What some signs and symptoms of preeclampsia?
Hypertension (≥140/90), proteinuria, headache, visual disturbances, edema (especially facial/hand), hyperreflexia, RUQ/epigastric pain
List three common discomforts during pregnancy and appropriate nursing interventions
Back pain → proper posture, support belt.
Nausea/vomiting → small frequent meals, avoid triggers.
Heartburn → sit upright after meals, avoid spicy/fatty foods
What are the four stages of labor?
Stage 1: Dilation of cervix
Stage 2: Pushing/Delivery of baby
Stage 3: Delivery of placenta
Stage 4: Postpartum recovery
What is the difference between true and false labor contractions?
True labor: Regular contractions, stronger/closer, cause cervical dilation/effacement, not relieved by rest.
False labor: Irregular, mild, no cervical change, relieved by rest/hydration.
What are the components of the APGAR score, and when is it assessed?
Appearance (color), Pulse, Grimace (reflex), Activity (muscle tone), Respirations.
Done at 1 minute and 5 minutes after delivery.
What does GTPAL stand for in obstetric history?
GTPAL = Gravida, Term births, Preterm births, Abortions/miscarriages, Living children.
A pregnant patient asks why her ankles swell in the evening. What is the best explanation?
This is normal and is caused by increased pressure from the uterus and fluid retention; advise rest with legs elevated.
Define the term “effacement.”
Thinning/shortening of the cervix (measured in %).
A laboring patient has late decelerations on the fetal monitor. What should the nurse do first?
Turn mother to left side.
Give oxygen.
Stop oxytocin.
Notify provider.
Which vitamin is routinely given to newborns, and why?
Vitamin K (to prevent hemorrhagic disease of newborn) because newborns lack clotting factors in their blood.
Which hormone is detected in a pregnancy test?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
How do you calculate a pregnant woman’s Estimated Date of Delivery (EDD) using Naegele’s rule?
First day of last menstrual period + 7 days – 3 months + 1 year
What does the term "station" mean in relation to fetal descent?
Relationship of fetal presenting part to maternal ischial spines.
0 = at spines; negative = above spines; positive = below spines (closer to delivery).
What is the purpose of Leopold’s maneuver?
Assess fetal position, lie, and presentation through palpation of maternal abdomen.
What immediate nursing interventions are necessary after a newborn is delivered?
Keep neonate dry and warm.
Clear airway if needed.
Stimulate breathing.
Apply identification bands.
Vitamin K, eye prophylaxis.
List 2 teaching points about fetal kick counts.
Count movements daily, usually after meals.
Expect ~10 movements in 2 hours. Report decreased or absent movements.
A patient at 34 weeks gestation reports sudden gush of fluid. What should the nurse’s priority action be?
Suspect rupture of membranes.
Priority: Assess fetal heart rate for distress
The fetal heart monitor shows variable decelerations. What is the likely cause?
Umbilical cord prolapse (risk of hypoxia).
What is happening in this picture? (What are those straps?)
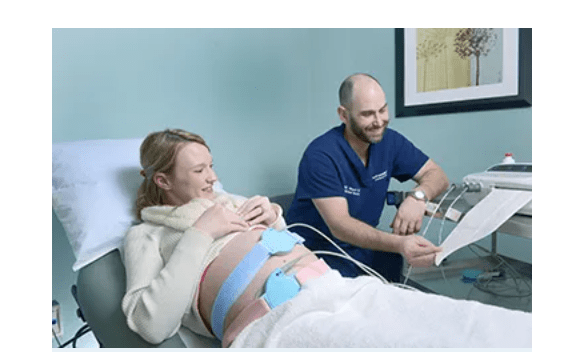
Fetal heart rate monitoring and contraction monitoring.
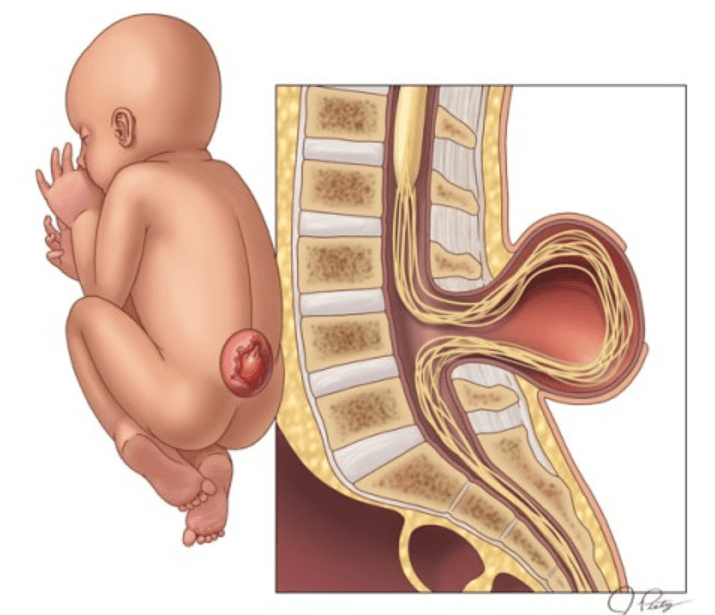
What is this condition called?
Spina bifida (meningocele, myelomeningocele)
Why is magnesium sulfate given to some pregnant patients, and what should the nurse monitor?
Purpose: Prevent seizures in preeclampsia/eclampsia.
Monitor: Reflexes, respiratory rate (>12/min), urine output (>30 mL/hr), magnesium levels (therapeutic 4–7 mEq/L).
A pregnant patient has painless vaginal bleeding at 32 weeks. What condition do you suspect?
Placenta previa
A laboring patient is given oxytocin (Pitocin). What must the nurse closely monitor?
Monitor uterine contractions (avoid hyperstimulation).
Monitor fetal heart rate.
Watch for water intoxication (rare).
What is the normal range for postpartum maternal blood loss in vaginal and C-section deliveries?
<500 mL for vaginal delivery; C-section <1000 mL.
What is this common occurrence with newborns called?
