These are three types of AKI
What are pre-renal, intrinsic, and post-renal?
This condition, commonly seen in diabetics, is characterized by delayed gastric emptying
What is gastroparesis
- Altered mental status
- Vomiting
- Intestinal obstruction/Ileus
- Ineffective against: Cyanide, Hydrocarbons, Toxic alcohols (Ethanol/Iso/Ethy), Metals, Iron, Caustics, Lithium, Camphor, Potassium (CHEMICal CAMP)
This is the first line test for multiple abdominal complaints in children
What is US?
This class of antibiotic can cause tendon rupture as one of its side effects.
What are fluoroquinolones?
What condition is demonstrated in this picture?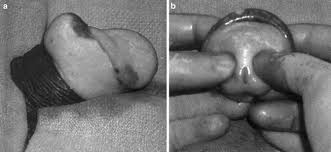
What is paraphimosis?
This is the most common cause of infectious diarrhea in the United States
What is norovirus?
What is the treatment for yellow oleander toxicity?
Digifab (Digibind) [Initial dose: 10-20 vials]
This is the definition of colic
What is crying for >3hrs per day for >3 days per week for >3 weeks
This class medication, commonly given for community acquired pneumonia and STIs, can deposit in teeth and bones
What findings on urinalysis are indicative of rhabdomyolysis?
What are positive for blood and zero or rare RBCs?
At least two of these three things are required for a formal diagnosis of pacnreatitis
What are clinical presentation consistent with pancreatitis, a serum lipase/amylase significantly elevated above upper limit of normal, and imaging findings characteristic of acute pancreatitis
What are the first AND second line therapies for acute cyanide toxicity?
- First-line: Hydroxycobalamin (increases B12 levels, increases RBC production/carrying capacity of oxygen, binds cyanide to make cyanocobalamin, which is excreted in the urine)
- Second-line: Amyl nitrite (converts met hemoglobin and binds cyanide) AND Sodium thiosulfate (converts cyanide to thiocyanate which is excreted in the urine)
This is the rate of fluid replacement in a moderate to severely dehydrated child
What is 20mL/kg?
Patients infected with spirochetes with have this reaction when given a penicillin
What is the Jarish-Herxheimer reaction?
What role does clindamycin play in treatment of Fourneir's Gangrene?
What is inhibition of protein synthesis?
This drug is the current mainstay for hepatic encephalopathy
What is Lactulose?
What level do you administer methylene blue for methemoglobinemia? (Asymptomatic vs symptomatic)
- Asymtpomatic (>20% on co-oximetry)
- Symptomatic (>10%)
What antibiotics are commonly used in the condition represented in the image below?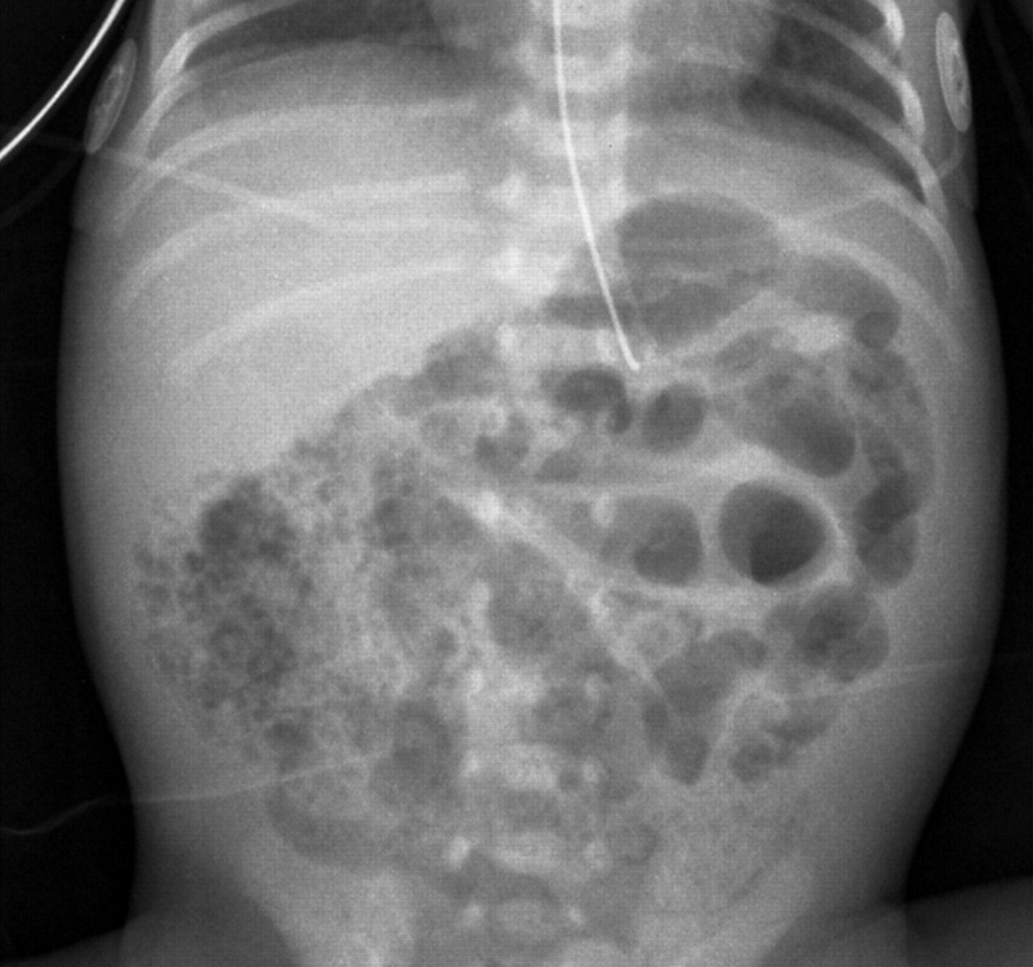
What are ampicillin plus gentamicin plus metronidazole? Piperacillin/tazobactam and vancomycin are also acceptable answers
This antibiotic is associated with a high risk of serotonin syndrome
What is linezolid?
Struvite kidney stones are most commonly found in which population?
What are women with recurrent UTIs?
Emphysematous cholecystitis is associated with what underlying condition?
What is diabetes?
What 2 interventions are contraindicated in Digoxin toxicity?
- Calcium (stone-heart)
- Transvenous pacing (bad outcomes due to increased risk of ventricular dysrhythmias secondary to irritable myocardium)
This image shows a condition that is associated with which condition?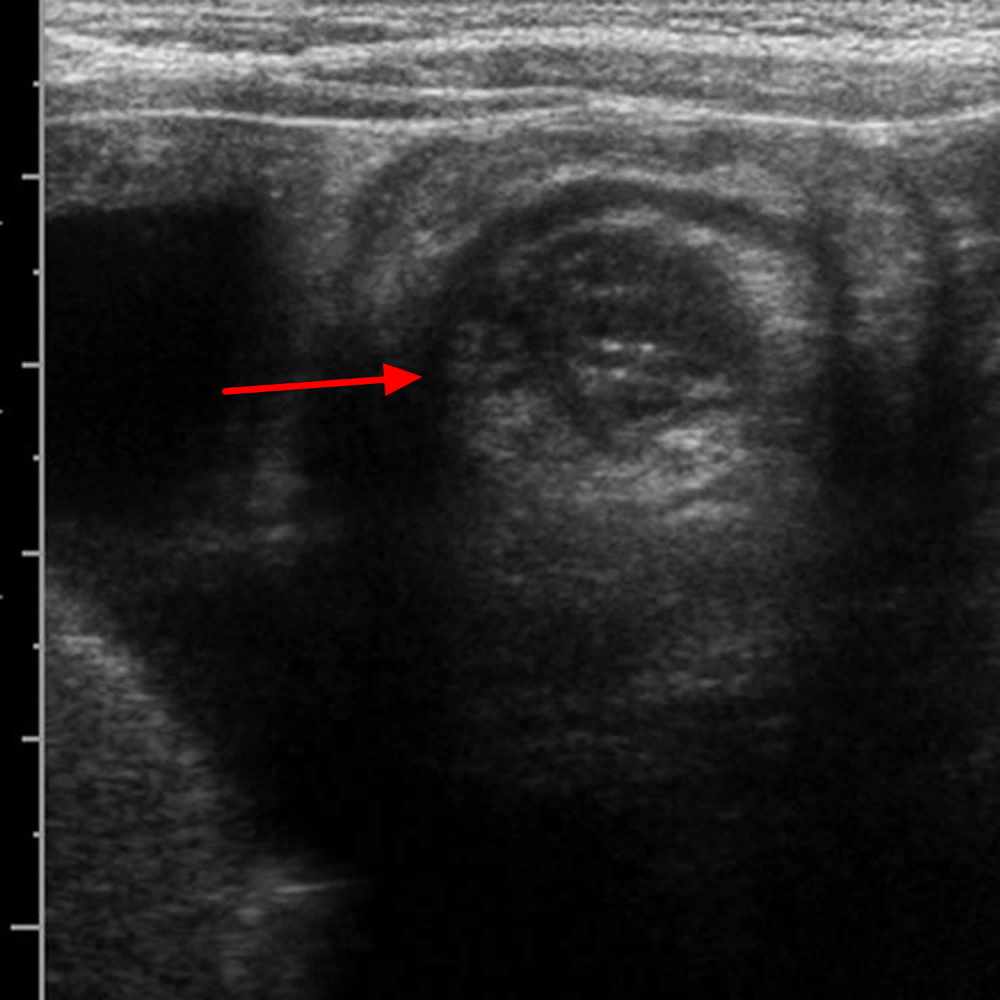
What is Henoch-Schonlein Purpura?
In a critically ill patient with ascending cholangitis and concern for ESBL organisms, this is often the drug of choice
What is meropenem?