Part of the brain responsible for procedural memory
Cerebellum
(Hippocampus is involved in all other memory)
Provide an example of telegraphic speech.
"Cat sleep" "Want bottle"
Two words that are not a formal sentence but express a full thought.
It is fair to believe that Erikson would say developing a sense of trust in the "trust vs. mistrust" stage of infancy would be important to developing secure attachment as described by what psychologist?
Mary Ainsworth - Attachment Styles
6 basic emotions
Happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, disgust, fear
What are the Big Five personality traits?
OCEAN or CANOE
Openness
Conscientiousness
Extraversion
Agreeableness
Neuroticism
Describe the difference between algorithms and heuristics with regards to thinking and problem solving.
For double points - include an example of each.
Algorithms are step by step problem solving methods that consider every possibility and select the correct/best one. Time consuming but accurate.
Heuristics is a rule of thumb approach where we select the most readily available solution. Fast but possibly inaccurate.
What are the three types of intelligence articulated by Sternberg's Triarchic Theory of Intelligence?
Analytic, Practical, and Creative
Elementary school aged kids are in what psychosocial stage according to Erik Erikson? And what does it mean?
Industry vs. Inferiority ; Emphasis on comparing oneself to your peers.
Functions of the lateral and ventromedial hypothalamus
Lateral hypothalamus - hunger on switch
Ventromedial hypothalamus - hunger off switch "full"
Higher stress and therefore greater risk of health problems is more associated with which "Type" of personality?
Type A
Provide an example of Proactive Interference ; Provide an example of Retroactive Interference.
Examples will vary. Proactive interference is when old information interrupts the retrieval of new information. Retroactive interferences is when new information interrupts the retrieval of old information.
What are Gardner's 8 types of intelligence in his theory of multiple intelligences?
1) Linguistic
2) Logical-mathematical
3) Naturalist
4) Spatial
5) Bodily Kinesthetic
6) Intrapersonal
7) Interpersonal
8) Musical
Indicate which of the following stages of morality Lawrence Kohlberg would pair with each scenario.
1) Becoming a doctor because you want to save lives.
2) Becoming a doctor because you want to make $$
3) Becoming a doctor because it will make your family proud.
4) Becoming a doctor because the healthcare system needs more qualified, caring physicians.
1) Post-conventional
2) Pre-conventional
3) Conventional
4) Post-conventional
You are walking in the woods, explain something that could happen through the lens of:
James-Lange
Cannon-Bard
S/S Two Factor Theory
James Lange: Physiological arousal happens after a stimulus and causes emotion
Cannon-Bard: Physiological arousal and emotion happen at the same time after a stimulus
SS Two Factor: Physiological arousal occurs after a stimulus, our mind labels or appraises the situation which causes the emotion
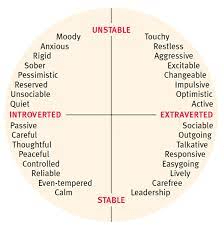
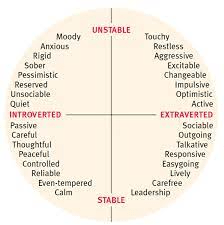 What are some descriptors Hans and Sybil Eysenck would use to describe someone who scored high on neuroticism and low on extraversion?
What are some descriptors Hans and Sybil Eysenck would use to describe someone who scored high on neuroticism and low on extraversion?
Provide 4 examples of elaborative rehearsal. Be sure one of them includes semantic encoding.
Examples will vary but all should highlight effortful processing of information and at least one should discuss the emphasis on meaning in what we learn.
Describe the theories on language development from Chomsky and Whorf respectively.
Whorf - linguistic determinism - how we speak influences how we think
Identify the stage of cognitive development for each of the following phenomenon.
1) Egocentrism
2) Logical thinking
3) Morality
4) Abstract thought
5) Stranger anxiety
6) Object permanence
7) Understanding conservation
8) Pretend play
1) Pre-operational
2) Concrete operational
3) Formal operational
4) Formal operational
5) Sensorimotor
6) Sensorimotor
7) Concrete operational
8) Pre-operational
Provide an example of a multiple approach avoidance motivational situation.
A situation that includes multiple positive and negative possibilities on either side.
Provide an example of someone going through General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) in response to stress.
Examples will vary but need to include 1) Alarm 2) Resistance 3) Exhaustion
A) What are schemas?
B) At what stage of Piaget's Cognitive Development do schemas begin to develop?
C) Provide examples of accommodation and assimilation.
D) Provide a schema topic and prototype example.
A) Schemas are our mental representations we use for organizing concepts.
B) Pre-operational
C) Accommodation is adjusting a schema to incorporate new information. Assimilation is new information fitting within existing schemas (even if incorrect)
D) Fruits - Apple
With a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 20, 68% of respondents will fall between what range of scores?
80 and 120
Match up age ranges from birth to 18 with each stage of Piaget, Kohlberg, and Erikson.
Infancy 0-18months: Sensorimotor, Pre-conventional, Trust vs. Mistrust
Toddler 18months-2: Pre-operational, Pre-conventional, Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Pre-school 3-5: Pre-operational, Conventional and Pre-conventional, Initiative vs. Guilt
School Aged 5-11/12: Concrete operational (around 7), Conventional and Pre-conventional, Industry vs. Inferiority
Adolescence 13-18: Formal operational, Post-conventional, Conventional, Pre-conventional, and Identity vs. Role Confusion
What might Maslow's hierarchy of needs look like for an AP Psychology scholar?
Psychological?
Safety and Security?
Belongingness?
Esteem?
Self actualization?
Self transcendence?
Imagine one is in the young adulthood stage of Intimacy vs. Isolation - provide examples of the following defense mechanisms that could apply in that stage of psychosocial development.
1) Denial
2) Projection
3) Displacement
4) Sublimation
5) Reactive Formation
Examples will vary but should focus on interactions with friends, family, and/or romantic partners.