Shows the average weather of a region, taking into consideration, temperature, precipitation, humidity, etc.
CLIMATE MAP
ROAD MAP
The day to day condition of the atmosphere. This includes temperature, rainfall and wind.
WEATHER
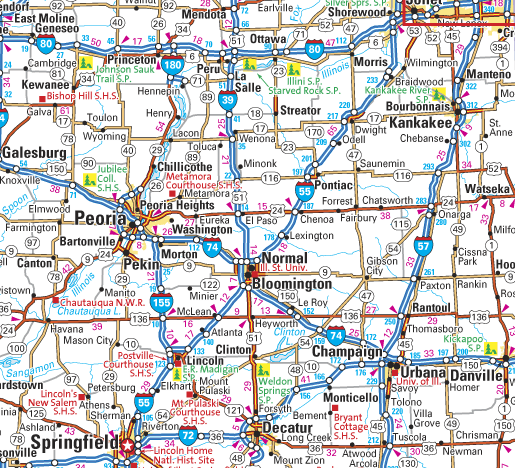
Shows a detailed depiction of roads in a given area. (ex. neighborhood streets, highways, interstates, toll roads)
ROAD MAP
Defined as the height above the ground or other surface, or a place or position of height. An example of ________ is a plane flying at 36,000 feet above the ground.
ELEVATION
Shows features of an area such as elevation, or height above sea level, mountains, rivers, lakes, etc.
PHYSICAL MAP

CLIMATE MAP
The weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period.
CLIMATE
The most important city or town of a country or region, usually its seat of government and administrative center.
CAPITAL
These things found on Earth's surface are formed by nature; Example: Trees, mountains, oceans, rivers, lakes, height above sea level, elevation, etc.
PHYSICAL FEATURES
POLITICAL MAP

NATURAL RESOURCE MAP
Any form of moisture which falls to the earth. This includes rain, snow, hail and sleet.
PRECIPITATION
POLITICAL MAP
The number of people in a geographic area. It can also be used for subgroups of people or animals.
POPULATION
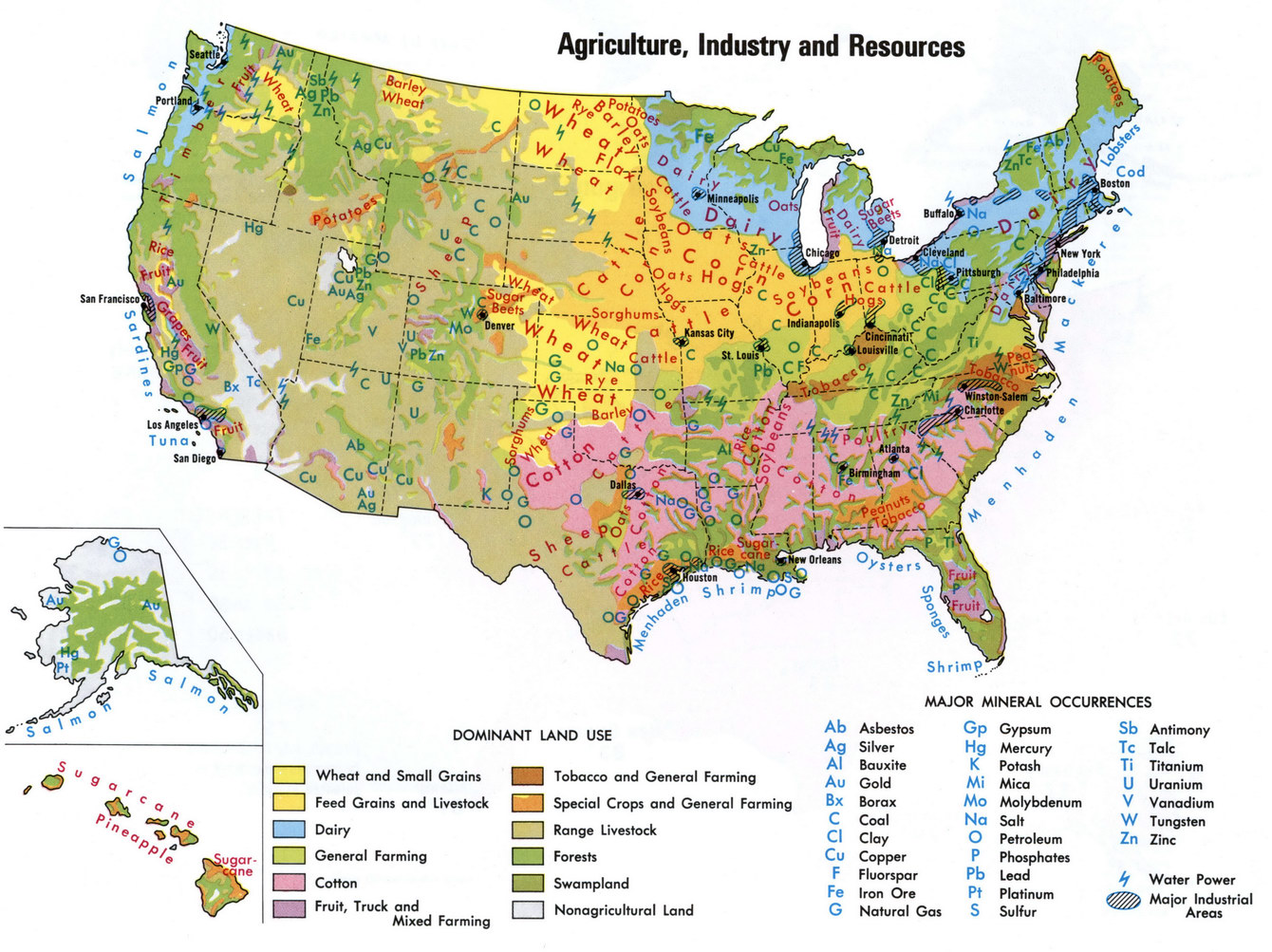
Shows the distribution of resources such as crops, minerals, animals, or plants.
NATURAL RESOURCE MAP
POPULATION DENSITY MAP
The degree of hotness or coldness of the atmosphere on some chosen scale. It is commonly measured in Celsius or Fahrenheit
TEMPERATURE

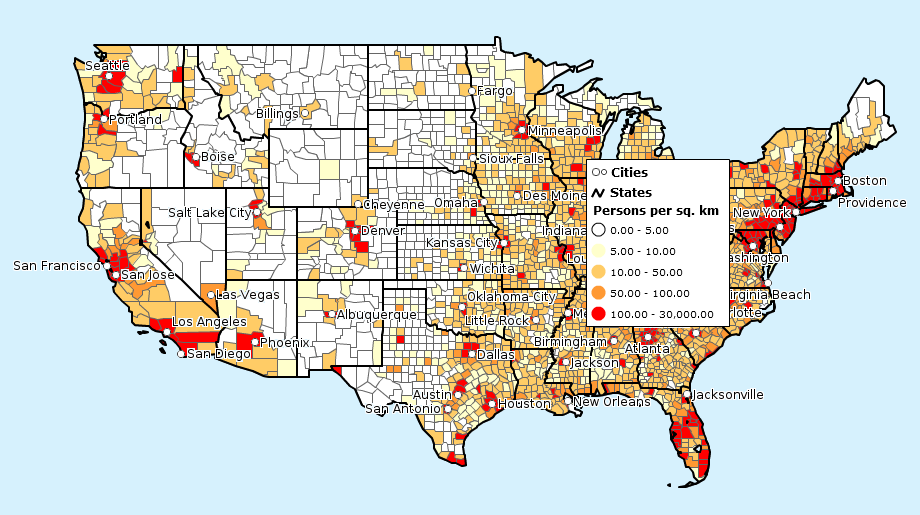
POPULATION DENSITY
A line that marks the limits of an area; a dividing line.
BOUNDARY
Shows how many people live per unit of land (ex. per square mile) in a given area.
POPULATION DENSITY MAP

PHYSICAL MAP
The amount of water vapor in the air. If there is a lot of water vapor in the air, the ______ will be high. The higher the______, the wetter it feels outside.
HUMIDITY
NAUTRAL RESOURCE MAP
Refers to the way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area. The concept of _______ can be applied to nearly everything on Earth, from animal and plant species, to disease infections, weather patterns, and man-made structures.
DISTRIBUTION