Which of the following claims about nonpolar R groups in an aqueous solution is most likely accurate?
A. They hide inside proteins and are hydrophilic.
B. They are hidden within proteins and are hydrophobic.
C. They are present on protein surfaces and are hydrophilic.
D. They are present on protein surfaces and are hydrophobic.
B. They are hidden within proteins and are hydrophobic.
Nonpolar R groups (hydrophobic side chains) tend to avoid water, so in an aqueous (water-based) environment, they are generally hidden within the interior of proteins, where they can interact with other nonpolar groups and avoid the surrounding water. This helps stabilize the protein's structure by minimizing interactions with the polar (hydrophilic) water molecules.
Which of the following is/are true regarding bipolar disorders?
I. They have little, if any, genetic heritability.
II. They are associated with increased levels of serotonin in the brain.
III. They all require at least one depressive episode for diagnosis.
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and III only
D. II and III only
The correct answer is: B
Bipolar disorders have been shown to be highly heritable and are associated with increased levels of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain. Bipolar I disorder can be diagnosed with a single manic episode and does not require a major depressive episode. Bipolar II disorder requires at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode. Cyclothymic disorder contains at least one hypomanic episode and dysthymia.
Starch is hydrolyzed into maltose by enzymes from the:
I. salivary glands.
II. brush border.
III. pancreas.
A. I only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, and III
B: Starch is hydrolyzed to maltose by two enzymes: salivary amylase (secreted by the salivary glands) in the mouth and pancreatic amylase (secreted by the pancreas) in the duodenum. Brush-border disaccharidases can further break down maltose, but do not break down starch.
Which of the situations below would be most analogous to the situation faced by a potential tort plaintiff, based on the information in paragraph 4?
A. A young basketball prospect trying to make it to the NBA
B. A group of children picking sides for a baseball game
C. A young, qualified woman looking for a job
D. An injured woman trying to reach an emergency room
A: The best description of the situation faced by a potential tort plaintiff is found in paragraph 4: Galanter’s pyramid findings demonstrated that only a tiny number of tort claims actually result in decisions in favor of the plaintiff. The main point is that there must be a tiny number of success stories from a much larger pool of in-dividuals. This matches to choice (A). In each of the other cases, close to 100% success would be expected (or at least a much higher percentage than the number of young basket-ball prospects who make it to the NBA).
What is the highest-energy orbital of elements with valence electrons in the n = 3 shell?
A. s-orbital
B. p-orbital
C. d-orbital
D. f-orbital
C: When n = 3, l = 0, 1, or 2. The highest value for l in this case is 2, which corresponds to the d subshell. Although the 3d block appears to be part of the fourth period, it still has the principal quantum number n = 3. In general, the subshells within an energy shell increase in energy as follows: s < p < d < f (although there is no 3f subshell).
Which of the following claims about peptide bonding is FALSE?
A. They have a partial double-bond personality.
B. Hydration reactions are involved in their production.
C. They serve as the main ties that connect amino acids.
D. They are created when an amino group and a carboxyl group react.
B. Hydration reactions are involved in their production.
This statement is false because peptide bonds are actually formed through dehydration (condensation) reactions, not hydration reactions. In this process, a water molecule is removed when the amino group of one amino acid reacts with the carboxyl group of another, forming a peptide bond.
A group of men and women are going to be rated on their driving abilities. The role of gender is emphasized in the experiment and the women perform worse than the men. In another experiment, the role of gender is not mentioned and the ratings are comparable between the two groups. Which principle do these results support?
A. Institutional discrimination
B. Stereotype threat
C. Prejudice
D. The just-world hypothesis
The correct answer is: B
Stereotype threat refers to the concept of people being concerned or anxious about confirming a negative stereotype of their social group. Stereotype threat can hinder performance, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy.
At the venous end of a capillary bed, the osmotic pressure:
A. is greater than the hydrostatic pressure.
B. results in a net outflow of fluid.
C. is significantly higher than the osmotic pressure at the arterial end.
D. causes proteins to enter the interstitium.
A: The exchange of fluid is greatly influenced by the relative balance between the hydrostatic and osmotic pressures of blood and tissues. The osmotic (oncotic) pressure remains relatively constant; however, the hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end is greater than the hydrostatic pressure at the venous end. As a result, fluid moves out of the capillaries at the arterial end and back in at the venous end. Fluid is reabsorbed at the venous end because the osmotic pressure exceeds the hydrostatic pressure. Proteins should not cross the capillary wall under normal circumstances.
Which of the following would most WEAKEN the conclusion implied in paragraph four of the text?
A. Galanter’s article was published in 1995.
B. A study that shows filings for divorce following a much different pattern.
C. The fact that Galanter’s study dealt with only product liability cases.
D. Most doctors carry medical malpractice insurance.
C: This is a Strengthen–Weaken (Beyond the Text) question, so let’s start by determining the conclusion implied by paragraph 4. The main point of Galanter’s argument stems from the assumption that analyzing all of the empirical data will give the fullest picture and not allow anecdotal bias. If it was possible that the data Galanter used was false or incomplete for some reason, this would seriously weak-en his argument overall. Choice (C) details exactly that prediction; if Galanter’s study was only specific to product liability, then it can’t be generalized to other similar cases or other tort suits. Choice (A) reflects on the dates given in the passage—Galanter’s study seems to investigate data until 1994. As long as Galanter’s study was published after this point, there is no negative effect on his argument, eliminating this answer. The pattern of divorce cases, as described in choice (B), has no effect on the argument because there is no reason to believe that divorce would (or wouldn’t) follow the same patterns as tort cases. Finally, whether or not physicians have malpractice insurance does not appear to be related to the number of cases brought to court or decided in favor of the plaintiff, so choice (D) would also have no effect on Galanter’s argument.
Which of the following actions does NOT affect the equilibrium position of a reaction?
A. Adding or removing heat.
B. Adding or removing a catalyst.
C. Increasing or decreasing concentrations of reactants.
D. Increasing or decreasing volumes of reactants.
B: The equilibrium of a reaction can be changed by several factors. Adding or subtracting heat, choice (A), would shift the equilibrium based on the enthalpy change of the reaction. Increasing reactant concentrations would shift the equilibrium in the direction of the product, and the opposite would occur if reactant concentrations were decreased, eliminating choice (C). Changing the volume of a reactant would affect any reaction with gaseous reactants or products, eliminating choice (D). While adding or removing a catalyst would change the reaction rates, it would not change where the equilibrium lies.
Acetylation of lysine residues in histones increases gene expression because
A.DNA is tightly bound to negatively charged amino acids on histones.
B.the carboxyl oxygen atoms in acetyl groups form hydrogen bonds with nitrogenous bases.
C.the salt bridges between charged amino acids and phosphate groups are disrupted.
D.lysine residues in histones associate with positively charged phosphate groups in DNA.
C. The salt bridges between charged amino acids and phosphate groups are disrupted.
A student is volunteering in a hospital with a stroke center. When asked what he believes is the prevalence of stroke among those greater than 65 years old, the student states that it is probably about 40% even though data analysis indicates that it is significantly lower. What accounts for this error?
A. Deductive reasoning
B. Representativeness heuristic
C. Base rate fallacy
D. Confirmation bias
C
The base rate fallacy occurs when prototypical or stereotypical factors are used for analysis rather than actual data. Because the student is volunteering in a hospital with a stroke center, he sees more patients who have experienced a stroke than would be expected in a hospital without a stroke center. Thus, this experience changes his perception and results in base rate fallacy. Deductive reasoning, choice (A), refers to drawing conclusions by integrating different pieces of evidence. The representativeness heuristic, choice (B), involves categorization and classification based on how well an individual example fits its category. Confirmation bias, choice (D), occurs when a person only seeks information that reinforces his or her opinions.
Which of the following statements concerning growth hormone is NOT true?
A. Overproduction of growth hormone in adults results in acromegaly.
B. It promotes growth of bone and muscle.
C. It is produced by the hypothalamus but secreted by the pituitary.
D. A childhood deficiency in growth hormone results in dwarfism.
C: Growth hormone is a direct hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary. Among its many functions, GH promotes growth in bone and muscle, eliminating choice (B). An overproduction of growth hormone in children results in gigantism, whereas in adults it results in acromegaly (enlargement of the small bones in the extremities and of certain facial bones, such as the jaw), eliminating choice (A). On the other hand, a childhood deficiency of growth hormone results in dwarfism, eliminating choice (D). GH is synthesized and secreted in the anterior pituitary; choice (C) de-scribes antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin, not GH.
The author primarily mentions Liebeck’s award (paragraph 1) in order to:
A. give an example to support his overall claim.
B. give an example of a verdict that is blatantly excessive.
C. give an example of a verdict that has caused legislators to call for tort reform.
D. introduce evidence for a conclusion made later in the passage.
C: This Function question should direct use to our Outline. Paragraph 1 mentions extreme examples the tort system awards. Even without rereading, predict that Liebeck must be one of those very high monetary awards that caused lob-byists to be so aggressive in fighting against the tort system in general and call for reform. This matches to choice (C). Choice (A) is not possible simply because the author does not overtly make any claims. Our author is very neutral and simply sets the facts in front of us to make our own decisions. Choice (B) Distorts the author’s mention of jury verdicts that appear, on superficial inquiry, to be blatantly exces-sive—the use of the phrase on superficial inquiry implies that the author may not agree that these damages actually are excessive. Finally, choice (D) is vague enough that it could sound plausible, but there is no later argument or conclusion that requires Liebeck’s award specifically. Generally, there isn’t any conclusion about coffee, McDonalds, burns, or the elderly, that would depend on this example either.
At standard temperature and pressure, a chemical process is at equilibrium. What is the free energy of reaction (ΔG) for this process?
A. ΔG> 0
B. ΔG< 0
C. ΔG = 0
D. There is not enough information to determine the free energy of the reaction.
C: Standard temperature and pressure indicates 0°C and 1 atm. Gibbs free energy is temperature dependent, but if a reaction is at equilibrium, ΔG = 0.
A protein collected through affinity chromatography displays no activity even though it is found to have a high concentration using the Bradford protein assay. What best explains these findings?
A. The Bradford reagent was prepared incorrectly.
B. The active site is occupied by free ligand.
C. The protein is bound to the column.
D. The protein does not catalyze the reaction of interest.
The correct answer is: B
Protein activity and concentration are generally correlated. Because we have a high concentration of protein, we expect a high activity unless the protein has been damaged or inactivated in some way. The protein could have been inactivated by experimental conditions like detergents, heat, or pH; however, these are not answer choices. Rather, we must consider how the experimental procedure works. Protein elutes off of an affinity column by binding free ligand. In this situation, the binding may not have been reversed and thus the free ligand competes for the active site of the enzyme, lowering its activity.
Adult prison systems may attempt to change the behavior of inmates through all of the following mechanisms of socialization EXCEPT:
A. primary socialization.
B. secondary socialization.
C. anticipatory socialization.
D. resocialization.
The correct answer is: A
Primary socialization is the teaching of acceptable actions and attitudes during childhood, which would occur too early to be part of the adult prison system. Resocialization, choice (D), is the process by which one changes behaviors by dis- carding old routines and patterns and transitions to new behaviors necessary for a life change. The prison environment is designed to change bad behavior into desired behavior, making this an incorrect choice. When entering prison, an inmate must also undergo secondary socialization, choice (B), learning the rules of the specific social environment of the prison. Finally, if the inmate is not incarcerated for life, attempts at anticipatory socialization, choice (C), must be made before releasing the inmate in preparation for life outside of the prison.
Which pairs of substances are released from exocrine glands?
A.Glucagon and tears
B.Bile and insulin
C.Insulin and digestive enzymes
D.Tears and bile
D. Tears and bile
The analogy between an international balance of power and the interrelations between neighbors is based on which of the following assumptions?
A. Both neighbors and neighbor states must avoid conflict whenever possible.
B. Power relations between neighbors are dependent on similar factors to those between neighbor states.
C. A degree of cultural similarity is required for peaceful coexistence.
D. The use of force for self-preservation is always justifiable.
B: The word assumption immediately lets us know this is an Inference question of the Assumption subtype. Here, we want to identify an assumption the author makes while form-ing the analogy in paragraph five. As discussed in Chapter 6 of MCAT CARS Review, analogical reasoning relies on two pieces of evidence: that the two entities (neighbors, N, and international balances of power, I) share similar corresponding characteristics (N1 and I1, N2 and I2, an so on), and that one of the entities has an additional characteristic (Nx)—from this, the conclusion is drawn that the other entity also has that characteristic (Ix). This might sound like a bunch of jargon, but it provides a quick way to answer this question: one assumption in an analogy is always that the two entities are similar enough to be compared in this way. Therefore, we should look for an answer that, were it not to be true, would mean that neighbors and states are actually not so similar. Choice (B) matches this assumption—if power relations between neighbors were not dependent on similar factors to those between neighbor states, then the comparison made in the last paragraph would make no sense. Choice (A) is a Distortion; while it makes sense that both neighbors and states would aim to avoid conflict whenever possible, the word must makes this answer too Extreme. Even if neighbors occasionally quarreled, and neighbor states occasionally fought, the analogy would still hold. In fact, the analogy even suggests that a conflict may occur over the lawnmower. Choice (C) is also too Extreme; while the author suggests that cultural similarity facilitates cooperation, there is no suggestion that this similarity is absolutely required for peaceful coexistence. Finally, choice (D) is Out of Scope. The author seems to suggest that force may be needed to maintain a balance of power, but does not make any reference to what is justifiable. Note the use of always also makes this answer choice Extreme.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the difference between a sigma (σ) and a pi (π) bond?
A. Pi bonds form from the side-to-side overlap of hybridized sp, sp^2, sp^3 superscript orbitals.
B. Sigma bonds form from the end-to-end overlap of two hybridized s or p orbitals.
C. The maximum number of σ versus π bonds between two atoms are different, but the energy level of the two bonds are the same.
D. Only sigma bonds use hybridized orbitals to overlap in forming the bond.
D
only sigma bonds use hybridized orbitals to overlap in forming the bond.
Which of the following DOES NOT constitute an effect of enzymes that lowers the activation energy of biological reactions?
A. Creating momentary covalent connections
B. Changing the immediate environment of charge
C. Taking on the roles of electron donors or receptors
D. Breaking the bonds in the enzyme to release energy
D. Breaking the bonds in the enzyme to release energy
This statement does not describe how enzymes lower activation energy. Enzymes lower activation energy by stabilizing the transition state through various mechanisms (options A, B, and C), but they do not lower activation energy by breaking their own bonds to release energy. Instead, they act as catalysts that facilitate reactions without undergoing permanent changes themselves.
Which of the following population pyramids depicts the population that is most likely to decrease in size in the near future?
A.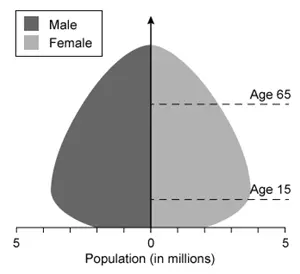
B.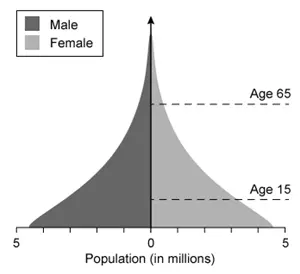
C.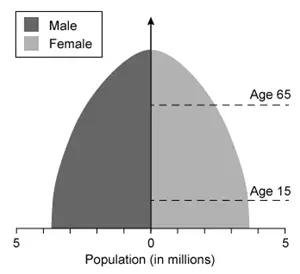
D.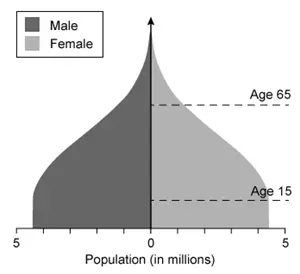
A
Population pyramids, which display the relative number of males and females in each age cohort in a given population, have three general shapes:
Expanding pyramids have broad bases (lots of younger people) and narrow tops (few older people) and are characteristic of developing countries with high birth/death rates and an increasing population size.
Stationary pyramids have broad bases and broad tops and are characteristic of developed countries with low birth/death rates and a stable population size.
Contracting pyramids have narrower bases than middles and are characteristic of developed countries with very low birth rates and a gradually declining population size.
Which of the following is likely to be found in maternal blood during pregnancy?
A. Immunoglobulins produced by the fetus
B. Fetal hemoglobin released from fetal red blood cells
C. Progesterone produced by placental cells
D. Carbon dioxide exhaled from fetal lungs
C: During pregnancy, the placenta produces estrogen and progesterone to maintain the endometrium. These hormones are necessary for proper gestation of the fetus and should be measurable in maternal blood because they act on maternal organs. Prior to birth, the fetus is immunologically naïve and does not yet produce immunoglobulins, eliminating choice (A). It is worth noting, though, that maternal immunoglobulins cross the placenta to enter fetal blood. Fetal hemoglobin is a large protein and, thus, cannot easily cross the placenta. Further, red blood cells are much too large to cross the barrier themselves, eliminating choice (B). Carbon dioxide from fetal metabolism can be found in maternal blood, but the lungs are nonfunctional prior to birth as the fetus is suspended in amniotic fluid. Carbon dioxide is transferred across the placenta directly from the fetal bloodstream, eliminating choice (D).
Which of the following helps explain why a balance of power is generally characterized by a “common ground of culture” (paragraph 3)?
A. Countries with similar cultures often have mechanisms of diplomacy in place.
B. Cultural differences between two nations are often the source of military conflict.
C. A hegemon often influences the cultures of all nations surrounding it.
D. Alliances among nations are more common if there are shared cultural beliefs.
D: In this Detail question, we need to pick the choice that matches the explanation for this claim in the passage. The author clarifies the phrase common ground of culture by pointing out that states with similar culture are more likely to align in cooperative manner. This is almost identical to choice (D). Choice (A) is a Faulty Use of Detail; while mechanisms of diplomacy are needed for balance of pow-er according to the author, they are a separate third factor needed mentioned in this paragraph (in addition to having at least three states and common culture) and are not part of the common ground of culture described. Choice (B) is Out of Scope because the passage does not have any discussion of cultural differences causing military conflict—it just states that cultural similarities foster cooperative behavior. Choice (C) is similarly out of scope because the author does not discuss the influence of a hegemon on the culture of surrounding states.
Which of the following correctly lists the enthalpy changes for these three steps, respectively?
The process of formation of a salt solution can be better understood by breaking the process into three steps:
1. Breaking the solute into its individual components
2. Making room for the solute in the solvent by overcoming intermolecular forces in the solvent
3. Allowing solute–solvent interactions to occur to form the solution
A. Endothermic, exothermic, endothermic
B. Exothermic, endothermic, endothermic
C. Exothermic, exothermic, endothermic
D. Endothermic, endothermic, exothermic
D: The first step will most likely be endothermic because energy is required to break molecules apart. The second step is also endothermic because the intermolecular forces in the solvent must be overcome to allow incorporation of solute particles. The third step will most likely be exothermic be-cause polar water molecules will interact with the dissolved ions, creating a stable solution and releasing energy.