State the most common cause of wheezing in both infants and children.
What is:
1) Infants: bronchiolitis
2) Children: asthma
<1 yr = bronchiolitis
1-2 yrs = mixed
>2 yrs = asthma
?
State the three pathophysiologic processes of asthma.
What are
1) Inflammation
2) Bronchospasm
3) Airway obstruction
Inflammatory cascade ->mucosal edema -> mucous hypersecretion, mucous plugs and structural changes (airway remodeling) ?
Four comorbid diseases that likely will require admission for management of pneumonia in a pediatric patient, state two.
What are cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, underlying immunodeficiency, and/or malignancy?
Annual influenza vaccine administration recommended beginning at what age?
What is 6 months?
Most commonly used medication to treat diagnosis of pneumonia, dosage, and route.
What is Ceftriaxone (50mg/kg/day) IV?
State the most common cause of bronchiolitis?
What is respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
State the O2 saturation to start oxygen, the goal SpO2, and the rationale.
What is <92% start O2 with goal 93-98%, because high O2 saturations may dec minute ventilation resulting in elevation in pulmonary end tidal carbon dioxide?
Recurrent aspiration pneumonia in pediatric patient should make you suspicious for possible for this medical condition.
What is: chronic GERD
tracheoesophageal fistula
developmental delay
neuromuscular disorders
immobility?
These symptoms indicate dyspnea in infants.
What are intermittent apnea, grunting, and inability to feed?
Best intravenous induction agent while anesthesia/CRNA is intubating pediatric patient with near fatal asthma, include 1) medication, 2) dose, and 3) rationale.
What is 1) ketamine, 2) 2 mg/kg, and 3) sympathomimetic properties and bronchodilation effects?
State four medical diagnosis for wheezing (not including asthma or bronchiolitis).
What are: pneumonia, GERD, Tracheoesophageal fistula, Congenital HD with L to R shunt, CHF, Myocarditis, foreign body aspiration, vocal cord dysfunction, laryngomalacia, tracheomalacia, vascular ring/sling/malformation/airway hemangioma or polyp, epiglottitis, CF, and/or ciliary dyskinesia?
State if the PaCO2 should be _______ (higher/lower) than normal in patient with asthma exacerbation due to this _________.
PaCO2 should be lower than normal in patient with asthma exacerbation due to increased minute ventilation?
Child’s respiratory rate remains within age-appropriate parameters; there are no rales, crackles, or other adventitious breath sounds; chest tubes function effectively. State the section of the care plan this information should be found.
What is outcome evaluation?
This leukotriene inhibitor helps in the treatment of asthma.
What is montelukast?
Name the antibiotic associated with the contraindication:
1) can displace bound bilirubin in neonates
AND
2) increased reported risk of pyloric stenosis in 1-3 month olds.
What is...
1) Ceftriaxone - can displace bound bilirubin in neonates
AND
2) Azithromycin - increased risk pyloric stenosis in 1-3 month olds?
State the peak of symptoms and illness time frame in bronchiolitis.
What is peak between days 3-5, and illness 7-21 days worst in 1st week?
North America: November - March
Name 3 of the 5 scoring categories of Pediatric Respiratory Assessment Measure (PRAM).
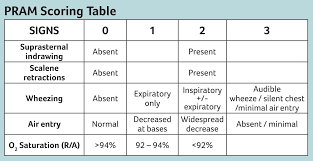
0-3 Mild l 4-7 Moderate l 8-12 Severe
You are reading the radiologist's report, and note that there are nodular findings in the lungs suggesting possible infection. The provider diagnoses the patient with right lower lobe pneumonia. State the priority nursing diagnosis.
What is ineffective gas exchange?
Apnea is a serious symptom that indicates a potential complication of infection in very young infants. Name the three potential causes of infection.
What are respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), Chlamydia, and Bordetella pertussis?
Albuterol belongs to this classification of medications, and name three of the routes of administration.
What is Beta 2 Agonists, and inhaled (aerosol or powder metered-dose inhaler, nebulized, and oral (tablet, tablet-ER, syrup)?
This is when is viral testing recommended in bronchiolitis.
What is
Patients on respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis presenting with bronchiolitis
Consider discontinuation of ppx for remainder of bronchiolitis season
Also consider testing in planned admission for patient cohorting and infection control
?
State the initial ventilator settings in an intubated pediatric patient with asthma.
Mode, TV, peak pressure, RR, I:E
What is/are?
Controlled Hypercapnic Hypoventilation
Mode: Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation/pressure-regulated volume control
TV: 6-10 mL/kg
Peak pressure: 45 cm H2O
RR: 8-15/min
Inspiratory time: 0.5-1.0 s
Expiratory time: 4-8 s
1) Bacterial pathogen that follows influenza infection
2) MC cause of pneumonia in peds > 1 mos
3) Staccato cough, "afebrile pneumonitis", b/l infiltrates
4) Hacking dry cough, HA, sore throat, arthralgias, rash, CNS involvement
5) URI prodrome followed by paroxysmal cough, gasping, stridor, color change
1) Bacterial pathogen that follows influenza infection - Staph aureus
2) MC cause of pneumonia in peds > 1 mos - RSV
3) Staccato cough, "afebrile pneumonitis", b/l infiltrates - Chlamydia trachomatis
4) Hacking dry cough, HA, sore throat, arthralgias, rash, CNS involvement - Mycoplasma pneumoniae
5) URI prodrome followed by paroxysmal cough, gasping, stridor, color change - Bordetella pertussis
Pediatric patient with URI sx and then develops rash (palms of hands and feet), vomiting, liver damage without jaundice, high fever, AMS
What may be the cause?
Reye Syndrome
2/2 viral infection treated with Aspirin
Influenza, varicella
Pathogenesis
aspirin metabolites inhibit mitochondrial enzymes
disrupts oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid beta-oxidation pathways
microvesicular fatty changes in the liver
Pharmacology - route, dose (mg/kg), max dose
1) Prednisone
2) Methylprednisolone
3) Dexamethasone
4) Magnesium
What is...
Prednisone - PO, 1-2 mg/kg, max 60 mg, x3-10d
Methylprednisolone - IV/IM, 2 mg/kg load, then 0.5-1 mg/kg q 6 h
Dexamethasone - PO/IV/IM, 0.6 mg/kg, max 16 mg, x1-2d
Magnesium - IV, 25-75 mg/kg, max 2 g
?