fatty acids, triglycerides, butter/oil are all types of this macromolecule group.
lipids
This process is used to join monomers together to create a polymer.
What is dehydration synthesis?
This is the monomer of proteins.
amino acid
The macromolecule shown belowis: 
What is a lipid (triglyceride)?
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
Monosacchride
A cheese pizza is high in these macromolecule(s).
Name the 2.
lipids and carbohydrates
This macromolecule is used for genetic information.
nucleic acid
What is the elements that make up a carbohydrate and at what ratio?
(C, N, H, O, P)
CHO in a 1:2:1 ratio
The macromolecule shown below is:
What is a protein?
Mono means _____
What is one?
Provide 2 examples of carbohydrates.
starches, cellulose, glycogen
Lipids have longer lasting energy than Carbohydrates. (True or False)
true
Proteins are found in this food group.
meat
The macromolecule shown below is: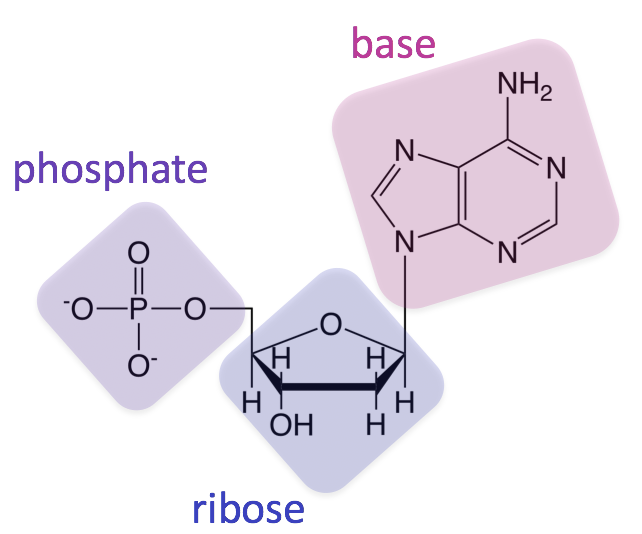
What is a nucleic acid?
Poly means _____
What is many/multiple?
What are the 2 monomers for a Lipid?
Glycerol and fatty acids
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are types this type of macromolecule. What is the difference between each of these?
What are carbohydrates?
Mono=1
Di=2
Poly=many
What elements make up a Lipid?
CHO
Nitrogen Base, phosphate, and a pentose sugar are the three parts of this macromolecule.
Nucleic Acid
This process is used to break down polymers into monomers.
What is hydrolysis?
What is the monomer of a protein?
amino acids
The 4 macromolecule groups are...
lipids, proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
Fats and oils are examples of this macromolecule.
lipids
The structure below is an example of this.
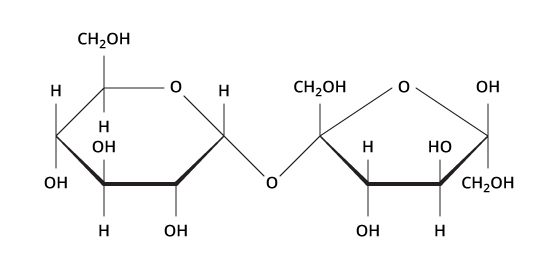
What is a carbohydrate or disaccharide(2).
Glycerol is needed to build this macromolecule.
What is a lipid?