The term for the process by which two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus?
What is "nuclear fusion"?
This is the force that opposes the motion (or attempted motion) of two surfaces in contact, arising from the interaction between those surfaces.
What is "friction"?
Condensation reactions involve the release of this molecule:
What is "water"?
This is the programmed destruction of a cell.
What is "apoptosis"?
A society places a high value on individual achievement and personal success. People are encouraged to pursue their own goals and aspirations, often at the expense of collective well-being. This sociological concept best characterizes this orientation:
What is "individualism"?
This is what an -OH group is also known as:
What is "hydroxyl" or "alcohol"?
If the acceleration of an object is zero, then the velocity has to be:
What is "constant" or "unchanging"?
Out of the following, this best describes the role of the ribosome during protein synthesis:
a) Ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA
b) Ribosome binds amino acids together to form peptide bonds using the information from tRNA
c) The ribosome provides a site for the viral assembly of proteins and genetic material
d) Ribosome is the primary site of transcription where mRNA is synthesized from DNA
What is "a"? (ribosome synthesizes proteins based on mRNA sequence)
The circulatory system contains numerous arteries. This one is the only one that carries deoxygenated blood:
What is "pulmonary artery"? (most arteries in the entire circulatory system carry oxygenated blood, but the pulmonary artery is the only exception)
A community experiences a rise in social protests and demonstrates advocating for racial justice and equality. These movements are driven by recognition of systemic racism and a desire to address historical and contemporary equalities. This sociological theory in particular best explains the motivation behind these movements:
a) Symbolic interactionism
b) Conflict theory
c) Structural fundamentalism
d) Feminist theory
What is "b" (conflict theory) (posits that society is characterized by inequality and competition for limited resources, leading to conflict and power struggles between different groups)
This is the type of reaction that electrochemical cells derive their energy from.
What is "redox reaction" or "oxidation-reduction reaction"?
This term describes the rate at which work is done.
What is "power"?
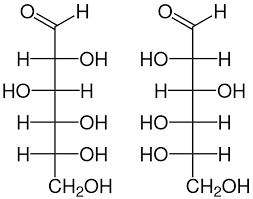
The name of this sugar is:
(Ignore that there's two, these are the L and D forms of the same sugar.)
What is "glucose"? (this is the linear form, glucose can also exist in cyclic form)
A scientist is measuring the absorbance of a solution using a spectrophotometer and notes that the absorbance at 500 nm is 0.1, while at 600 nm it is 0.5. If the scientist doubles the concentration of the solution, this will be the new absorbance at 500 nm:
What is "0.2" (Beer's law states that absorbance is directly proportional to concentration)
This is the neurotransmitter most directly involved in the reinforcement of rewarding behaviors.
What is "dopamine"?
Out of the following options, this chemical species is the best electrophile:
a) F-
b) Na+
c) O
d) S
What is "b" (Na+) (electrophile means best species at accepting electrons from an electron donating species)
This situation results in positive work being done on a system:
a) A person pushes a box and it moves in the direction of the push
b) Car slows down as it moves along a flat road due to air resistance
c) Person carries a bag of groceries horizontally at constant velocity
d) A ball is thrown straight up into the air and slows down as it rises
What is "a" (person pushes a box and it moves in the direction of the push) (positive work means the force on an object and its displacement are in the same direction, aka the force is acting in the object's direction of movement)
Out of the following, this will happen after adding an enzyme to a reaction:
a) Reaction equilibrium shifts to the right
b) Reaction equilibrium shifts to the left
c) Rate of forward and reverse reactions increases
d) Free energy difference between reactants and products is lowered
What is "c"? (rate of forward and reverse reactions increases)
In a laboratory experiment, researchers are measuring the rate of enzyme activity in different pH environments. If the optimum pH for an enzyme is found to be 7.4, this is the expected outcome of the enzyme activity at a pH of 5.0:
What is "decreased enzyme activity" or "enzyme denaturation" (second one is less likely, but still technically a possibility)
This function is what the Wernicke's area is directly responsible for.
What is "speech comprehension"?
A professor is running a lab in organic chemistry. She wants her students to perform an SN1 substitution on a particular alkyl halide. Out of the following solvents, the best to use would be:
a) Acetic acid
b) Acetonitrile
c) DMF
d) DMSO
What is "a" (acetic acid) (acetic acid here is the only polar protic solvent, meaning it is the only solvent that donates a proton. SN1 reactions favor these kinds of solvents)
This law states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it can only change from one form to another.
What is "Law of Conservation of Energy"?
This type of bond holds the fatty acids in a triglyceride together:
What is "covalent bond".
This is the hormone primarily involved in rebuilding the endometrium.
What is "estrogen"? (while progesterone helps to maintain the endometrium, estrogen secreted from follicular cells is what directly results in the rebuilding of the endometrium after it has been shed)
A patient exhibits persistent, excessive worry about various aspects of daily life, finding it difficult to control this worry. The patient also experiences restlessness, fatigue, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. This psychological disorder is most consistent with this presentation: