This autosomal dominant condition is characterized by the presence of this ECG finding.
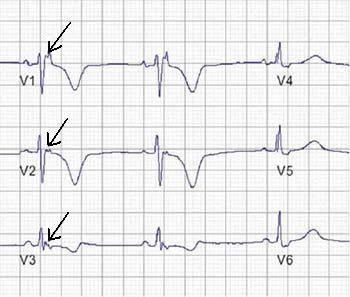
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do you expect the right atrium to collapse during tamponade?
Systolic
This WHO group of pulmonary hypertension is associated with left-sided valvular disease.
Group 2 Pulmonary Hypertension
Systolic ejection murmur that increases with abrupt standing and decreases with handgrip is indicative of what?
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Contrast filling the coronary sinus before the right atrium during a bubble study indicates?
Persistent Left SVC
This channelopathy (Long QT) was originally described as being inherited in what manner?
Autosomal Dominant
Respiratory variation of mitral inflow velocity greater than what percentage is supportive of cardiac tamponade?
25% or more
Name the phase of the cardiac cycle where pressure rises but volume remains constant.
Isovolumetric Contraction
What is the next best test for severe paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis?
Aortic Valve Calcium Score
What syndrome / complex is associated with multiple left sided obstructive lesions (i.e. parachute mitral valve, supravalvular mitral ring, subaortic stenosis, aortic coarctation)
Shone Complex (Syndrome)
What electrolyte is directly related to the mechanism of bi-directional VT (often seen in Digoxin toxicity or CPVT)?
Calcium
Which diagnosis is suggested by this RV pressure tracing finding? (hint: "square root sign")

Pericardial Constriction
Mutations in the gene producing this protein are strongly implicated in Marfan Syndrome.
Fibrillin-1
What high risk ECG finding is concerning for possible complete heart block after TAVR?
RBBB
What is the most common associated lesion found with a sinus venous atrial septal defect?
Anomalous right pulmonary vein connection
What is the name of this ECG abnormality?
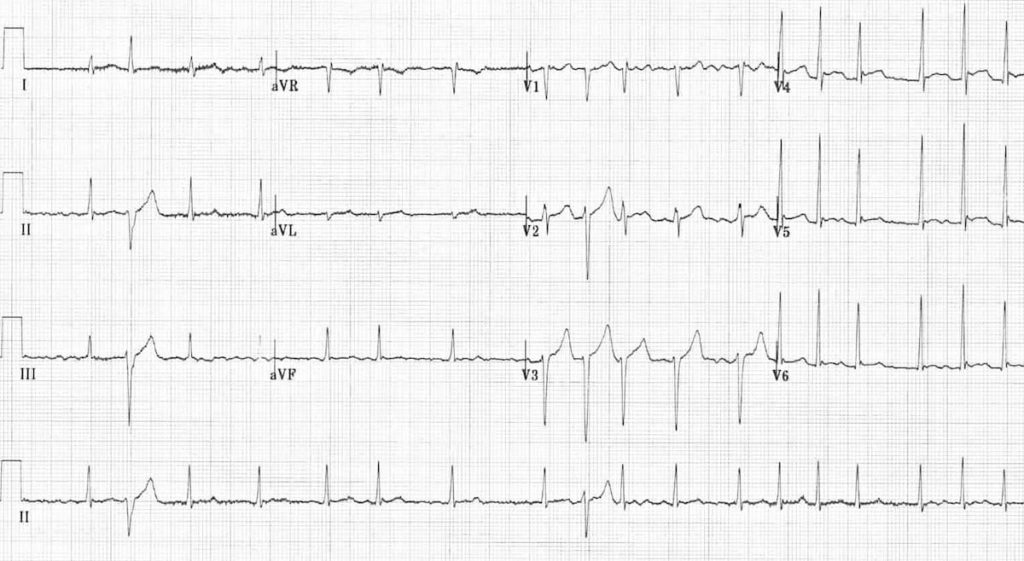
Ashman Phenomenon
What hepatic vein doppler finding is suggestive of pericardial constriction?
Expiratory diastolic reversal
For an HCM patient with paroxysmal AFib, name the first and second line anticoagulant options in sequence.
1st: DOAC; 2nd: Vitamin K Antagonist
In classic severe low-flow, low-gradient aortic stenosis, what flow reserve do we want to see on a dobutamine stress echo?
>/= 20%
This pulse wave doppler finding was obtained in the descending aorta. What does it represent?
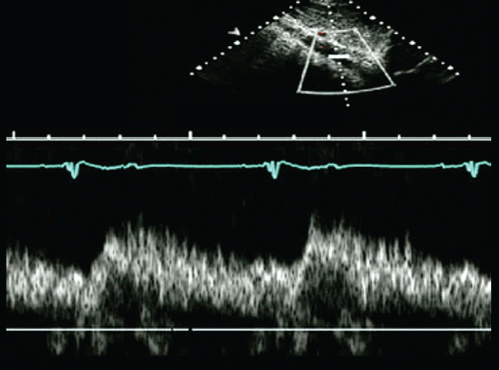
Aortic Coarctation
In Brugada syndrome, fever increases arrhythmic risk by worsening dysfunction of this ion channel.
SCN5A (Sodium Channel)
This structure forms the lower boundary of the transverse pericardial sinus.
The Left Atrium
What receptor is at risk of causing AV blocks during pharmacological stress tests?
Adenosine A1
Name the 3 Carpentier classes of mitral regurgitation and what type of motion they are associated with.
Type 1 - Normal motion (i.e. annular dilation, perforation)
Type 2 - Excessive motion (i.e. prolapse, flail)
Type 3 - Restrictive motion (i.e. rheumatic disease, ischemic)
A membrane dividing the left atrium into two chambers is known as?
Cor Triatriatum Sinister