Experiential
Models
Structural Models
Cognitive Behavioral
Models
Emotionally-focused
Models
In Family Therapy, these have evolved sets of rules, organized power structures, and nuanced overt and covert forms of communication.
What are "families"?
A child internalizes the image of his mother into a good object and a bad object, he is engaging in ________.
What is "splitting"?
A simple pictorial device to depict family transactional patterns.
What is a "Family Map" or "Genograms"
All communication takes place at two-levels; this is the level which emotionally informs what was said on the surface level of content.
What is "metacommunication"?
In Narrative Family Therapy, the _______ is the problem.
What is the "problem"?
The double-bind concept was first introduced to account for the development of _______.
What is "schizophrenia"?
Expounding: Early Family Therapy theorists began to redefine schizophrenia as an interpersonal problem.
Defending against anxiety by externalizing unwanted parts of oneself onto others who, in turn, are unconsciously manipulated to behave according to these unwanted parts.
What is "projective identification"?
In Bowen's view, this is the opposite of differentiation, which is the capacity to which a person can think, plan, and follow his or her OWN values or convictions without having his or her behavior automatically driven by the emotional cues from others.
What is "fusion"?
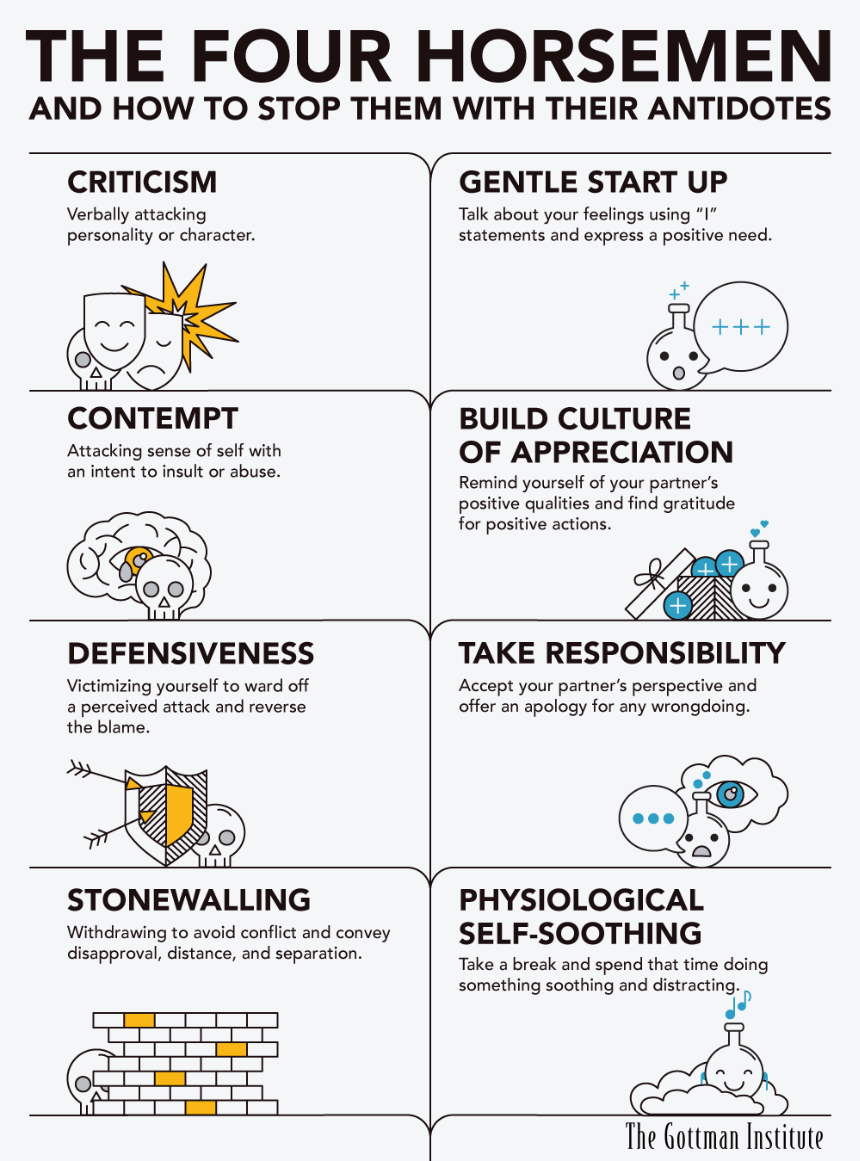
According to John Gottman's extensive research into relationships, four primary predictors of divorce, also known as The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse, are criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and ____________.
What is "stonewalling"?
A characteristic technique of the solution-focused model that attempts to place the client in a problem-free imagined future.
What is the "miracle question"?
A ____ order change doesn't deeply change the system or the problems.
What is "first" order change?
This is one of Virginia Satir's interventions in family therapy
What is the Parts Party, Family Sculpting, or Family Reconstruction?
This behavior reflects a problem (i.e. underlying fusion between generations), solves a problem (i.e. reducing anxiety associated with making contact), and creates a problem (i.e. isolating people who might benefit from closer contact).
What is "emotional cutoff"?
A quarreling couple wherein each feels justified in responding (i.e. - reacting) to what each perceives as an attack from the other are each imposing his or her own ___________ on their interactions.
What is "punctuation"?
A primary intervention or technique of a Narrative Family Therapist that is designed to separate the person from the problem.
What is "externalizing"?
"A bad mother produces sick children" is a statement of this type of causality.
What is "linear" causality?
Explanation: The view that one event/factor causes the next in unidirectional stimulus-response fashion, like Newtonian billiard balls.
In Carl Whitaker’s therapeutic approach, it is essential that the therapist win the battle for this.
What is the "battle for structure"?
A structural therapist actively encourages and brings a family conflict into the therapy room.
What is an "enactment"?
A pattern of communication that emphasizes the maximization of difference between partners.
What is a "complementary pattern"?
In Solution-focused Family Therapy, the therapist supports the family in shifting the conversation from ________ to ________.
What is "Problem-talk" & "Solution-talk"?
The birth of a child with a disability may constitute a _______ stressor within a family.
What is a "horizontal" stressor?
According to Sue Johnson, of Emotionally-focused Family Therapy, what therapists should first try to help families do is to identify ________ ________ ________.
What are "negative interaction sequences"?
A therapeutic intervention that attempts to change the hierarchical arrangement between members of a subsystem.
What is "unbalancing"?
This is one of Albert Ellis’ A-B-C’s of dysfunctional behavior.
What are Activating event, or Beliefs, or Consequences?
In Minuchin's form of family therapy, this is how change happens.
What is changing the structure of the family?
In the life cycle, families with an adolescent must frequently adjust to and deal with _____ setting and _____ negotiation.
What are "LIMIT" setting & "ROLE" negotiation?
In Virginia Satir's Growth Model, these are 2 of the 4 styles of dysfunctional communication.
What are "blaming, placating, super-reasonable, irrelevant"?
According to Bowen, there are four common ways people manage anxiety. Name 2.
What are "conflict, dysfunction in one person, triangulation, & distance"?
Behavior Therapy is founded on the principle of __________.
What is "learning"?
The is the important and prominent theory that Emotionally-focused Therapy is based on.
What is Attachment Theory?