SCIENCES
Which of the following is NOT a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
A. Lipid synthesis
B. Poison detoxification
C. Protein synthesis
D. Transport of proteins
C. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the transport of materials throughout the cell, in lipid synthesis, and in the detoxification of drugs and poisons. Proteins from the rough ER can cross into the smooth ER, where they are secreted into cytoplasmic vesicles and transported to the Golgi apparatus. Thus, from the given choices, protein synthesis is not a function of the smooth ER, but rather of the free ribosomes or the ribosomes associated with the rough ER. Choice (C) is therefore the correct answer.
What is the highest-energy orbital of elements with valence electrons in the n = 3 shell?
A. s-orbital
B. p-orbital
C. d-orbital
D. f-orbital
C: When n = 3, l = 0, 1, or 2. The highest value for l, in this case, is 2, which corresponds to the d subshell. Although the 3d block appears to be part of the fourth period, it still has the principal quantum number n = 3. In general, the subshells within an energy shell increase in energy as follows: s < p < d < f (although there is no 3f subshell).
An electron is known to be in the n = 4 shell and the l = 2 subshell. How many possible combinations of quantum numbers could this electron have?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 5
D. 10
D: An electron in the n = 4 shell and the l = 2 subshell can have five different values for ml: –2, –1, 0, 1, or 2. In each of these orbitals, electrons can have positive or negative spin. Thus, there are 5 × 2 = 10 possible combinations of quantum numbers for this electron.
Which of the following statements regarding electric current is true?
A. Electric current will only flow from a higher potential to a lower potential.
B. Electric current will only flow from a lower potential to a higher potential.
C. Oscillate between potentials of higher and lower energy.
D. Remain in equilibrium
Correct Answer: A. Electric current will only flow from a high potential to a lower potential.
Electric current moves in the direction positive charges move in. Therefore, the electric flow of current flows from the point of higher potential to lower potential, similar to how water falls from the top of the waterfall to the bottom.
Which area of the brain is responsible for receiving visual stimulation?
A. Frontal lobe
B. Occipital lobe
C. Temporal lobe
D. Cerebellum
Occipital lobe- is the region of the brain that is responsible for receiving visual stimulation.
Frontal lobe- controls speech production, emotional behaviors, makes decisions, and the motor cortex initiates movement.
Temporal lobe- processing auditory information and with the encoding of memory.
Cerebellum- Helps modulate emotions, discriminate sounds and textures, coordinates movement, balance.
Which of the following organelles is surrounded by a single membrane?
A. Lysosomes
B. Mitochondria
C. Nuclei
D. Ribosomes
A. Lysosomes are vesicular organelles that digest material using hydrolytic enzymes. They are surrounded by a single membrane. Both mitochondria and nuclei are surrounded by double membranes, eliminating choices (B) and (C). Ribosomes must not be surrounded by membranes because they are found not only in eukaryotes, but also in prokaryotes, which lack any membrane-bound organelles, eliminating choice (D).
SN1 reactions show first-order kinetics because:
A. the rate-limiting step is the first step to occur in the reaction.
B. the rate-limiting step involves only one molecule.
C. there is only one rate-limiting step.
D. the reaction involves only one molecule.
The correct answer is: B
An SN1 reaction is a first-order nucleophilic substitution reaction. It is called first-order because the rate-limiting step involves only one molecule. Choice (A) is true, but does not explain why SN1 reactions have first-order kinetics; the rate- limiting step of an SN2 reaction is also the first (and only) step of that reaction, but SN2 reactions have second-order kinetics, not first-order. Choice (C) is a true statement as well, but again does not explain why the reaction is first- order. Finally, choice (D) is incorrect because it is the rate- limiting step, not the reaction overall, that involves only one molecule.
What would be the charge of aspartic acid at pH 7?
A. Neutral
B. Negative
C. Positive
D. There is not enough information to answer the question.
B: The amino acid in question is aspartic acid, which is an acidic amino acid because it contains an extra carboxyl group. At neutral pH, both of the carboxyl groups are ionized, so there are two negative charges on the molecule. Only one of the charges is neutralized by the positive charge on the amino group, so the molecule has an overall negative charge.
A scientist looks through a microscope with two thin lenses with m1 = 10 and m2 = 40. What is the overall magnification of this microscope?
A. 0.25
B. 30
C. 50
D. 400
D: The overall magnification of a system of multiple lenses is simply the product of each lens’s magnification. In this case, that is 10 × 40 = 400.
Which type of conflict is associated with the LEAST amount of stress?
A. Approach–approach conflict
B. Avoidance–avoidance conflict
C. Approach–avoidance conflict
D. Avoidance–escape conflict
A: Approach–approach conflict is one in which both results are good outcomes. While one must be chosen, neither choice results in a negative outcome: for example, choosing between two desserts. Avoidance–escape conflict, choice (D), is not a recognized form of conflict; these two terms are related to types of negative reinforcers.
Suppose that in a mammalian species, the allele for black hair (B) is dominant to the allele for brown hair (b), and the allele for curly hair (C) is dominant to the allele for straight hair (c). When an organism of unknown genotype is crossed against one with straight, brown hair, the phenotypic ratio is as follows:
25% curly black hair
25% straight black hair
25% curly brown hair
25% straight brown hair
What is the genotype of the unknown parent?
A. BbCC
B. bbCc
C. Bbcc
D. BbCc
The correct answer is: D
In this dihybrid problem, a doubly recessive individual is crossed with an individual of unknown genotype; this is known as a test cross. The straight- and brown-haired organism has the genotype bbcc and can thus only produce gametes carrying bc. Looking at the F1 offspring, there is a 1:1:1:1 phenotypic ratio. The fact that both the dominant and recessive traits are present in the offspring means that the unknown parental genotype must contain both dominant and recessive alleles for each trait. The unknown parental genotype must therefore be BbCc. If you want to double-check the answer, you can work out the Punnett square for the cross BbCc × bbcc:
Which of the following actions does NOT affect the equilibrium position of a reaction?
A. Adding or removing heat.
B. Adding or removing a catalyst.
C. Increasing or decreasing concentrations of reactants.
D. Increasing or decreasing volumes of reactants.
B: The equilibrium of a reaction can be changed by several factors. Adding or subtracting heat, choice (A), would shift the equilibrium based on the enthalpy change of the reaction. Increasing reactant concentrations would shift the equilibrium in the direction of the product, and the opposite would occur if reactant concentrations were decreased, eliminating choice (C). Changing the volume of a reactant would affect any reaction with gaseous reactants or products, eliminating choice (D). While adding or removing a catalyst would change the reaction rates, it would not change where the equilibrium lies.
Butanoic anhydride can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with which of the following compounds?
A. Butanoic acid
B. Ethanoic acid
C. Butanol
D. Methanal
A: Butanoic anhydride is an anhydride with two butane R groups. Anhydrides are produced by the reaction of two carboxylic acids with the loss of a water molecule. Therefore, butanoic anhydride would be produced by the reaction of two molecules of butanoic acid.
Mechanical advantage and efficiency are both ratios. Which of the following is true regarding the quantities used in these ratios?
A. Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of power.
B. Mechanical advantage compares values of forces; efficiency compares values of work.
C. Mechanical advantage compares values of power; efficiency compares values of energy.
D. Mechanical advantage compares values of work; efficiency compares values of forces.
B: Mechanical advantage is a ratio of the output force generated given a particular input force. Efficiency is a ratio of the useful work performed by a system compared to the work performed on the system.
Which of the following is NOT a dimension of the system for multiple level observation of groups (SYMLOG)?
A. Friendliness vs. unfriendliness
B. Dominance vs. submission
C. Conformity vs. contrast
D. Instrumentally controlled vs. emotionally expressive
C: SYMLOG is a method for analyzing group dynamics and considers groups along three dimensions: dominant vs. submissive, friendliness vs. unfriendliness, and instrumentally controlled vs. emotionally expressive.
A patient presents to the emergency room with an asthma attack. The patient has been hyperventilating for the past hour and has a blood pH of 7.52. The patient is given treatment and does not appear to respond, but a subsequent blood pH reading is 7.41. Why might this normal blood pH NOT be a reassuring sign?
A. The patient’s kidneys may have compensated for the alkalemia.
B. The normal blood pH reading is likely inaccurate.
C. The patient may be descending into respiratory failure.
D. The patient’s blood should ideally become acidemic for some time to compensate for the alkalemia.
The correct answer is: C
When a patient with an asthma attack does not respond to treatment and has been hyperventilating for over an hour, he or she may become fatigued and may not be able to maintain hyperventilation. In this case, the patient begins to decrease his or her breathing rate and is not receiving adequate oxygen. By extension, carbon dioxide is trapped in the blood, and the pH begins to drop. Despite the fact that this pH is normal at the moment, this patient is crashing and may start demonstrating acidemia in the near future. While the kidneys should compensate for alkalemia, this is a slow process and would not normalize the blood pH within an hour; further, adequate compensation by the kidneys would actually be a reassuring sign, eliminating choice (A). There is no evidence to believe the measurement was inaccurate, eliminating choice (B). Finally, after treatment, the patient should return to a normal blood pH with adequate ventilation and would not be expected to overcompensate by becoming acidemic, eliminating choice (D).
Which of the following correctly lists the enthalpy changes for these three steps, respectively?
The process of formation of a salt solution can be better understood by breaking the process into three steps:
1. Breaking the solute into its individual components
2. Making room for the solute in the solvent by overcoming intermolecular forces in the solvent
3. Allowing solute–solvent interactions to occur to form the solution
A. Endothermic, exothermic, endothermic
B. Exothermic, endothermic, endothermic
C. Exothermic, exothermic, endothermic
D. Endothermic, endothermic, exothermic
D: The first step will most likely be endothermic because energy is required to break molecules apart. The second step is also endothermic because the intermolecular forces in the solvent must be overcome to allow incorporation of solute particles. The third step will most likely be exothermic be-cause polar water molecules will interact with the dissolved ions, creating a stable solution and releasing energy.
All of the following are true with respect to carbonyls EXCEPT:
A. the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic.
B. the carbonyl oxygen is electron-withdrawing.
C. a resonance structure of the functional group places a positive charge on the carbonyl carbon.
D. the π electrons are mobile and are pulled toward the carbonyl carbon.
D: The reactivity of the carbonyl can be attributed to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen atoms. The more electronegative oxygen atom attracts the bonding electrons and is therefore electron-withdrawing. Thus, the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic. One resonance structure of the carbonyl pushes the π electrons onto the oxygen, resulting in a positively charged carbonyl carbon.
A 40 kg block is resting at a height of 5 m off the ground. If the block is released and falls to the ground, which of the following is closest to its total mechanical energy at a height of 2 m, assuming negligible air resistance?
A. 0 J
B. 400 J
C. 800 J
D. 2000 J
D. Assuming negligible air resistance, conservation of energy states that the total mechanical energy of the block is constant as it falls. At the starting height of 5 m, the block only has potential energy equal to
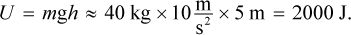
A rat is trained to press a lever to obtain food under a fixed-interval schedule. Which of the following behaviors would the rat most likely exhibit?
A. Pressing the lever continuously whenever it is hungry.
B. Pressing the lever exactly once and waiting for the food pellet before pressing it again.
C. Pressing the lever slowly at first, but with increasing frequency as the end of the interval approaches.
D. None of the above; the association formed by fixed-interval schedules is too weak to increase behavior.
C: In a fixed-interval schedule, the desired behavior is rewarded the first time it is exhibited after the fixed interval has elapsed. Both fixed-interval and fixed-ratio schedules tend to show this phenomenon: almost no response immediately after the reward is given, but the behavior increases as the rat gets close to receiving the reward.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) enters the human body and remains dormant in the nervous system until it produces an outbreak after exposure to heat, radiation, or other stimuli. Which of the following statements correctly describes HSV?
A. While it remains dormant in the nervous system, the virus is in its lytic cycle.
B. During an outbreak, the virus is in the lysogenic cycle.
C. Herpes simplex virus integrates itself into the DNA of the cell.
D. The herpes simplex virus contains a tail sheath and tail fibers.
C. Viruses can exist in either the lytic or lysogenic cycle; they may even switch between them throughout their lifetime. During the lytic cycle, the virus's DNA takes control of the host cell's genetic machinery, manufacturing numerous progeny. In the end, the host cell bursts (lyses) and releases new virions, each capable of infecting other cells. In the lysogenic cycle, viral DNA is integrated into the host cell's genome, where it can remain dormant for days or years. Either spontaneously or as a result of environmental circumstances, the provirus can reemerge and enter a lytic cycle. Thus, choices (A) and (B) are incorrect because they reverse which part of the cycle the virus is in. Choice (D) describes features of bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect bacteria—not the human nervous system. Choice (C) accurately describes how HSV operates during the lysogenic cycle, making it the correct answer.
Which reagents would carry out the following transformation?

A. SOCl2
B. Cl2, light and heat
C. HCl, H2O
D. Cl2, FeCl3
Correct Answer: D. Cl2, FeCl3
This is an electrophilic ring transformation; it proceeds efficiently via electrophilic chlorination (“Cl+”) of the aromatic ring, which usually involves chorine plus a suitable Lewis acid (aluminum chloride).
Consider (E)-2-butene and (Z)-2-butene. This is a pair of what type(s) of isomers?
I. Cis–trans isomers
II. Diastereomers
III. Enantiomers
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II only
D. I and III only
C: (E)-2-butene can also be called trans-2-butene; (Z)-2-butene can also be called cis-2-butene. As such, they are cis–transisomers. Remember that cis–trans isomers are a subtype of diastereomers in which the position of substituents differs about an immovable bond. Diastereomers are molecules that are non-mirror-image stereoisomers (molecules with the same atomic connectivity). These are not enantiomers because they are not mirror images of each other.
In the pulley system shown below, which of the following is closest to the tension force in each rope if the mass of the object is 10 kg and the object is accelerating upwards at 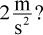
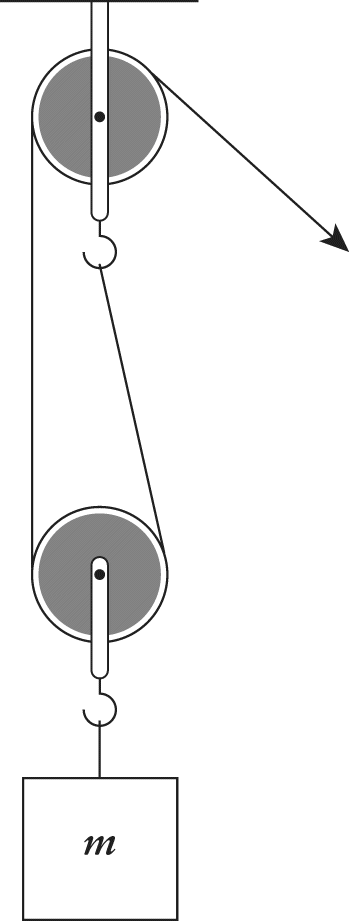
- A. 50 N
- B. 60 N
- C. 100 N
- D. 120 N
B. From the force diagram, notice that there are two tension forces pulling the mass up. The net force for this system (Fnet) is equal to 2T – mg. Now we can use Newton's second law:

A physician is attempting to diagnose a patient’s mental disorder based on a set of symptoms. The confirmed symptoms currently include appetite disturbance, substantial weight change, decreased energy, a feeling of worthlessness, and excessive guilt.
What two disorders could these symptoms indicate?
A. Major depressive and bipolar disorders
B. Dissociative amnesia and depersonalization/derealization disorder
C. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease
D. Specific phobia and panic disorder
The symptoms listed indicate a major depressive episode. However, depressive episodes can be a part of bipolar dis-orders, which also contain manic episodes. Thus, if manic episodes have not yet been asked about, one cannot choose depression or bipolar disorder as the correct diagnosis yet.