What is DC?
The point on the hysteresis loop that represents the point of magnetic saturation.

What is point A/D?
The amount of magnetism that is present in the middle of a magnetized bar.
What is zero?
The distance at which black lights are measured for intensity.
What is 15 inches?
Imaginary magnetic lines used as a means of explaining the behavior of magnetic fields.
What are flux lines?
What type of defect is this?

What is porosity?
The ability of the magnetic particles to move freely over the surface of the part so they can be attracted, gathered, and held at leakage fields to form indications. This ability is affected by many different factors including the type of wave form used.
What it particle mobility?
The point on the hysteresis loop that represents permeability ?

What is curve z?
The use of externally applied magnetic field to induce current in a part to produce a magnetic field . Useful for parts where flowing current would risk damage.
This test determines if the output setting on a wet-bench matches the output the machine is actually putting out.
What is the shunt meter test or the amperage indicator check?
The determining of the cause and significance of indications of discontinuities from the standpoint of whether they are detrimental defects or false or nonrelevant indications.
A welding defect that occurs when the root of the weld does not penetrate throughout the base material.
What is lack of penetration?
This wave form tends to concentrate near the surface of a conductor, making it the best choice for locating surface defects.
What is AC?
The point on the hysteresis loop that represents retentivity.

What is point B/E?
The use of current passed through the part via contact heads or prods to produce a magnetic field
What is direct contact magnetization?
The test used to determine if the magnetic field strength coming from Yokes is adequate for magnetic particle inspection.
What is the dead weight test?
An electrical conductor that is passed through the opening in a ring or tube or any hole in an article for the purpose of creating a circular field around the hole.
What is a central conductor (central bar conductor (CBC))
A service induced defect that occurs due to cyclic loading.
What is a crack?
The process of converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing only one polarity of the AC waveform to pass.
What is rectification?
The point on the hysteresis loop that represents cohersive force?

What is C/F?
A material that is repelled by magnets.
What is diamagentic?
The test used to determine if the ratio of magnetic particles to the carrying fluid is within acceptable limits.
What is the concentration/settling test?
The unit of electrical current.
What is an Ampere (Amps)?
A surface defect created when a portion of the metal folds over during rolling and becomes pressed into the surface, forming an unbonded or poorly bonded fold.
What is a lap?
The tendency of alternating current (AC) to concentrate near the surface of a conductor, so that current density is highest at the surface and decreases with depth into the material.
What is the skin effect?
The axis on the hysteresis loop that represents flux density.
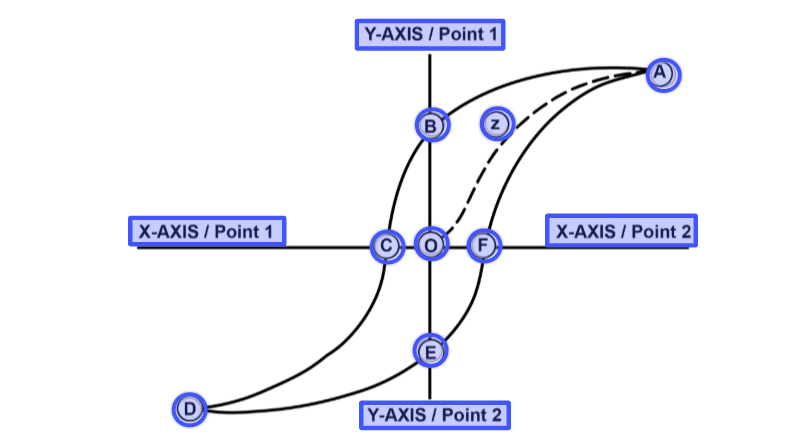
What is the Y-axis?
This equation describes the amount of electrical force that is produced based on the number of wraps in a coil, and the rate of change of the magnetic field.

What is Faraday's equation?
An led light blinks when the magnetic field collapses rapidly in the coil when performing this check.
What is the quick break test?
The area on a magnetized article from which the magnetic field is leaving or returning to the article.
Pole.
An internal defect formed by pre-existing non-metallic inclusions, blowholes, or internal cracks in the billet or slab that become elongated into thin layers during rolling.
What is a lamination?