EVOLUTION that takes place as a RESULT of ORGANISMS having to ADAPT to SIMILAR ENVIRONMENTS, even though the organisms have NO COMMON ANCESTOR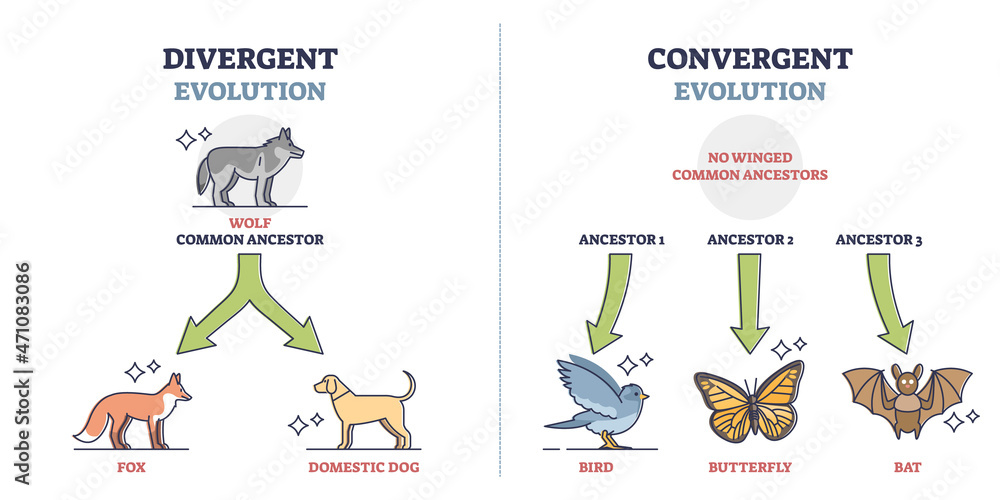
Convergent evolution
objective analysis of evolutionary relationships 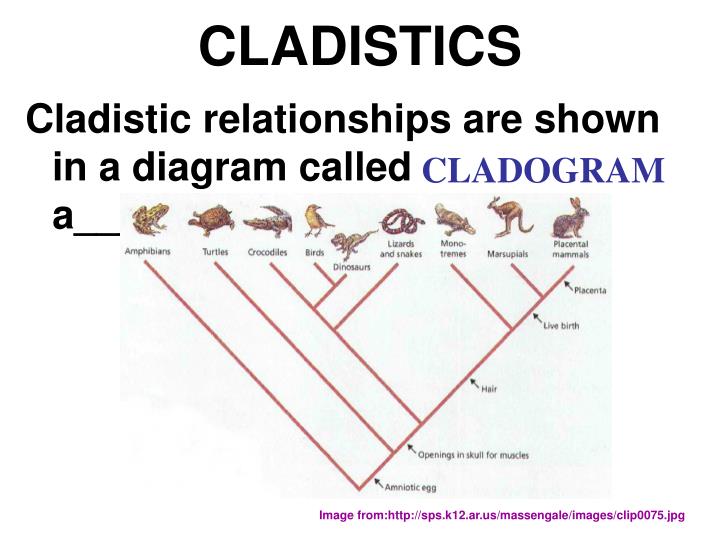
Cladistics
the most inclusive level of classification
Domain
The POPULATION of ORGANISMS that CAN INTERBREED and CAN'T INTERBREED with OTHER GROUPS of organisms
biological species
Percentage(%) of species on this planet that scientists believe have already been discovered
5-10%
level of classification that contains several phylum (between domain and phylum)
Kingdom
SIMILAR CHARACTERISTICS that organisms have, even though they DON'T HAVE a COMMON ANCESTOR
Analogous character
In LATIN; GENUS is the FIRST WORD and is CAPITALIZED; SPECIES is the SECOND WORD and is LOWERCASE
Rules for scientific name
level of classification that contains several families (between class and family)
Order
individuals of different species interbreed and produce offspring 
Hybrid
type of REPRODUCTION by which OFFSPRING ARISE from a SINGLE ORGANISM, and INHERIT the GENES of THAT PARENT ONLY 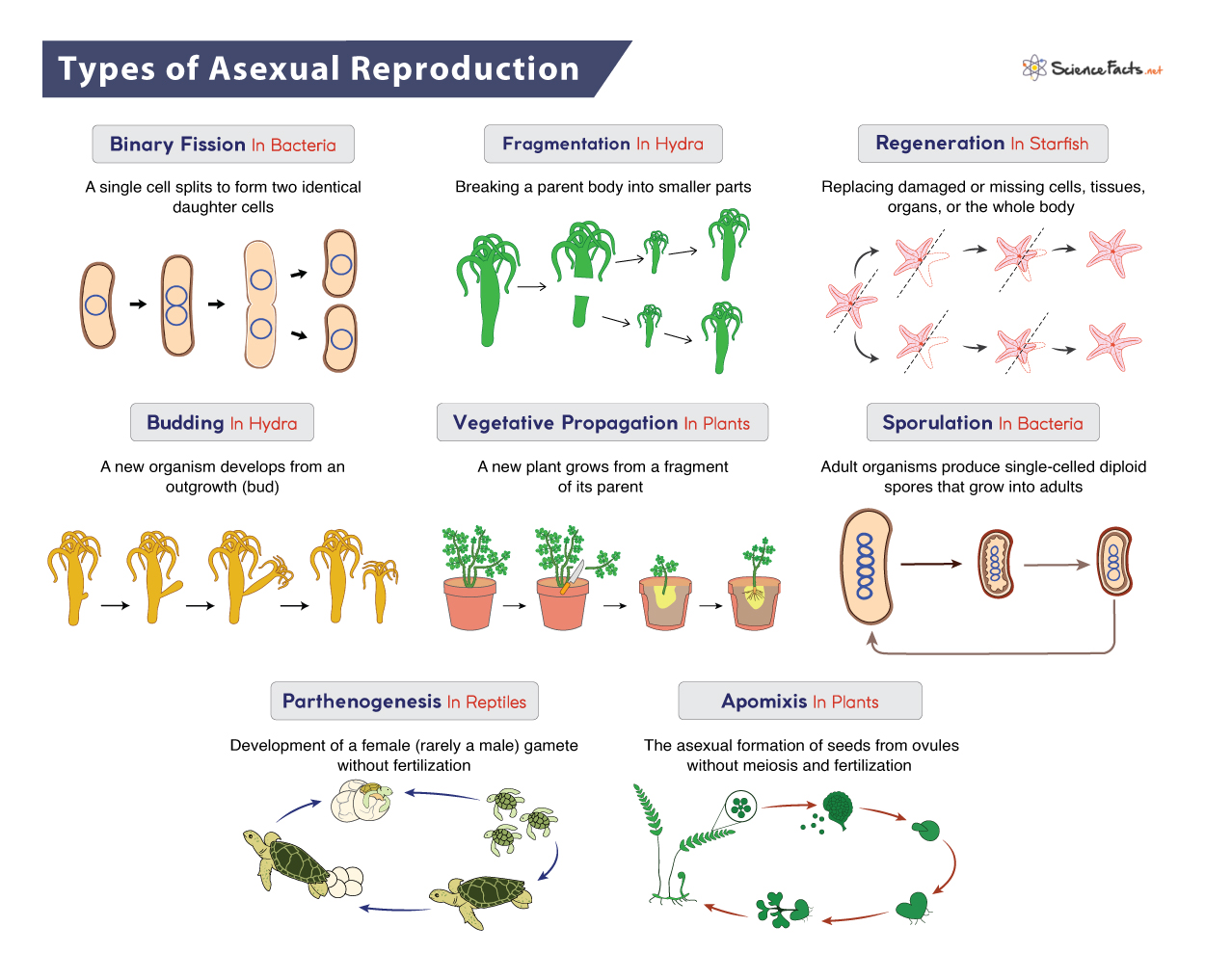
Asexual reproduction
the most exclusive level of classification; there are several of these in each genus
Species
SIMILARITIES that ARISE through CONVERGENT EVOLUTION. These similarities are derived from independent sources.
Analogous characters
two-part name (binomial nomenclature) to name a species 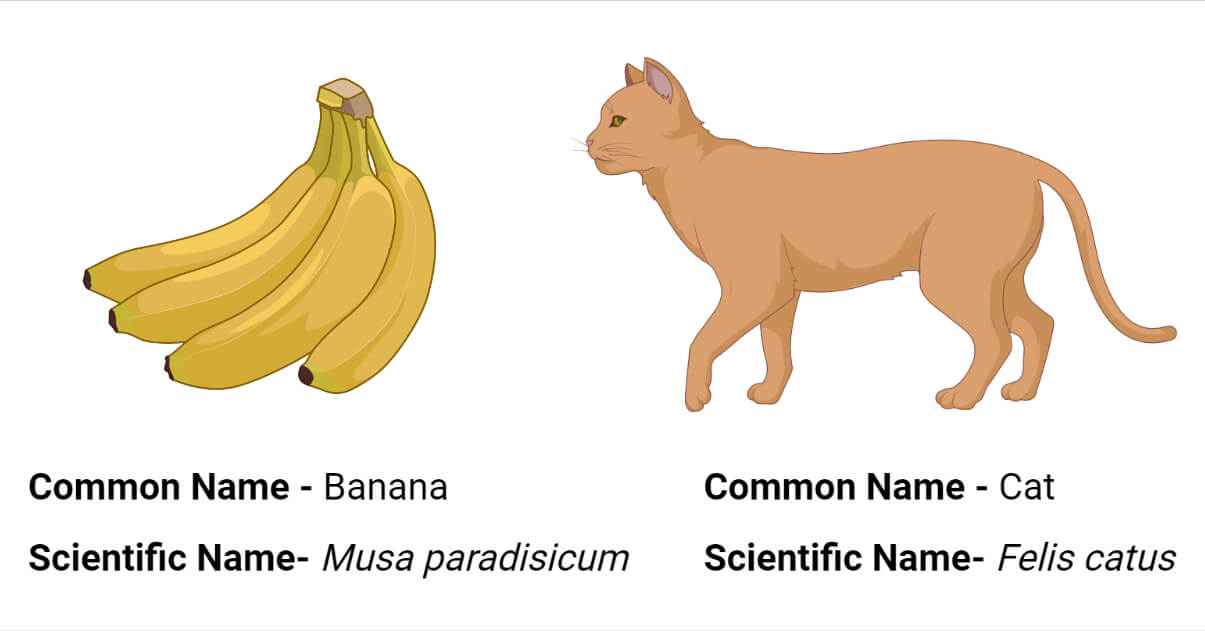
Scientific name
level of classification that contains several genus (between order and genus)
Family
Name for the study of classifying and naming organisms 
Taxonomy
evolutionary history of an organism 
Phylogeny
level of classification that contains several orders (between phylum and order)
Class
SIMILAR CHARACTERISTICS that organisms have BECAUSE they have a COMMON ANCESTOR
Ancestral character
method whereby an ORGANISM is given a TWO PART LATIN NAME 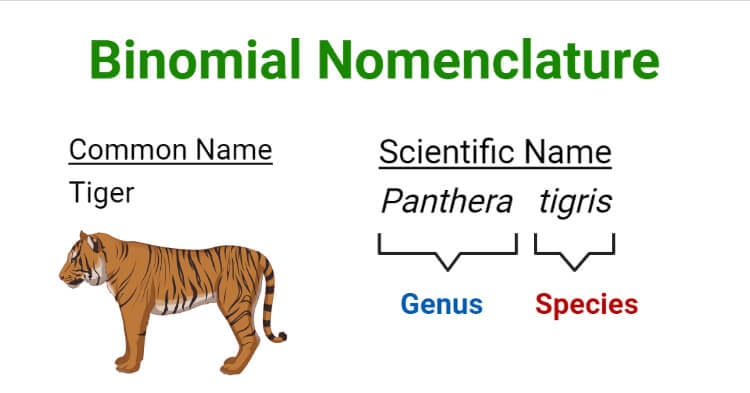
Binomial nomenclature
level of classification that contains several classes (between kingdom and class)
Phylum
Organisms are classified based on their __________________. 
Form & structure
a branching diagram to show evolutionary relationships in evolutionary systematics 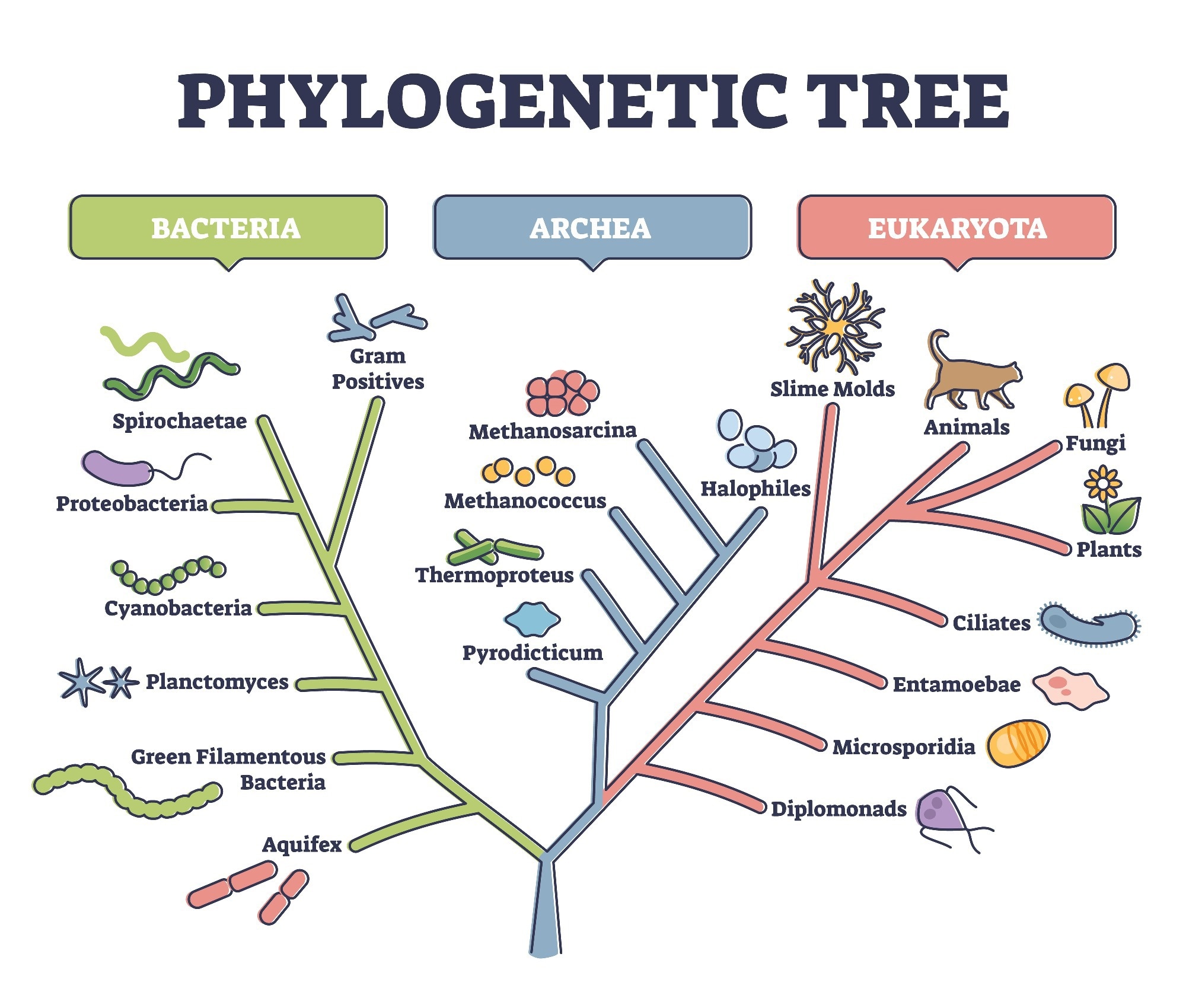
Phylogenic tree
EVOLVED in an ANCESTOR of ONE GROUP but NOT of THE OTHER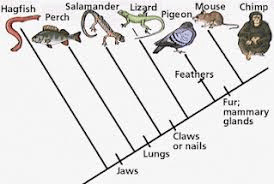
Derived character
When a NEW ORGANISM is DISCOVERED, this is WHO AGREES ON a NAME for the newly discovered organism
International Commission of Scientists
level of classification that contains several species (between family and species)
Genus
BRACHING DIAGRAM which SHOWS EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS AMONG groups of ORGANISMS (cladistics) 
Cladogram
subjective analysis of evolutionary relationships 
evolutionary systematics
