What are the three types of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes, Alkenes, & Alkynes
What are the 4 functional groups?
Hydroxls, Carbonyl, Carboxyls, & Amino groups.
What are the elements and their ratio for a carb?
Carbs are made from C, H, and O in an 1:2:1 ratio.
What are 3 examples of lipids?
Oils, waxes, fats, cholesterol, and phospholipids.
What are all proteins (polymers) made up with (monomer) and how are ___ arranged?
Which type(s) are fully saturated and why?
Alkanes; because they have the maximum amount of hydrogens bonded.
What do hydroxyls (OH or HO) make up?
Sugars and alcohols.
What are the 3 types of saccharides and how do they differ?
Monosaccharides: Simple sugars/simple carb with 1 sugar monomer (ex. glucose <-(isomers)-> fructose, and galactose)
Disaccharides: 2 sugar units/simple carb (ex. sucrose=table sugar and fructose) made by dehydration synthesis (glycosidic bond)
Polysaccharides: Many sugar units, these are complex carbs (ex. starch in plants, glycogen in animals, and cellulose)
*cellulose is for plants and animals cannot extract fiber USUALLY, but certain gut bacteria can extract it*
What fats (lipids) are normally solid at room temperature, and which are liquid at room temperature?
Saturated fats are normally solid at room temperature, and unsaturated fats are normally liquid.
What are the main jobs of proteins?
Proteins are used to build cells, act as hormones & enzymes, and do much of the work in a cell.
What are the formulas for alkanes, alkenes, & alkynes?
CnH2n+2
CnH2n
CnH2n-2
What are the differences between carbonyls and carboxyls?
Carbonyls (CO) make up aldehydes, ketones and some sugars. Carboxyls (COOH) make up amino acids, proteins, some vitamins, and fatty acids.
What is dehydration synthesis vs hydrolysis and what do each accomplish on a molecular level?
Dehydration synthesis is whenever 2 or more molecules bond by taking a H and an OH, then linking with the other molecule with this leftover space.
Hydrolysis breaks up a bond by forcing an H2O molecule in between a place that's bonded, causing the molecules to break up.
What is a triglyceride?
It's a monomer of lipids, composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains.
How do amino acids bond, and what are the bonds called?
Amino acids bond with dehydration synthesis and they are called peptide bonds.
What are the differences between alkanes, alkenes, & alkynes?
Alkanes are fully saturated with only single bonds, while alkenes have at least one double bond and are unsaturated. Alkynes however have at least one triple bond and are also unsaturated.
Name this functional group.
Caroboxylic acid
What are complex carbohydrates?
Complex carbs are many sugar molecules bonded together. (ex. glycogen and starch)
What is the base steroid for your body to produce others?
Cholesterol.
What are the types of proteins ( primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) and how are they built?
Primary- ribbon-like and has a specific sequece (called a polypeptide)
Secondary- Occur when protein structures coil and fold (alpha heliz-coil & beta sheet-fold). They are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary- When polypeptides join together, the tertiary structure forms an R group.
Quaternary-In a watery environment of a cell, and they become globular. It's made of 2 or more peptide chains joined together.
What bond would C30H58 be?
Alkyne bond
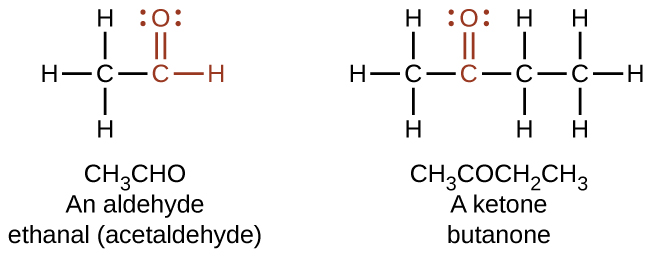
What is the difference between a ketone and an alehyde?
While they both contain a double carbon-oxygen bond, aldehydes have their carbonyl group on the end, and ketones have theirs in the middle of the chain.
What is the main purpose for carbs?
Carbs store energy.
Draw and label a phospholipid.
Top: Polar head (circle)-contains phosphate/hydrophilic
Two lines: Nonpolar tail and fatty acid chain/hydrophobic
Enzymes (globular proteins) control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction. They act as biological catalysts.
*Each enzyme has a specific isomer for its active sight, which makes it specific for one kind of substrate*