Olive oil is an example of a
What is a lipid?
These are the 4 major macromolecules
What are lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids?
Lowers activation energy
Enzymes
What is this a structure of?
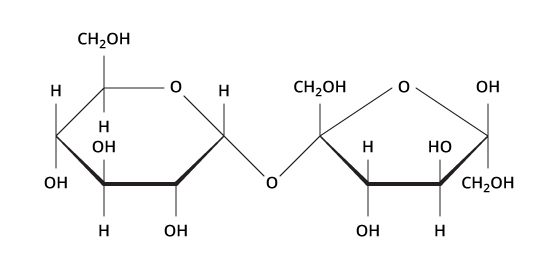
What is a carbohydrate?
The charge of phosphates
What is a negative?
Carbohydrate that we cannot digest
What is fiber?
Lipids have longer lasting energy than Carbohydrates. True or False.
What is true?
Name a food that is a protein.
Meat, beans, fish, eggs, nuts, etc.
These elements make up nucleic acids
What is CHONP?
What type of molecule do we need to dissolve some vitamins
What is lipid/fat?
The monomer for a protein is
What is an amino acid?
These are used for genetic information.
What is nucleic acid?
If the DNA is 30% A, what percent G is it
What is 20%?
This type of molecule has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
What is a phospholipid?
Water is nonpolar. True or False
What is a false?
Lipids are also known as
What are fats and oils?
These are the two nucleic acids
What is DNA and RNA?
This is the monomer of proteins
What is amino acids?
Type of macromolecule that ends in -ose
What is a carb?
Something that is different for each amino acid
What is R groups or side chains?
What pairs with this sequence: ATGCAAC
hint- think of the 2 strands of DNA and which bases go together
What is TACGTTG?
This is the difference between saturated and unsaturated
What is Saturated is straight and unsaturated is bent?
List all of the nitrogen bases
What is Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Uracil?
The base that replaces thymine (T) in RNA
What is Uracil?
Inhibitor that is the same shape as the substrate
What is a competitive inhibitor?