What are the coordinates for the origin?
(0, 0)
In an integral pair, which axis coordinate comes first?
The x coordinate
(x coordinate, y-coordinate)
This term explains that the transformation does not change the size or shape of the original shape (pre-image).
Congruent
Describe the translation.
(x - 6, y + 6)
Describe the Reflection
Reflection over the y-axis.
What direction is this?
![]()
Counter-Clockwise
What is the relationship bewtween line segments AB and CD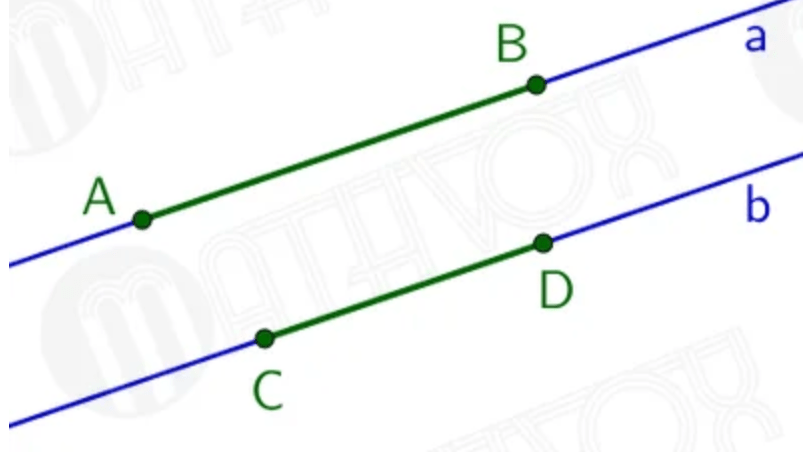
They are Parallel
What is the name for the horizontal axis?
x-axis
Find the Coordinate for A.
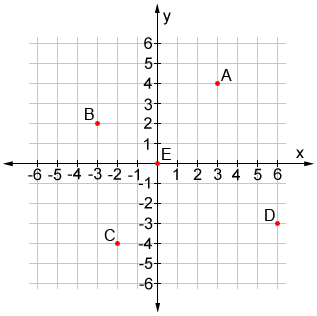
(3, 4)
This transformation is a slide of the pre-image.
Translation
Describe the Translation.
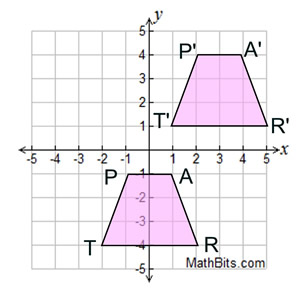
(x + 3, y + 5)
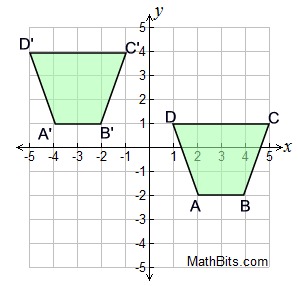
Trapezoid ABCD has coordinates:
A(-4,5), B(-2,4), C(-2,2) and D(-4,1).
After a reflection over the x-axis, what are the coordinates of the image of point B'?
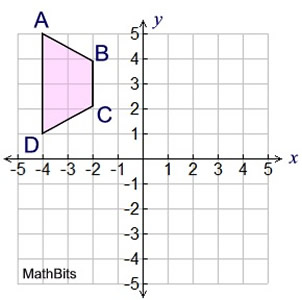
(-2, -4)
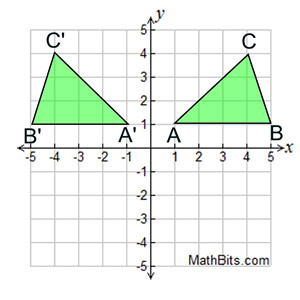
Which of the triangles shown is not a rotation of triangle A about the origin?
What type of transformation occurred to make that image?
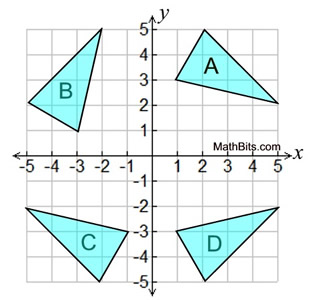
Triangle D
It is a reflection over the x-axis.
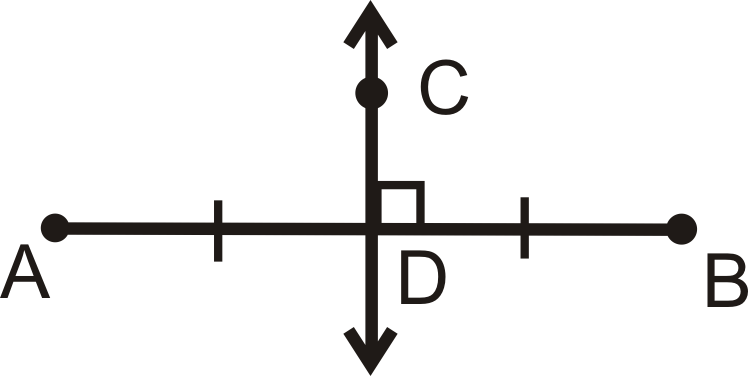
This shows what type of construction?
A perpendicular Bisector
What is the name for the vertical axis?
y-axis
Find the Coordinate for B.

(-3, +2)
This transformation is a flip over a mirror line
Reflection
Point Q is (+4, +7)
Point Q' is (-3, +9)
Describe the translation
(x - 7, y + 2)
7 units left, 2 units up
Describe the Reflection
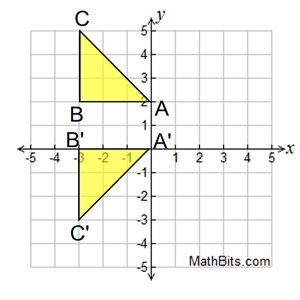
A reflection over the line y= +1
Find the image of the point (-3,3) after a rotation of 90º counterclockwise about the origin.
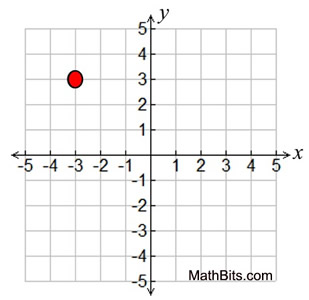
(-3, -3)
How do we describe line AD on angle BAC
Angle Bisector
What are the signs (+ or -) for a coordinate in Quadrant II?
(-, +)
Find the Coordinate for C.

(-2, -4)
This transformation is a turn about/around a single point.
Rotation
A translation is defined by the rule
(x, y) → (x + 2, y - 5) or "right 2, down 5"
If point P is (3, 6), what are the coordinates of P'?
(+5, +1)
Describe the reflection ABC --> A'B'C'
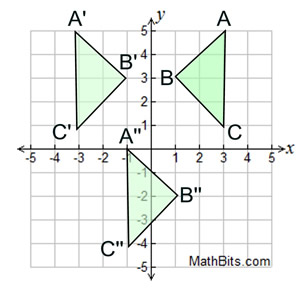
Reflection over the y-axis.
ΔFUN is shown below. Find the coordinates of vertex U' after a clockwise rotation of 90º about the origin.
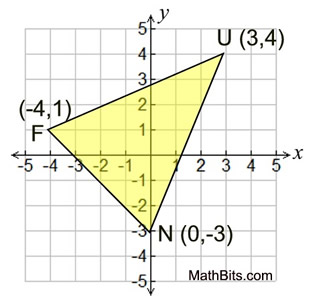
(4,-3)
perpedicular bisectors of the sides of a rectangle will always intersect at the ____________.
At the center.
What are the signs (+ or -) for a coordinate in Quadrant IV?
(+, -)
Find the Coordinate for D.

(+6, -3)
This is how we distinguish between the original and image vertices.
A triangle PQR has a point P (+3, +2) translated to P' (-5, +4).
What are the coordinates for Q if Q' is (-5, -1)?
(+3, -3)
ΔFUN is shown below. Find the coordinates of its image ΔF'U'N' after a reflection over the x-axis.

F'(-4,-1),
U'(3,-4),
N'(0,3)
ΔABC with A(1,1), B(7,-2) and C(1,-2) is rotated 90º counterclockwise about point R (-2,-4).
What are the coordinates of the image of point B'?
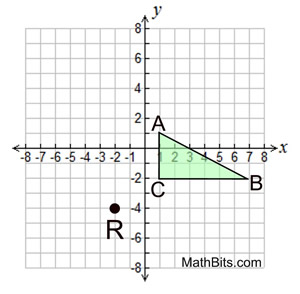
B' (-4,5)
What is the relationship between angle BAD and DAC?
They are the same.
A BISECTOR splits angle BAC exactly in half.