Most common/#1 risk factor for Aortic Dissection.
Risk factors associated with AD include:
Hypertension (76%)
Atherosclerosis (27%)
Aortic aneurysm (16%)
Previous cardiac surgery (16%)
Marfan syndrome (5%)
Iatrogenic injury (4%)
Cocaine use (1.8%)
Most is the most common physical exam finding associated with this diagnosis/chest x-ray?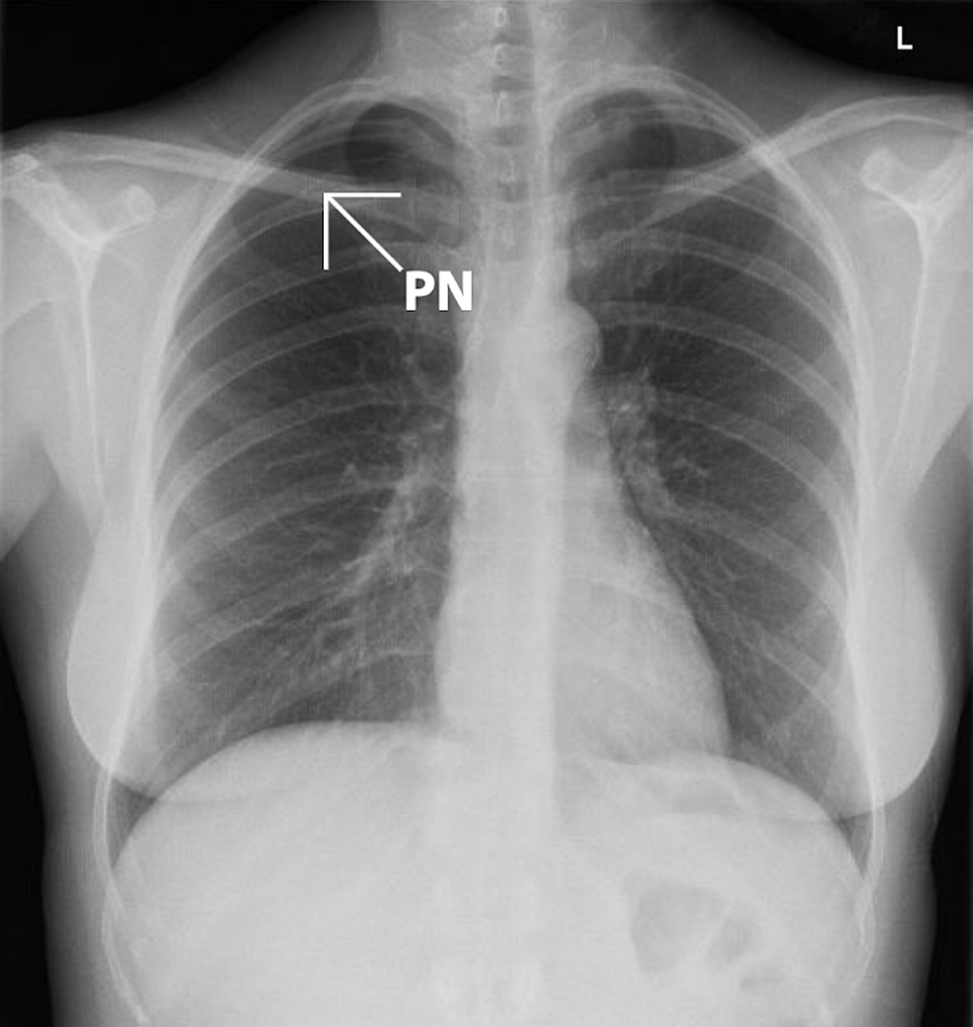
What is Tachycardia. (sinus tachycardia >120 bpm is the most common physical finding)
Most common cause of esophageal perforation
The most common etiology of an esophageal perforation is iatrogenic as a result of endoscopic interventions
D dimer cutoff for a pregnant patient with signs of dvt?
What is 500.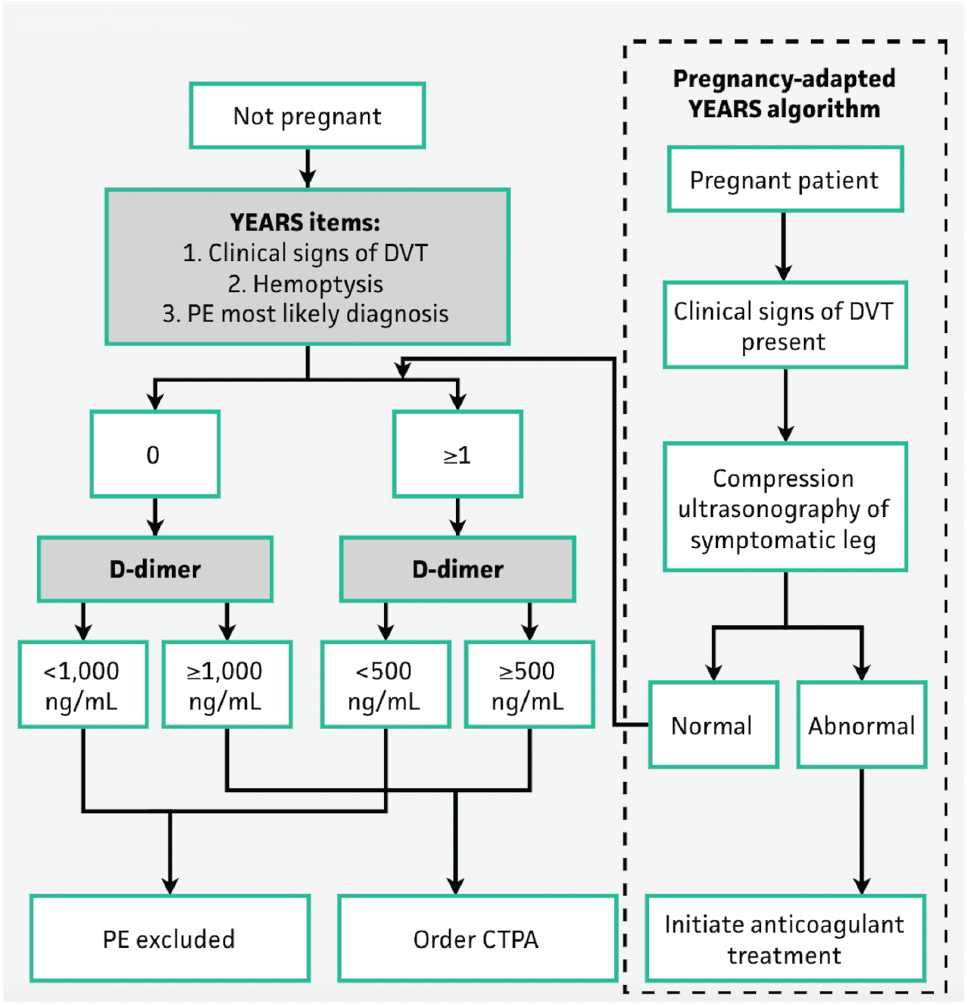
If you suspect endocarditis, how many blood cultures should you obtain/order?
3. Standard diagnostic criteria include 3 separate sets of positive blood cultures (20 mL each) and positive cardiac echocardiography findings
35 y/o male presents for evaluation of hemoptysis. What is the most common cause of hemoptysis?
Answer: Bronchitis
Name the type of dissection and usual definitive management?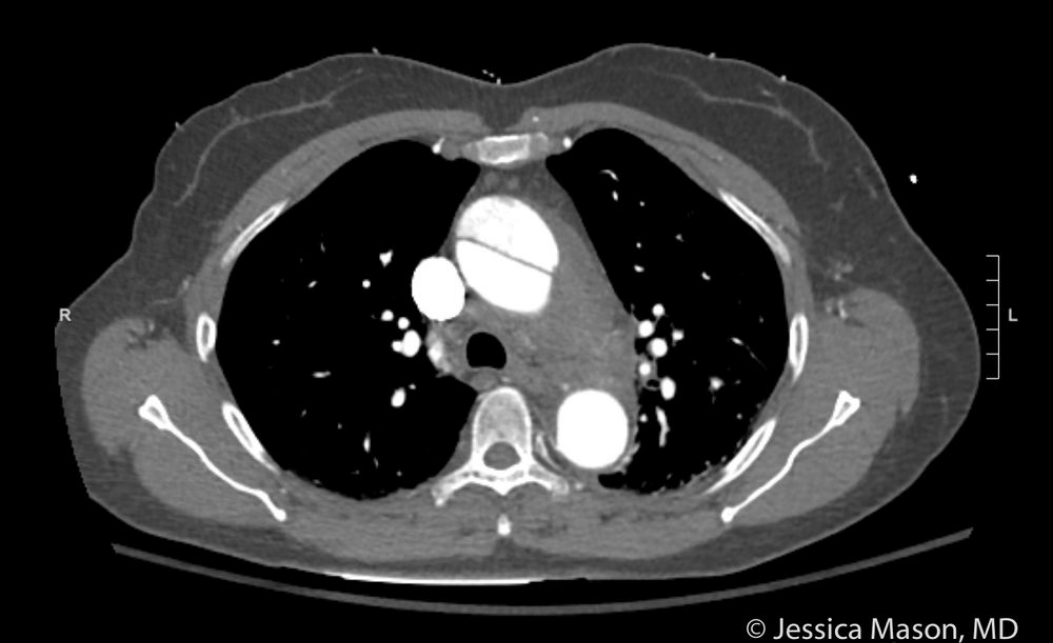
What is Stanford A/Debakey 2. Surgical 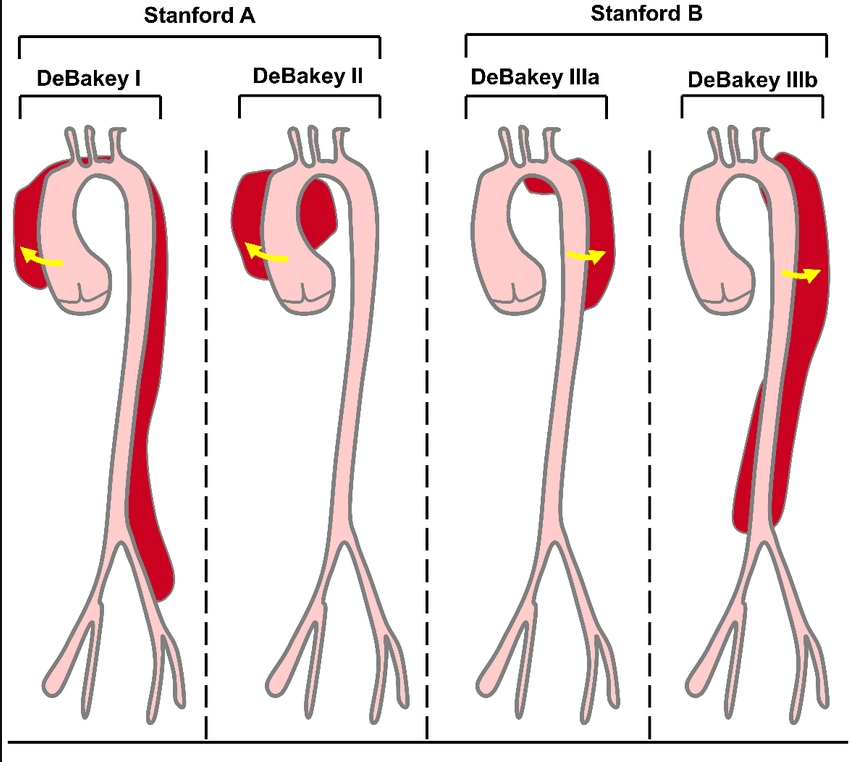 STANDFORD A/DEBAKEY 2. SURGERY
STANDFORD A/DEBAKEY 2. SURGERY
You suspect a tension pneumothorax on 25 y/o male that presents with chest pain after an altercation. How will you relieve the tension pneumothorax.
What is needle decompression with tube thoracostomy in 3rd/4th intercostal space midclavicular line or 4th/5th midaxillary line.
True or False: Antibiotics are recommended for esophageal perforation?
True. Empiric antimicrobial therapy is recommended
Broad-spectrum IV antibiotics.
- Option A: Piperacillin/tazobactam + vancomycin.
- Option B: Meropenem + vancomycin.
- Option C: Cefepime + Metronidazole + Vancomycin.
Dosage of heparin for pulmonary embolism
What is 80 units/kg intravenous bolus (maximum 10,000 units), followed by 18 units/kg/hour continuous intravenous infusion (maximum 2,000 units/hour).
Name the EKG finding and the cause.
What is Electrical alternans. Electrical alternans occurs when a large pericardial effusion is present and the heart swings back and forth, beat-to-beat, inside the distended, fluid-filled pericardial sac.
A 2-year-old girl is brought to the ED by her parents after a choking spell. She began coughing and spitting up suddenly after playing with some small toys. She initially had stridor at triage; however, during her evaluation, she becomes apneic and loses consciousness. What critical action indicated immediately?
Unresponsive children with a suspected airway foreign body should receive immediate chest compressions to help dislodge the object, even if a pulse is palpable.
Name one physical exam finding in a patient with aortic dissection?
Normal
Tachycardia
Rales
Absent/Diminished pulses
Neurological deficits
Muffled heart sounds
Most common cause of this chest x-ray?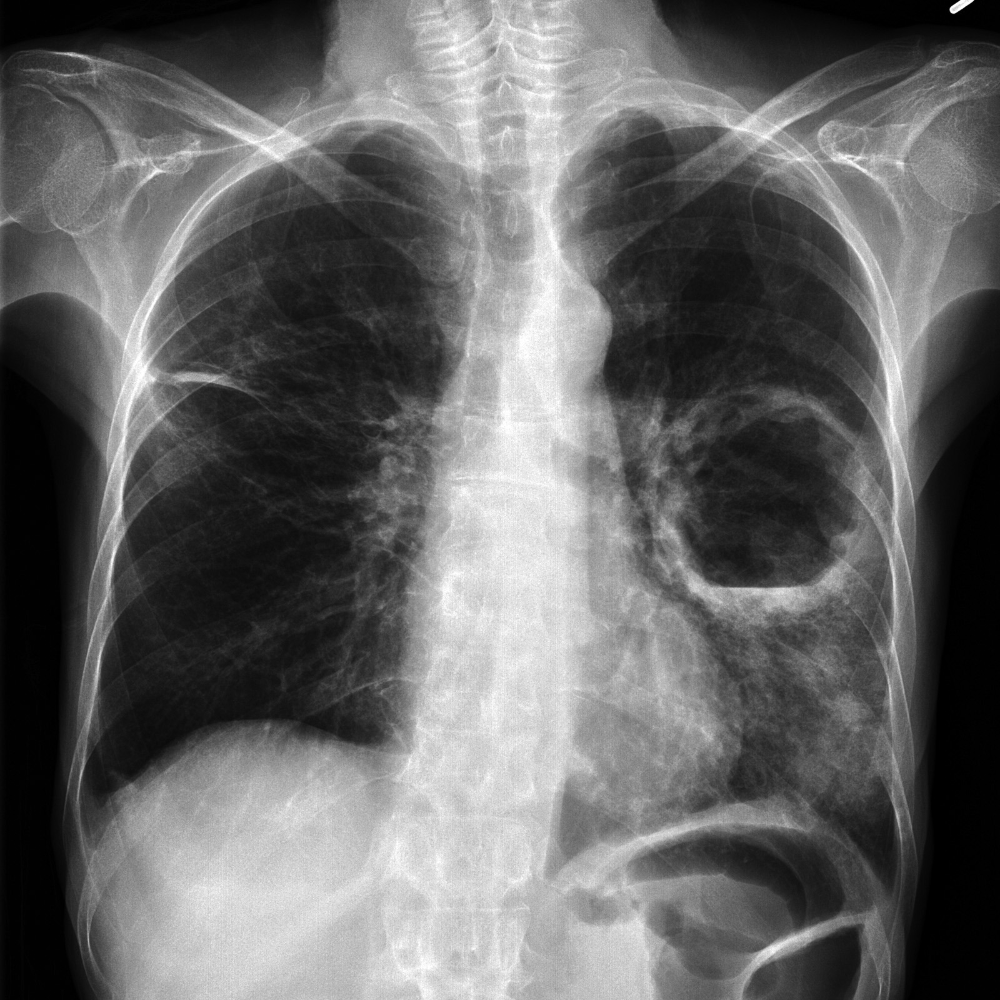
What is aspiration pneumonia
Imaging modality of choice to diagnose esophageal perforation.
CT with IV contrast or CT esophagram with gastrograffin is the imaging modality of choice in esophageal perforation. Gastrografin helps to avoid the inflammatory reaction seen with barium.
The most common complaint in a patient with pulmonary embolism
What is dyspnea.
The most common presenting complaints are dyspnea (81%), chest pain (39%), syncope (22%), hemoptysis (5%), and unilateral leg complaints (38%).
What ECG findings help distinguish STEMI from pericarditis?
What is
Reciprocal ST-segment depression (ie, reciprocal changes) in leads other than V1 and aVR (odds ratio for STEMI is 31)
Horizontal or convex upward ST-segment morphology (odds ratio for STEMI is 6)
ST elevation in lead III > lead II (odds ratio for STEMI is 21)
The following are ECG abnormalities that suggest pericarditis
The absence of reciprocal changes
PR-segment abnormalities (depression in multiple leads and elevation in lead aVR).
A 70-year-old immunosuppressed patient from Arizona presents with 1 week of cough, fevers, and chill, and CXR reveals an upper lobe infiltrate and multiple thin-walled cavitary lesions
 What organism should you suspect and treatment?
What organism should you suspect and treatment?
Coccidioidomycosis.
Consider in patients living or traveled in 1537Southwestern U.S. states: Arizona, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico
Treatment may not be needed in healthy patients with mild symptoms
Immunocompetent patients with moderate disease : Fluconazole 400 mg by mouth
What is Beck's triad?
Findings of tamponade. muffled heart sounds, jugular vein distension, low BP

20 y/o female on her menses presents with chest pain. Past medical history significant for endometriosis. Chest x-ray shown below. What is the diagnosis
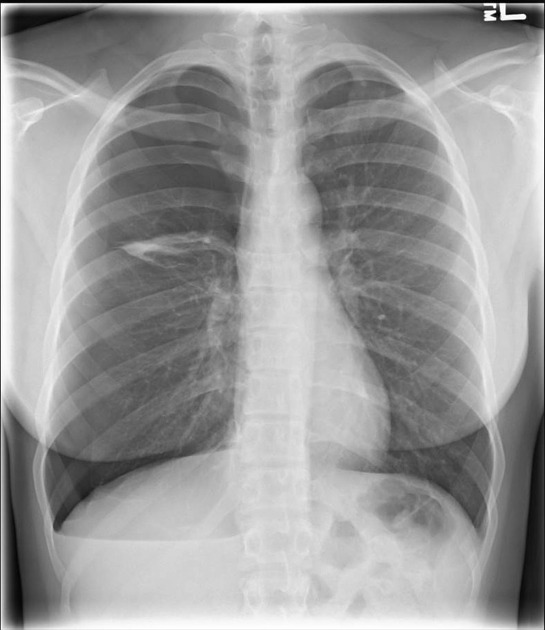
What is Catamenial pneumothorax. Catamenial pneumothorax is a rare condition that affects the membranes surrounding the lungs.
The resuscitation fluid of choice for ruptured AAA is
What is blood products. A 1:1 ratio of packed red blood cells to fresh frozen plasma appears to reduce the risk of mortality.
A patient diagnosed with pulmonary embolism goes into cardiac arrest. The drug/treatment of choice is
What is alteplase 100mg IVP or 50mg IVP followed by 50mg IVP 15minutes later. Tenectaplase CPR for 30 minutes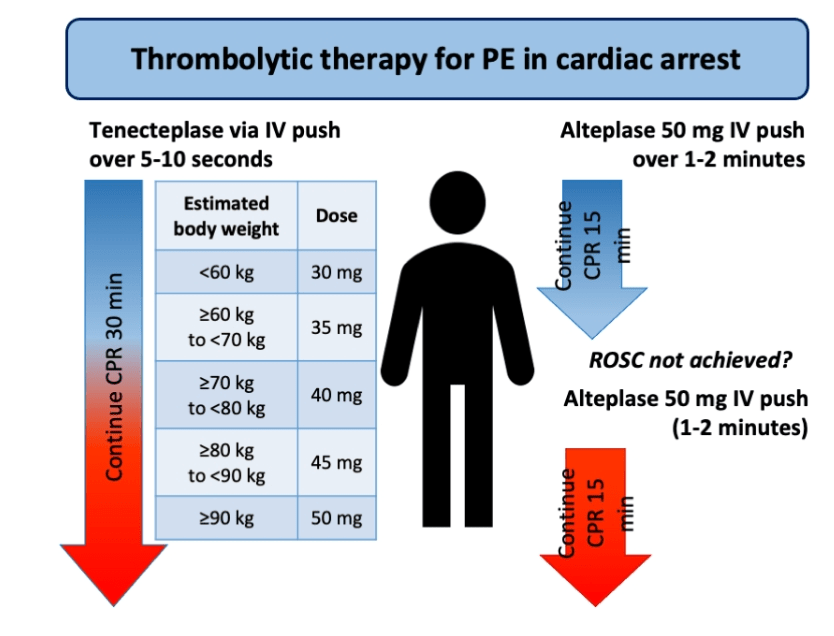
Interpret this ekg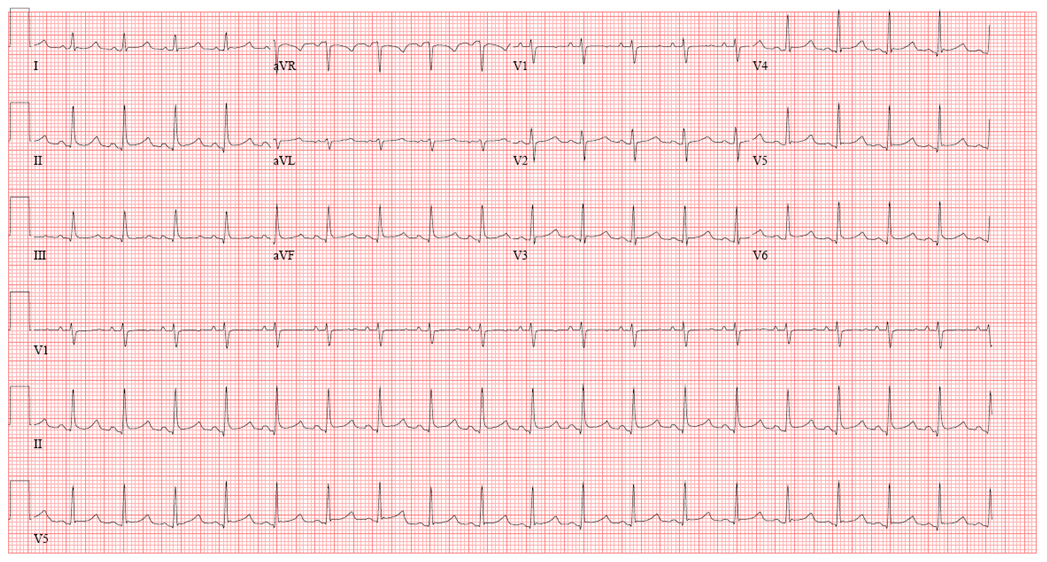
Pericarditis
12 Lead ECG shows diffuse ST elevations (most prominent in leads V4-V6, II, aVF) with diffuse PR depressions (most notable in V5-V6) and PR elevation in lead aVR.
A 42-year-old male presents with cough and frothy pink sputum approximately 3 days after arriving at Everest Base Camp. He is tachypneic with retractions and is hypoxic.
What is the definitive treatment?
The definitive treatment for all altitude-related illnesses is to descend to an altitude that is at least 1,000 m (3,280 feet) lower than your starting point.
True or False: A normal exam excludes aortic dissection.
False.
Physical examination may be completely normal upon presentation.
Examination findings classically associated with thoracic AD are present in less than one-third of all cases.
Most clinical findings associated with AD are insensitive in isolation. However, a combination of findings increases the accuracy of the clinical assessment for AD.
This ultrasound finding is indicative of what process
What is pneumothorax.
What is the eponym for the crunching sound with heartbeat auscultated over the precordium.
Hamman sign (simultaneous crunching sound with heartbeat auscultated over the precordium, especially in the left lateral decubitus position)
65 y/o male presents hypotensive, short of breath, with muffled heart sounds. Ultrasound shows the findings below. Emergent treatment is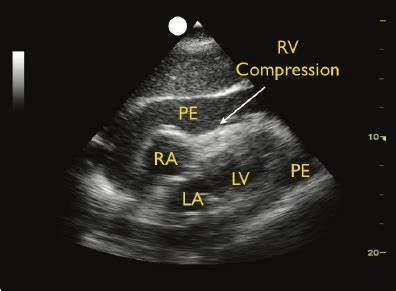
US guided pericardiocentesis
Gold standard for the diagnosis of myocarditis
What is histology.
No ECG findings are specific to the diagnosis of myocarditis Chest X-ray appears normal in patients without a pericardial effusion or tamponade.
65 y/o male presents with shortness of breath and generalized weakness. Abnormal diagnostic findings include the x-ray below and and a sodium of 120. Name the paraneoplastic syndrome.
SIADH
A 52-year-old woman with a history of hypertension presents with severe chest pain. Vitals are: HR 130, BP 70/40, RR 30. A left sided diastolic murmur is noted. A point of care cardiac ultrasound is performed (see below). What is the most likely diagnosis and best next step in management?
This patient’s presentation is most consistent with a thoracic aortic dissection with extension into the aortic root and pericardium causing cardiac tamponade. Bedside pericardiocentesis. Performing a pericardiocentesis to remove fluid from around the heart is likely to improve hemodynamics while the patient awaits surgical intervention.
60 y/o alcoholic presents with cough and generalized weakness. X-ray is shown below. What are the most common organisms associated with this condition?
Commonly caused by Staphylococcus, Gram-negatives, and anaerobes.
What is Mackler's triad?
The Mackler triad for spontaneous esophageal rupture includes vomiting followed by chest pain and the presence of subcutaneous emphysema. This triad is only present in up to 50% of patients.
What is the most common ECG finding of a patient with pulmonary embolism?
Sinus Tachycardia
What is the significance of this x-ray finding?

Pneumomediastinum
What is the preferred agent for heart rate control in the setting of aortic dissection and its dose?
What is esmolol 500microgram/kg bolus over 1 minute followed by 50 μg/kg/minute continuous infusion
What occupations are risk factors for pneumoconiosis?
Coal Minor
Roofers
Plumbers
Textile Workers
A 62-year-old man is brought to the ED with respiratory distress. Vitals are: HR 100, BP 185/125, RR 30, SpO2 91% on O2 via non-rebreather mask. Portable chest x-ray is shown. What is the most appropriate treatment to initiate ?
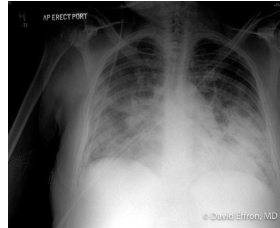
This patient is presenting with signs of hypertensive emergency in the form of acute pulmonary edema. Apart from non-invasive ventilation, acute pulmonary edema in the setting of extreme hypertension should be managed with afterload and preload reduction. Nitroglycerin is ideal, as it can achieve both as it is titrated higher. Nitroprusside or clevidipine in this setting, primarily afterload reducers, may also be considered as well.
In patients presenting with acute pulmonary edema, first line management includes the use of nitroglycerin and non-invasive ventilation.
A 56-year-old woman with lung cancer presents with several weeks of worsening facial swelling, shortness of breath, and cough. She has also noticed some left arm swelling. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Superior vena cava syndrome
A history of lung cancer with upper extremity edema and facial swelling or ‘plethora’ suggests mass effect on the superior vena cava.