The Third Interval in a Scale.
What is Submediant?
Has the Pattern of W-W-H-W-W-W-H. [T-T-S-T-T-T-S]
What is the Major Scale?
A Major Key Signature with no Sharps/Flats.
A different word for 'Whole Step'.
What is Tone?
Comprised of Root, Third, & Fifth.
What is a Triad?
Octave-Spanning Intervals.
What is a Compound Interval?
Has three variants: natural, melodic, and harmonic.
What is Minor Scale?
A Major Key Signature with two flats.
What is Bb?
The 'do, re, mi' of a Scale.
What is Solfege?
This Diatonic Chord has a Root, Major Third, Perfect 5th, and Minor Seventh.
What is a V7? (Dominant Seventh)
Unison, 4th, 5th, & 8th.
What are the Perfect Intervals?
Among its number are the "---" Ionian, Lydian, and Dorian
What are the 7 Diatonic Modes?
A Minor Key Signature with 4 Sharps.
What is c#?
A Simple Time Signature, often known as Alla Breve.
What is 2/2 OR [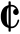 ] ?
] ?
Often used in hymns, a Subdominant(VI) or Supertonic(II) Chord moving to the Tonic(I).
What is the Plagal Chord?
A Whole-Step/Tone higher than a Major Interval.
What is a Doubly Augmented Interval?*
[*A Half-Step/Semitone would be Augmented]
This Hexatonic Scale has a Sharp/Flat pitch between the fourth and fifth intervals.
What is Blues Scale?
A Major Key Signature with Six Flats.
What is Gb?
The Minor Scale that has different patterns ascending and descending.
What is the Minor Melodic Scale?
Interestingly, Intervals chosen for "__" must equal 9 when added together.
What is Chord Inversion?
In the Scale of A Major, the distance from B4 to A5 would be an example of this specific Imperfect Interval.
What is a Minor Seventh?
Diatonic Mode whose Scale Pattern is the same as 'a natural minor'.
What is Aeolian Mode?
A Minor Key Signature with 7 Sharps.
What is a#?
The 'Mathematical Term' for how intervals are counted from the tonic up.
What are Bounded Intervals?
The V7 chord ' G - B - D - F' becomes ' F - G - B - D' with this Inversion.
What is V4/2? [V7 3rd Inversion]