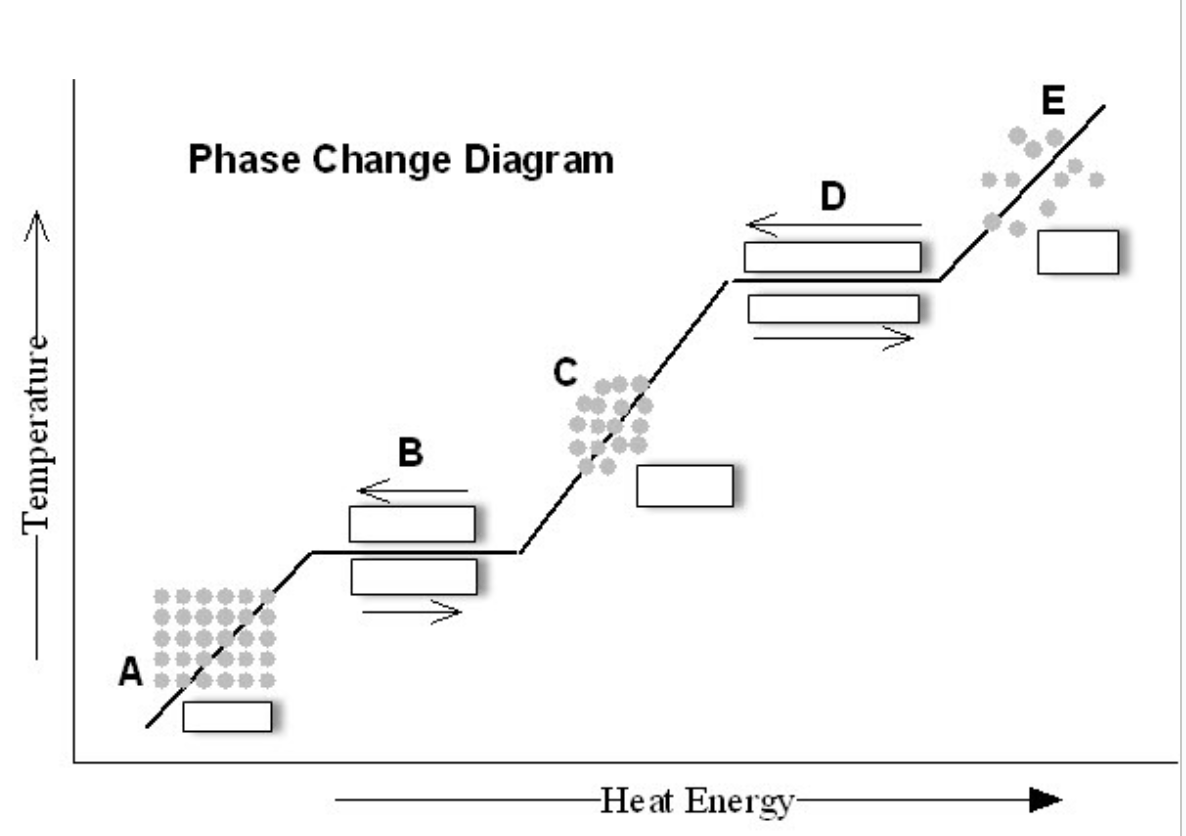
Is the phase change diagram representing heat be added or released?
Added
If the q in the equation q = mCΔT is positive for the SYSTEM, is the reaction Endothermic or Exothermic?
Endothermic
In the equation q = mcΔT, label what each variable represents.
q = heat/energy
m = mass
c= specific heat
ΔT = change in temperature
The specific heat capacities for the following objects are listed below. Put them in order of which one would heat up the fastest to the slowest.
Steel = 0.45 J/g°C
Aluminum = 0.910 J/g°C
Copper = 0.390 J/g°C
Copper, Steel, then Aluminum
The point at which all three states of matter exist at the same time in equilibrium.
Triple Point
Label parts B and D. Give me your answer as if your heating it up FIRST then as you are cooling it down. So, B heat up answer, then D heat up answer, then B cool down answer, and finally D cool answer. 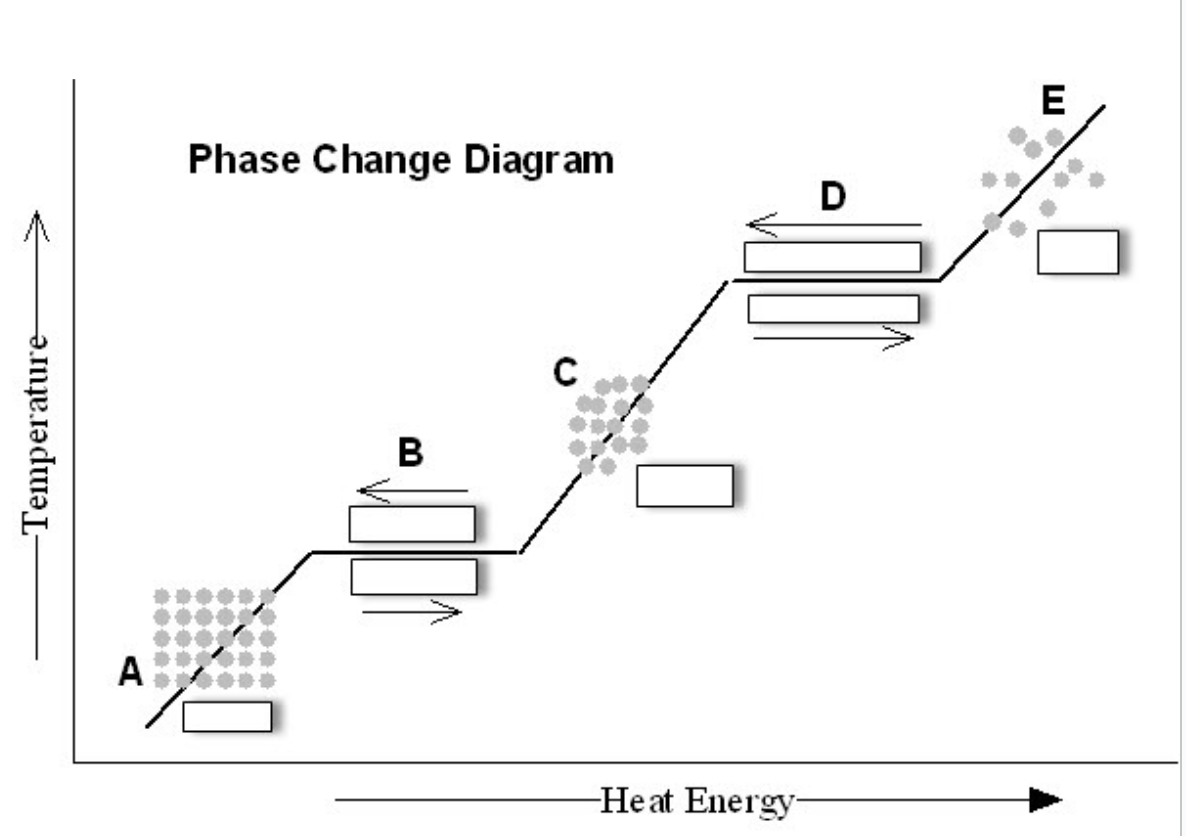
B heat up is melting
D heat up is boiling/evaporating
B cool down answer is freezing
D cool down answer is condensing
Which graph is (left or right) is endothermic and which graph (left or right) is exothermic?
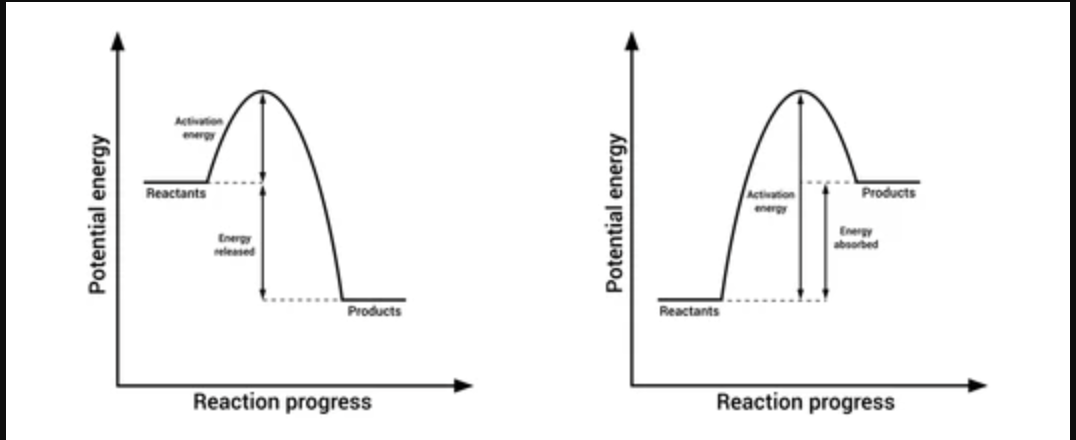
Left is exothermic
Right is endothermic
Define specific heat.
The amount of energy needed to raise a 1g substance's temperature by 1°C.
This object measures to amount of heat that is either released or absorbed in a reaction.
Calorimeter
The point at which you can no longer distinguish between a liquid and a gas.
Critical Point
How long did it take for the substance to condense? How long to freeze?
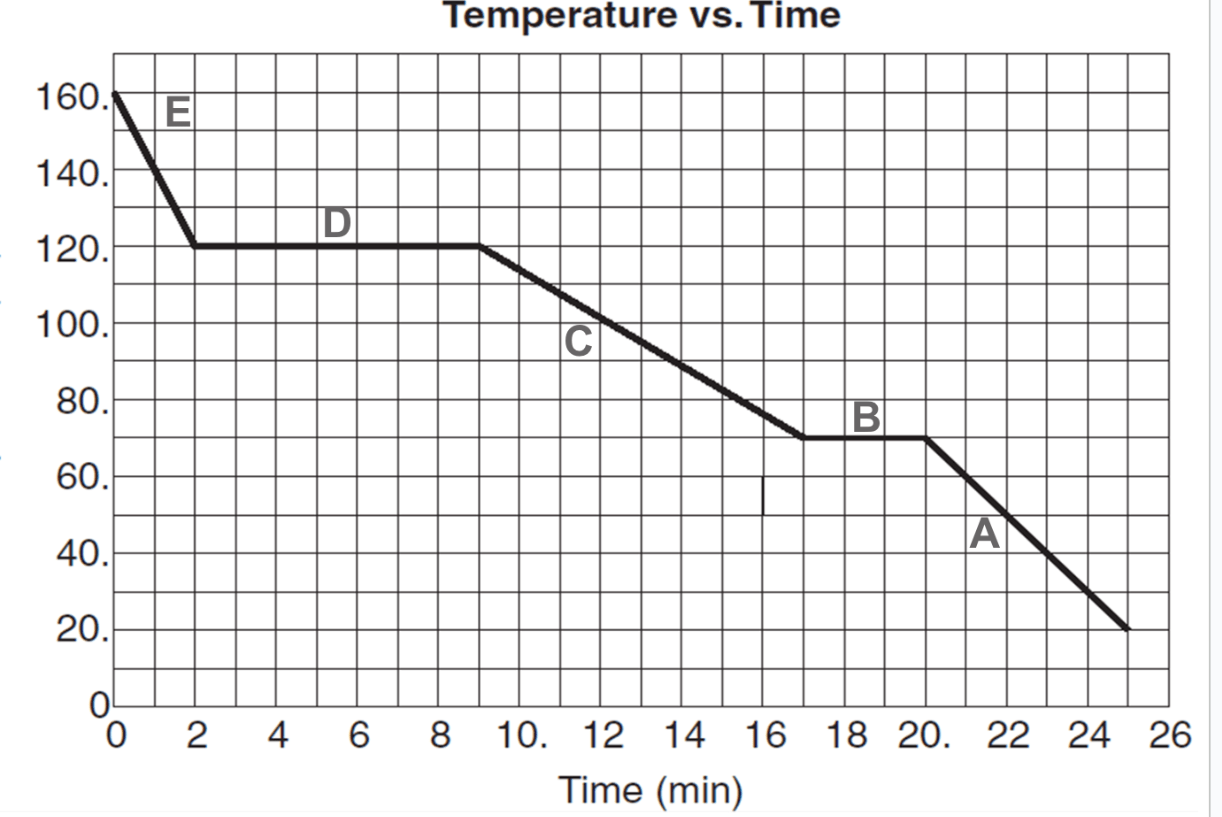
Condense: 7 minutes
Freeze: 3 minutes
If you place water in the freezer to turn it into ice, is this process endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic because heat is being released from the water to the freezer to make ice.
When boiling water in a metal pot, the metal pot gets hotter quicker than the water. That means the metal pot has a (lower or higher) specific heat than water.
Lower
The specific heat for water in both Joules and Calories.
cwater = 4.18 J/g°C
cwater = 1.00 Cal/g°C
What is the name for the substance that exists past the critical point?
Supercritical Fluid
Label all parts of this diagram. Word bank below:
Solid, Liquid, Gas, Evaporation/Boiling, Melting, Freezing, Condensation, Sublimation, Deposition, Triple Point, & Critical Point. 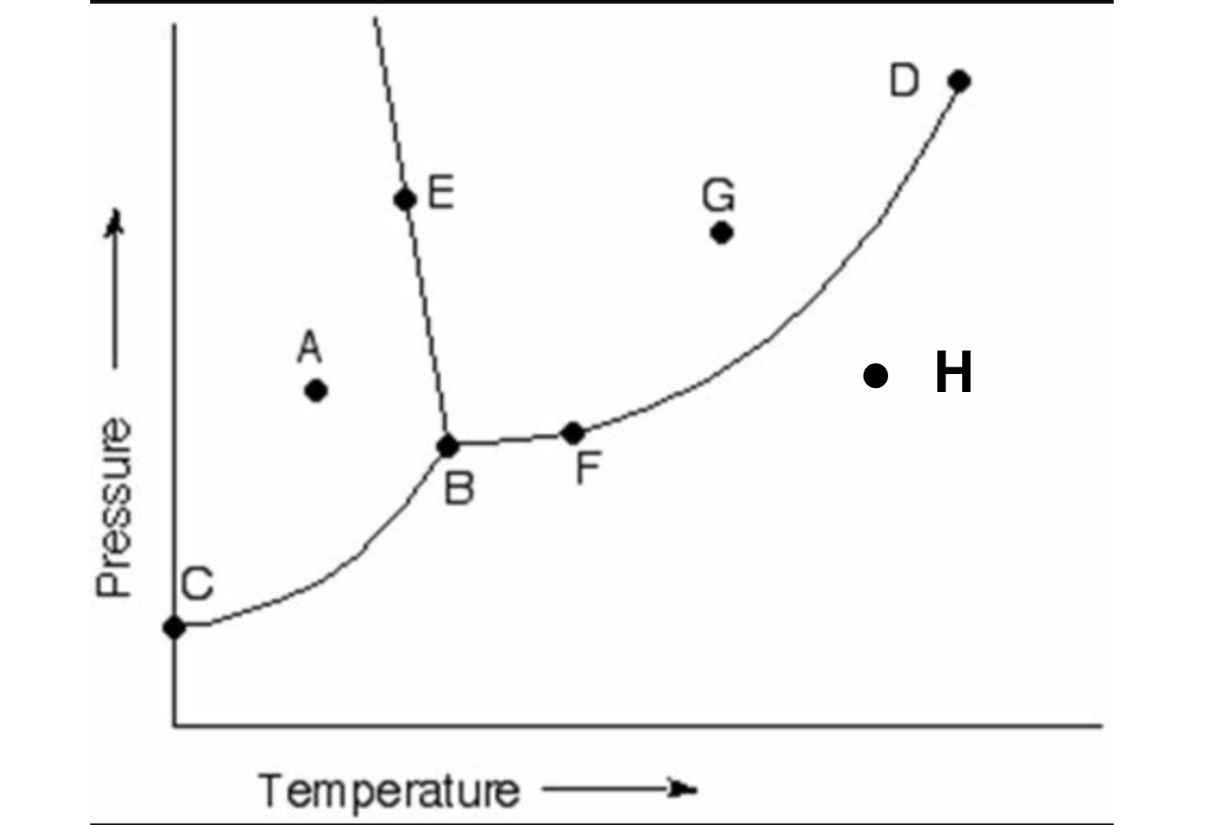
A = Solid
B = Triple Point
C= Sublimation/Deposition
D = Critical Point
E = Melting/Freezing
F = Evaporation/Condensation
G = Liquid
H = Gas
Qsystem = -Qsurroundings
1. If Qsystem is (+) and Qsurroundings is (-), that means the system is (endothermic or exothermic). Explain.
2. If Qsystem is (-) and Qsurroundings is (+), that means the system is (endothermic or exothermic). Explain.
1. Endothermic because if the system is positive it is gaining heat.
2. Exothermic because if the system is negative it is losing heat.
How much energy (heat) is needed for a 50g substance with a specific heat of 4.2 J/g°C to raise its temperature from 5°C to 25°C?
q = 4200 J
In calorimetry, what is assumed to be conserved?
Energy
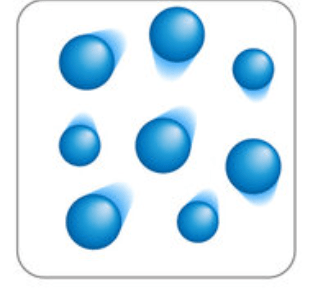
Draw a particle diagram that represents a solid turning into a gas via sublimation.
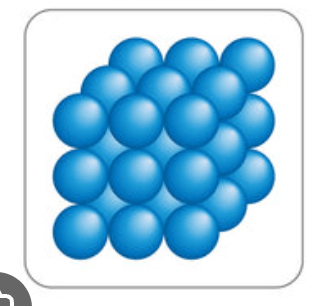
to
Draw the particle diagram for the state of matter represented by the blue region.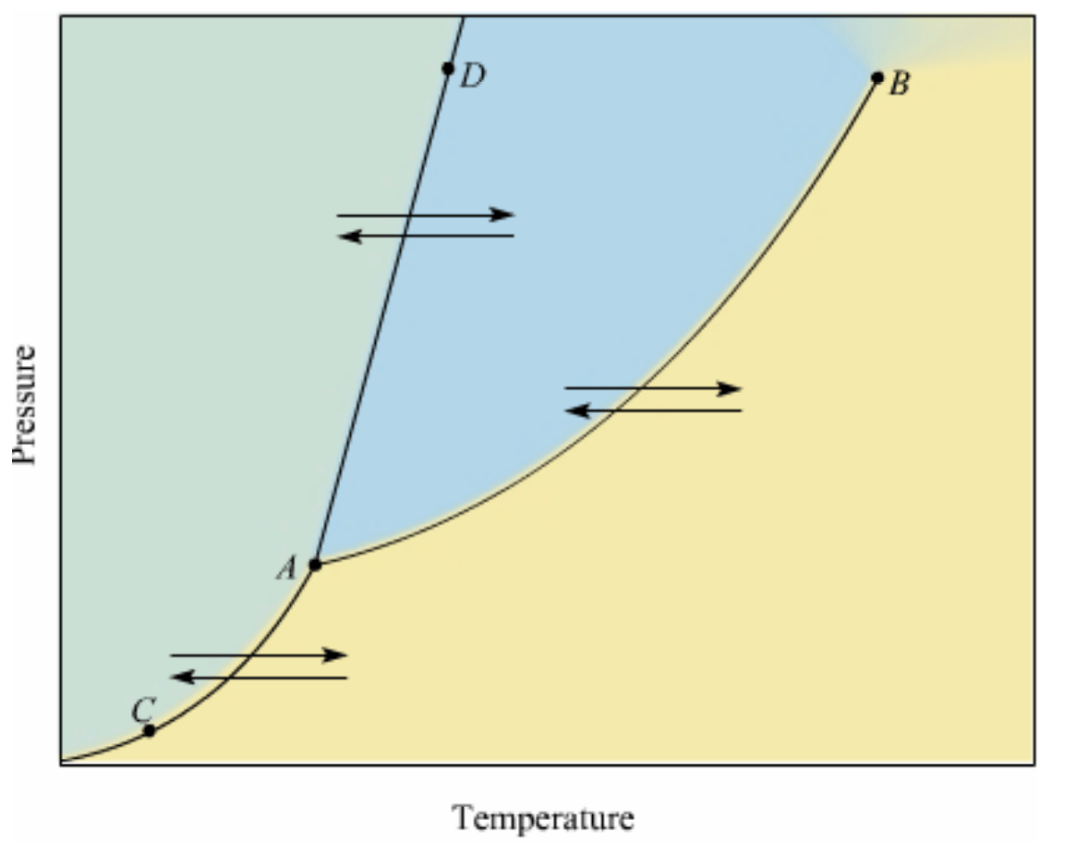
Liquid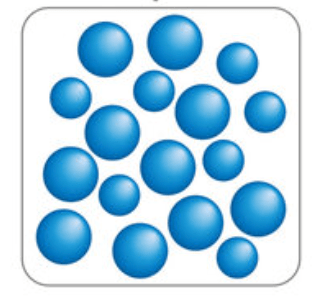
1. On an endo/exo graph, when the potential energy of the reactants is HIGHER than the potential energy of the products, the reaction is (endothermic or exothermic).
2. On an endo/exo graph, when the potential energy of the reactants is LOWER than the potential energy of the products, the reaction is (endothermic or exothermic).
1. Exothermic
2. Endothermic
In the chemical equation below, calculate the net bond enthalpy. Be sure to include the total bond energy on both sides along with your final answer. Also state if the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
H2 + Cl2 --> 2 HCl
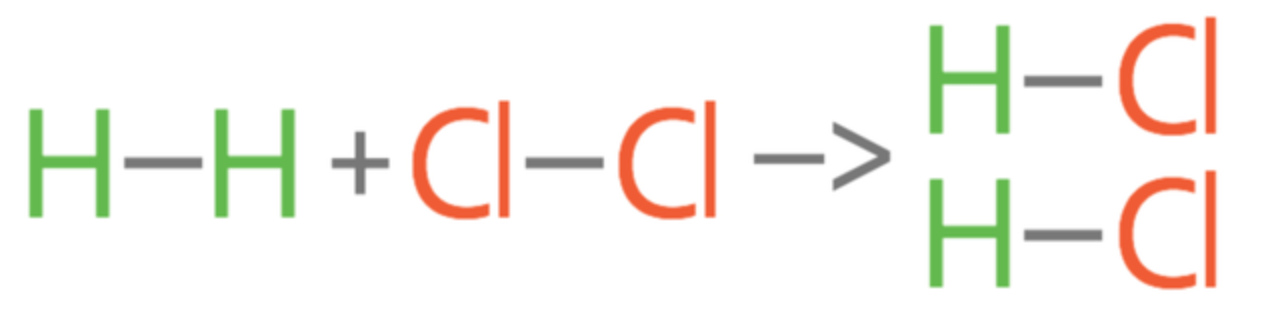
Bond Energies are:
H-H = 432 kJ/mol
Cl-Cl = 239 kJ/mol
H-Cl = 432 kJ/mol
(432 + 239) - 2(432)
671 - 864
= - 193 kJ/mol
Exothermic
If you have food that has just been heated, and you put that into the fridge, which is the system, and which is the surroundings.
What type of reaction is this?
Explain your answer.
Food is the system, and the surrounding is the fridge.
Exothermic
Because the food is releasing heat to the fridge.
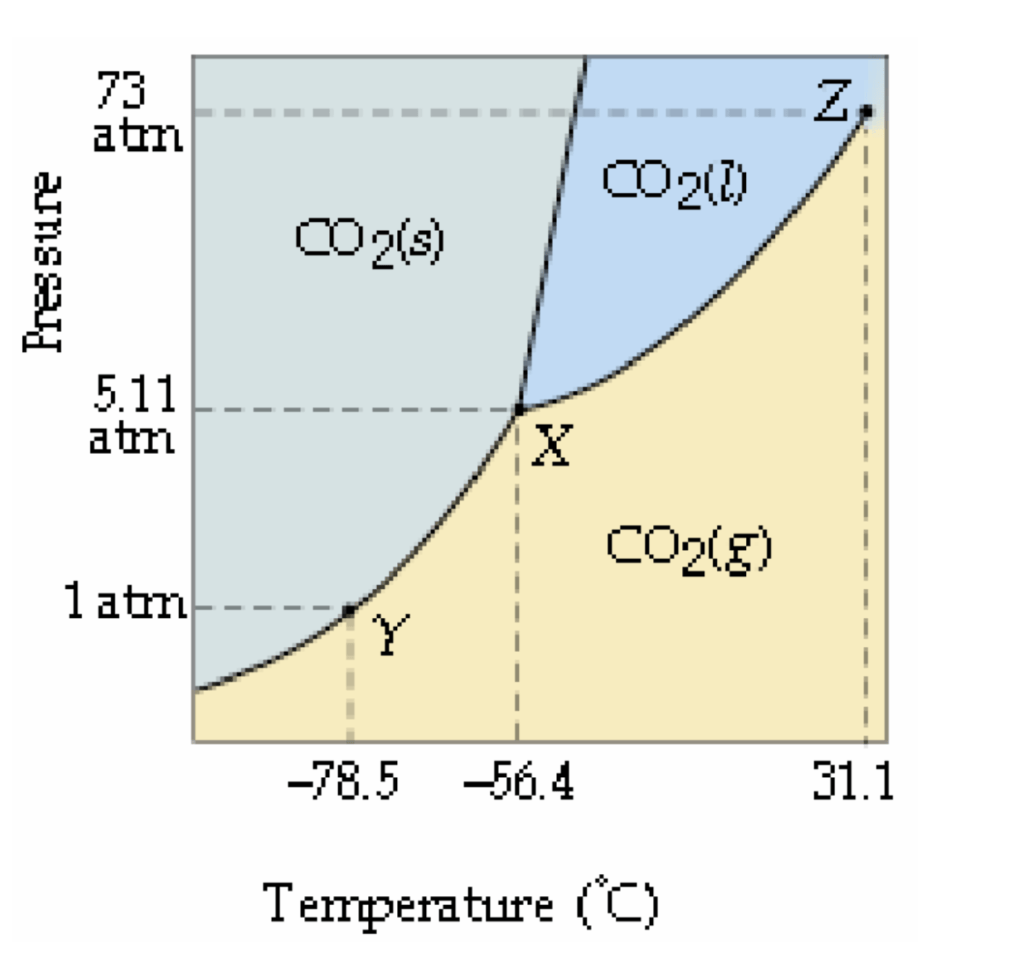 When CO2 is heated from -80°C to -20°C at a constant pressure of 3 atm:
When CO2 is heated from -80°C to -20°C at a constant pressure of 3 atm:
A. What phase change occurs?
B. At what temperature does the phase change occur?
A. Solid to Gas, Sublimation
B. Around -60°C