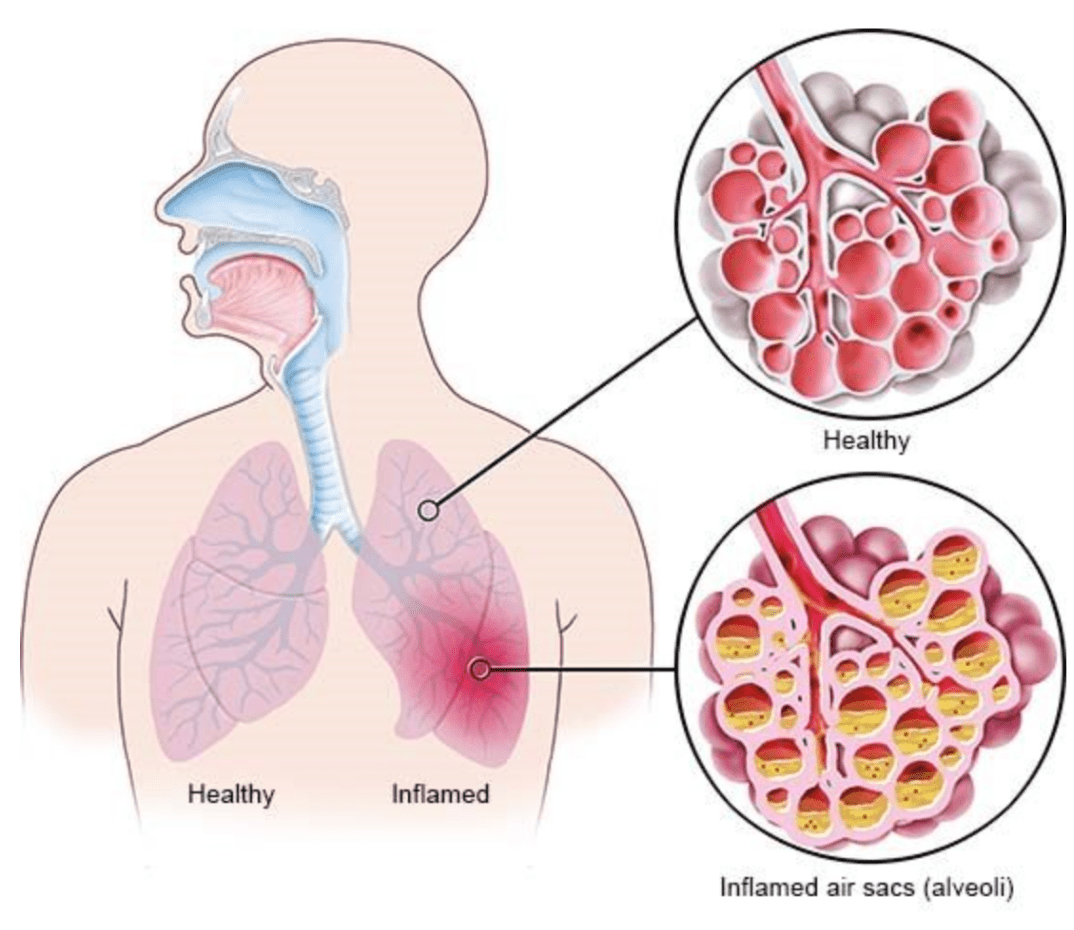
List the process for a diagnosis of pneumonia.
What is assessment, intake of patient complaints, and diagnostics (labs and rads)?
List five priority nursing interventions for a patient diagnosed with pneumonia.
What are airway management, oxygen therapy, medication administration, hydration support, and promoting lung expansion?
Name the antibiotic primarily used for the inpatient treatment of suspected pneumonia cases.
What is intravenous ceftriaxone?
Name this suspected medical disorder when a client complains of shortness of breath, persistent dry cough, and chest pain.
What is sarcoidosis?
Name this suspected medical condition when diminished, bronchial sounds are noted upon auscultation, and crackles in the bilateral bases, with fremitus and egophony.
What is tuberculosis?
Name this method that is used to determine whether a person has been infected with the TB bacillus and is used widely in screening for latent M. tuberculosis infection.
What is the Mantoux method?
List five priority nursing interventions for a patient diagnosed with tuberculosis.
What is promoting airway clearance, advocating adherence to the treatment regimen, promoting activity and nutrition, and preventing transmission?
Name the first-line medication and the active disease that it is used for, which normally tends to discolor bodily secretions orange.
What is Rifampin and tuberculosis?
Name this suspect medical disorder when a patient with an underlying history of an autoimmune disease complains of sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens when breathing deeply.
What is pleurisy?
Name this suspected medical condition when the patient complains of sternal soreness from coughing and has fever or chills, night sweats, headache, and general malaise.
What is acute tracheobronchitis?
These two techniques are primarily used in treatment to adequately drain a lung abscess.
What are postural drainage and chest physiotherapy?
List home care teaching for a client diagnosed with acute tracheobronchitis.
What is increased fluid intake, frequent position changes/sitting upright, deep breathing exercises to cough effectively, the need to complete the full course of antibiotics prescribed, and advise to patient to rest often.
Explain why the client diagnosed with a lung abscess is first started on a broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotic.
What is IV antimicrobial therapy depends on the results of the sputum culture and sensitivity and is given for an extended period?
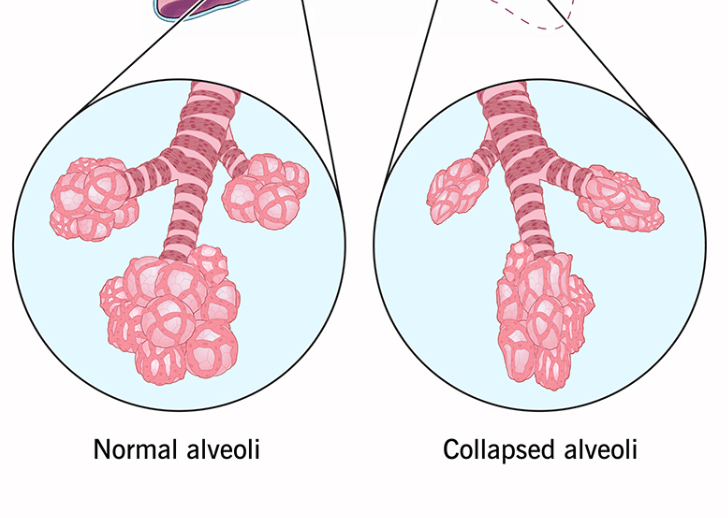
Name the suspected medical disorder when chest auscultation demonstrates the presence of adventitious or diminished lung sounds.
What is atelectasis?
Name this suspected medical disorder when a client with no teeth presents with a mild productive cough, with copious amounts of foul-smelling bloody sputum, and a fever.
What is a lung abscess?
List the two treatment goals for atelectasis.
What is to improve ventilation and remove secretions?
List the nursing interventions to prevent atelectasis in patients.
What is the ICOUGH Program?
Incentive spirometry, Coughing and deep breathing, Oral care (brushing teeth and using mouthwash twice a day), Understanding (patient and staff education), Getting out of bed at least three times daily, Head-of-bed elevation.
The beneficial medication commonly used to aid in the relief of sarcoidosis symptoms?
What is corticosteroid used in tapering doses for a year?
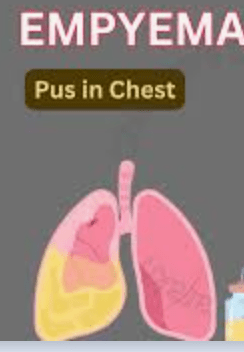
Name this suspected medical disorder when chest auscultation demonstrates decreased or absent breath sounds over the affected area, and there is dullness on chest percussion, as well as decreased fremitus.
What is empyema?
Name this suspected medical disorder when pus accumulates in the pleural space, coupled with inflammation, causing respiratory distress.
What is empyema?
Many patients undergo remission without specific treatment; name this condition.
What is sarcoidosis?
List the home care nursing interventions provided to the patient with empyema.
What are the coping strategies with the condition the patient in lung-expanding breathing exercises to restore normal respiratory function, and care specific to the method of drainage of the pleural fluid (e.g., needle aspiration, closed chest drainage, rib resection, and drainage)?
When the patient is discharged home with a drainage tube or system in place, the nurse instructs the patient and family on care of the drainage system and drain site, measurement and observation of drainage, signs and symptoms of infection, and how and when to contact the primary provider.
A patient was recently admitted with tuberculosis from a homeless shelter. Which medication should the nurse question and why?
What is Isoniazid? Possible alcohol withdrawal within 48-72 hours and drug interaction.