The two primary functions of the small intestine.
What are digestion and absorption?
A male client is recovering from small bowel resection. To relieve pain the physician prescribes morphine 50 mg IM Q6H. The nurse administers the medication at 0700. When would the patient's next dose be?
What is 1300 / 1:00pm?
True or False: IV fluid replacement and maintenance are not necessarily indicated for all patients with intestinal obstruction. Some patients only require bowel rest.
What is FALSE? IV fluid replacement and maintenance are indicated for ALL patients with bowel obstructions. A patient is NPO and they have an imbalance in their F&Es (potassium and sodium) as evidenced by vomiting and nasogastric suction.
Verification of NGT placement is by this diagnostic procedure.
What is x-ray?
Instructions for the patient status post SBO surgery.
What is to report any abdominal pain or distention, nausea, or vomiting, with or without constipation, because these symptoms might indicate recurrent obstruction?
Name two clinical manifestations of intestinal obstruction.
What are abdominal pain, vomiting, distension, and constipation?
A patient complains of gas pains and abdominal distention two days after a small bowel resection. This is the best nursing action to take.
A. Encourage the patient to ambulate.
B. Instill a mineral oil retention enema.
C. Administer the ordered IV morphine sulfate.
D. Offer the ordered suppository.
What is A. Encourage the patient to ambulate?
Name the expected IVF for a patient with SBO and dehyrdation.
What is NS with KCL or LR/D5LR with KCL?
True or False: Approximately 6 to 8 L of fluid enters the small intestine daily.
What is true?
The technique of placing a pillow over the abdomen and apply pressure when repositioning or coughing.
What is splinting?
True or False: The bowel sounds below the the area of obstruction are high pitched.
What is FALSE? The bowel sounds are high pitched above the area of obstruction and are usually absent below the area of obstruction.
The nurse caring for a client with a small bowel obstruction would plan to implement this nursing intervention first.
A. Administering pain medication.
B. Obtaining a blood sample for laboratory studies.
C. Preparing to insert a Foley.
D. Administering I.V. fluids.
What is D. administering I.V. fluids?
This is the most reliable indicator of fluid balance.
What is weight?
The nurse should place the client's head of bed in which position to receive bolus feed or continuous feeding via NGT during and for at least 30 minutes after.
A. supine.
B. right side-lying.
C. semi-Fowler's.
D. upright in a bedside chair. E. Both C and D, semi-Foweler's and upright in a bedside chair.
What is E? Both C and D, semi-Foweler's and upright in a bedside chair?
True or False: Teaching the patient to take laxatives routinely is safe. Laxatives increase abdominal muscle tone and allow for ease of stool passage.
What is FALSE? Teach patients not to routinely take laxatives because they decrease abdominal muscle tone and contribute to an atonic colon.
As the small bowel dilates, it's blood flow may become compromised and may lead to this condition.
What is necrosis or strangulation?
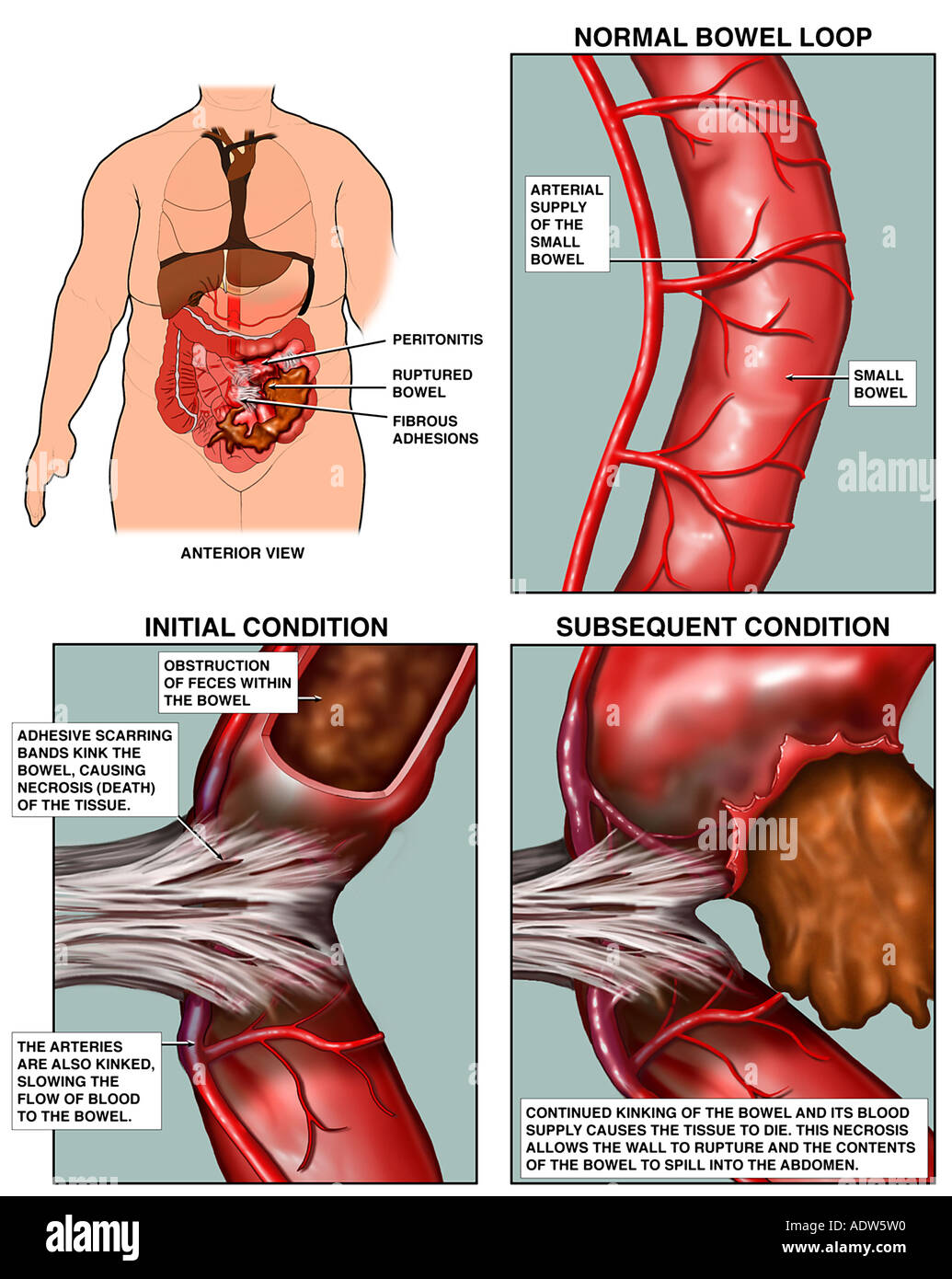
A nurse is assessing a client who has been admitted with a diagnosis of an obstruction in the small intestine. The nurse should assess the client for this. Select all that apply.
A. projectile vomiting
B. diarrhea
C. rapid onset of dehydration
D. increased/high pitched bowel sounds
What is A. projectile vomiting, C. rapid onset of dehydration, and D. increased/high pitched bowel sounds?
Other than weight, name three measures of fluid status.
What are urine output, skin turgor, and mucous membranes?
The normal pH range for NGT aspirate is this.
What is 1-5.5 / less than 5?
This is position of comfort to promote increased peristalsis with non-mechanical obstruction.
What is semi-Fowler's position which helps to alleviate the pressure of abdominal distention of the chest and promotes thoracic excursion to facilitate breathing?
Name two mechanical causes for a bowel obstruction.
What are adhesions, intussusception, volvulus, herniation, and neoplasms?
The nurse is caring for an 82-year-old patient admitted with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The patient has an abdominal mass, and a bowel obstruction is suspected. The nurse auscultating the abdomen listens for this type of bowel sounds that are consistent with the patient's clinical picture.
a. Low-pitched and rumbling above the area of obstruction.
b. High-pitched and hypoactive below the area of obstruction.
c. Low-pitched and hyperactive below the area of obstruction.
d. High-pitched and hyperactive above the area of obstruction.
What is b. High-pitched and hypoactive below the area of obstruction?
This nutrient may be indicated in strangulated obstruction because of blood loss into the bowel or peritoneal cavity.
What is blood?
Select the following labs that would be consistent with a bowel obstruction? Select all that apply.
A. decreased WBC
B. elevated BUN
C. elevated creatinine
D. decreased hemoglobin
What is B. elevated BUN, and C. elevated creatinine?
*There would be an increase in WBC and hemoglobin especially if strangulation is present.
True or False: Both types of obstructions (mechanical and non-mechanical), food or oral fluids aggravate the GI tract and increase pain. Teach the patient NPO and bowel rest.
What is TRUE?