Binary number of 100 is equal to what in decimal?
4
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 5; // for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { System.out.println("Java is fun"); }
} }
What is the output?
Java is fun
Java is fun
Java is fun
Java is fun
Java is fun
a person who developed a hypothetical machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape
Turing
Additive identity is a number when added to any number, gives the sum as the number itself.
Additive identity is ....
0
this theorem states that four colors suffice to color any map such as two adjacent regions will not share the same color
four color theorem
Base of 16 is called the....
Hexadecimal
Computer science algorithm to solve a problem by solving a smaller instance of the same problem
Recursion
inventor of bitcoin
Satoshi Nakamoto
Multiplicative identity property says that whenever a number is multiplied by a number it will give that number as a product.
This number is...
1
an+bn=cn has no solution for any integer n greater than 2
Fermat's last Theorem
In computer science, decimal numbers less than 32 bit in size are typically stored as...
float
a number whose square is equal to -1
i
His little theorem states that if p is a prime number then for any integer a, ap - a is a multiple of p...
Fermat
a+(b+c) = (a+b) + c
or
a x (b x c) = (a x b) x c
associative property
This process will eventually reach the number 1, regardless of which positive integer is chosen initially
Collatz conjecture
fruits = ["Strawberry", "Apple", "Banana"]
What kind of variable is "fruits?
array
OR
List
a variety of this include bubble, heap, quick, and insertion
sort
Who said "Cogito, ergo sum"
Also known as Father of Modern Philosophy
Descartes
a+b = b+a
or
axb = bxa
commutative property
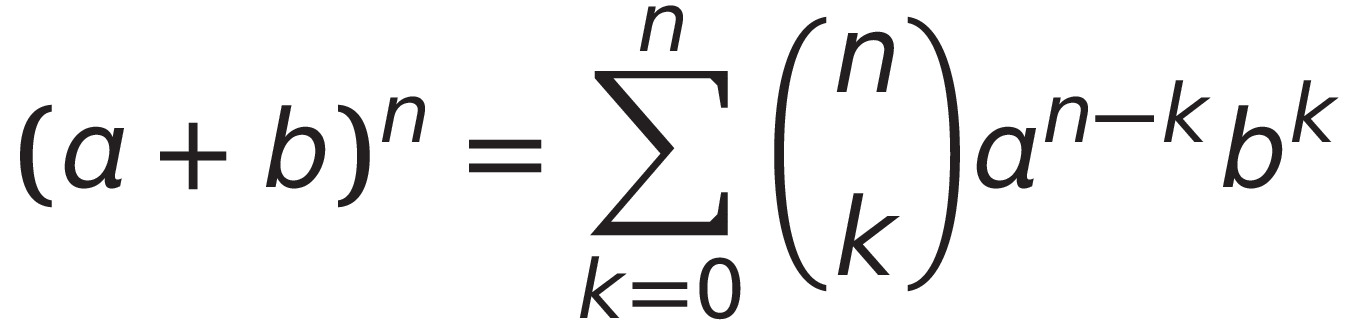
binomial theorem
A chunk of a computer code that takes some input and uses those inputs to do a task
Function
method
field of computer science where public key and private keys are used to provide security of data
cryptography
Whose identity?
Euler's
Are divisions commutative? Yes or no
No
a path where it covers all of the vertices in the graph exactly once
Hamiltonian path

