a short, thick structure that allows a bacterium to attach to another bacterium
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)
pili
Tuberculosis; dental cavities; strep throat; acne; anthrax; bubonic plague; etc.
bacterial diseases
Viral DNA that is inserted into the chromosome of the cell that has been attacked by a virus during the lysogenic cycle
provirus
a protein coat that surrounds the nucleic acid core in a virus

capsid
Viral replication that results in the killing of the cell that the virus attacks
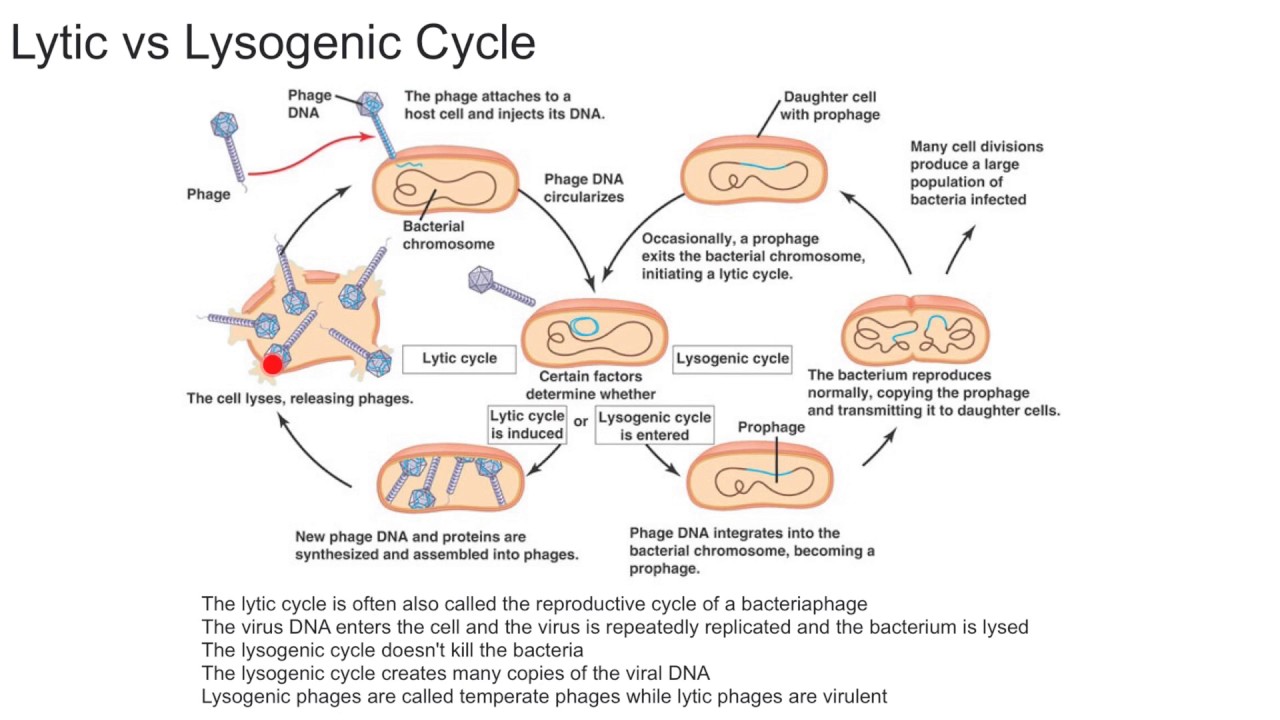
lytic cycle
Bacteria are prokaryotes; eukaryote cells are larger; bacteria are single cells; bacterial cells circular; bacteria reproduce by binary fission
bacteria different eukaryotes
Thick-wall around bacterial chromosomes that protect them from harsh conditions

endospore
Photosynthetic bacteria; chemoautotrophs; heterotrophic bacteria
ways to get energy
Protective gel-like layer outside the cell wall and membrane that helps protect bacteria from the immune system
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)
capsule
Process in which two organisms exchange genetic material

conjugation
Describes a process that requires oxygen
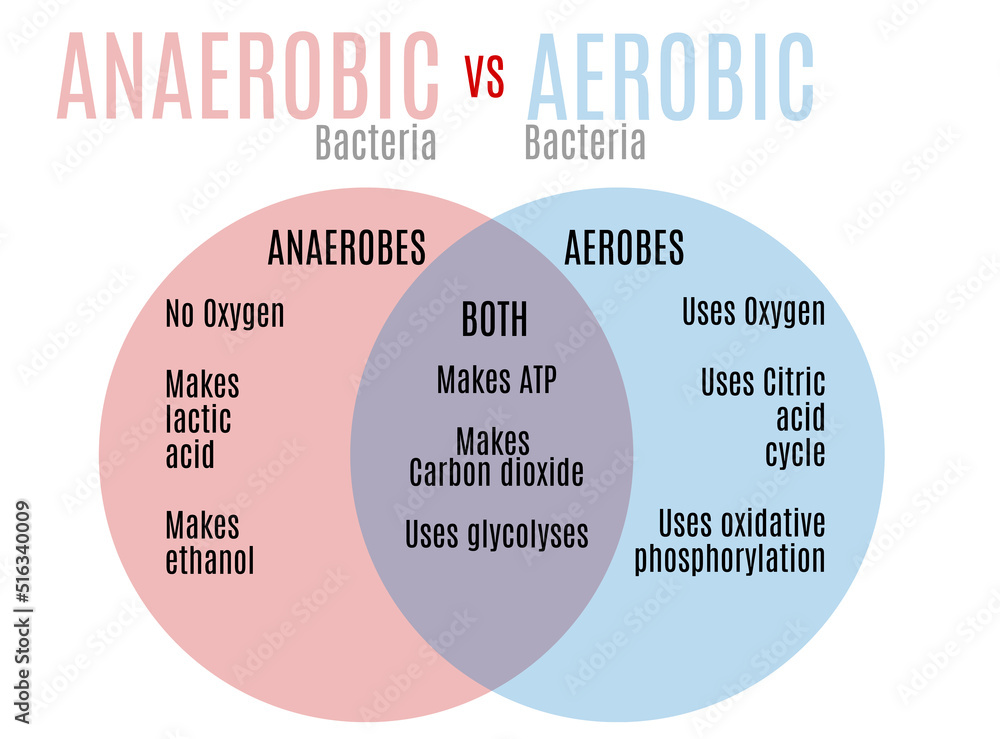
aerobic
Process food; make medicines; mining; clean up oil spills

uses of bacteria
a protein to which carbohydrate molecules are attached

glycoprotein
Viral replication is when a virus's DNA is copied as a provirus without destroying the cell

lysogenic cycle
Chemical that interfere with life processes in bacteria

antibiotic
a membrane like layer that covers the protein coat (capsid) of some viruses

envelope
Small pox; chicken pox; hepatitis; influenza; polio; common cold; mumps; etc.
viral diseases
______________ are the principal decomposers (break down the cells of dead organisms) of the living world
heterotrophic bacteria
Cells that do not have a nucleus
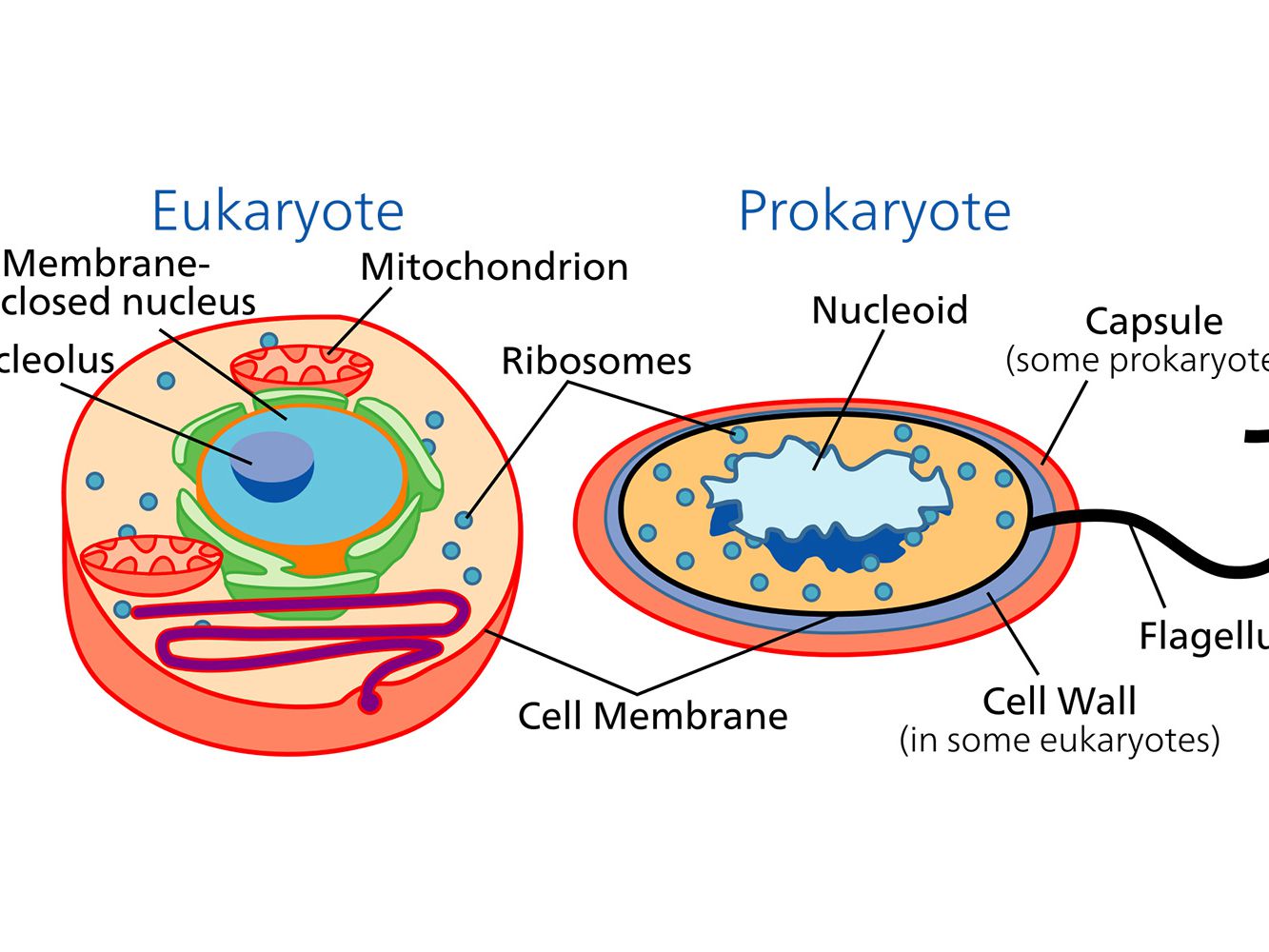
prokaryotic
A virus, microorganism, or other substance that causes disease

pathogen
a nonliving particle made up of a nucleic acid and a protein coat; it can infect and destroy a cell

virus
Cells that have a nucleus

eukaryotic
a bacterium that is shaped like a spiral
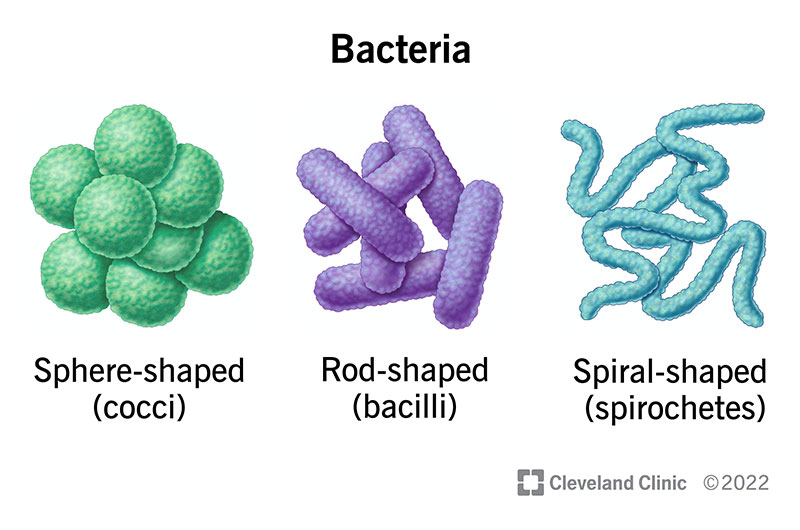
spirillum
Describes a process that does not require oxygen

anaerobic
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome

AIDS
When bacteria aren’t killed by antibiotics because of a mutation that allows to survive

antibiotic resistance
a virus that infects bacteria
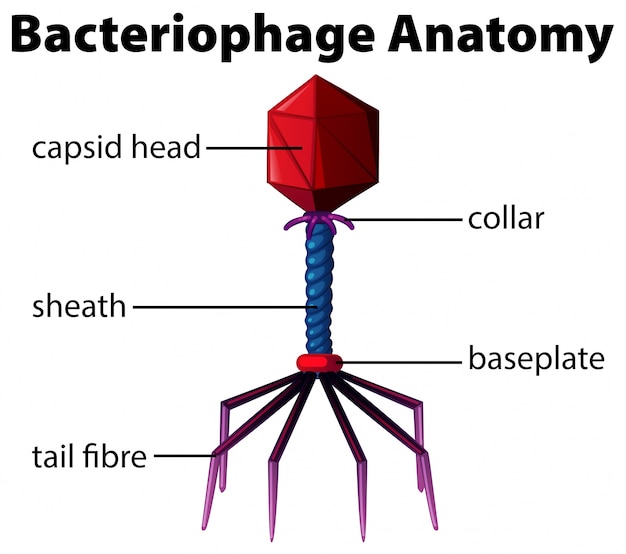
bacteriophage
Do not metabolize; do not reproduce; no homeostasis

viruses not alive
Deliberate exposure of people to biological toxins or pathogens
biowarfare
a bacterium that is shaped like a rod

bacillus