The heteroatoms found in carbohydrates (Both or nothing)
What is hydrogen and oxygen?
The element that carbon atoms continuously bond with in lipids
What is hydrogen?
The macromolecule that provides structure in membranes
What are lipids?
The individual elements that bond together to form a protein
What are amino acids?
What nucleic acids contain inside of them
What is genetic information?
What plants use carbohydrates for, that animals don’t
What is structure?
The process in cells that breaks down glucose into carbon dioxide and water
What is cellular respiration?
The process that breaks down starches into individual monosaccharides
What is hydrolysis?
The scientific name for the individual components of starch
What is a monosaccharide?
The two types of nucleic acids
What is ribonucleic acid (RNA), & deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)?
The common ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a monosaccharide
What is a 1:2:1 ratio?
The substance fatty acids bond to in a lipid
What is glycerol?
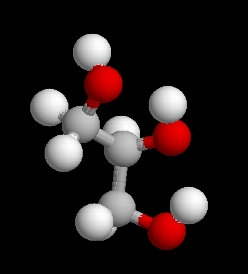
A lipid with multiple double covalent bonds between two carbon atoms in a fatty acid
What is a polyunsaturated lipid?
The four nitrogenous bases in a nucleotide
What is adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine?
What makes up a protein, and how it gets its shape
What are twisted and folded amino acids?
The type of lipid in cooking oils
What is a polyunsaturated lipid?
An immune purpose of a protein
What is fighting disease?
The amino acid that best supports muscle growth
What is leucine?
The two forces that maintain a protein’s shape
What are Van der Waals forces & hydrogen bonds?
The amount of sugars in one nucleotide
What are 5 sugars?
The chemical formula for the amino group in an amino acid
What is NH2?
The amount of hydrogen atoms that are in one molecule of lauric acid
What are 24 hydrogen atoms?
The chemical formula for glucose
What is C6H12O6?
The full chemical formula for an amino acid with a variable R-group
What is H2NCHRCOOH?

10000 POINTS
The full chemical name for the protein titin
