A 67-year-old woman is evaluated for left knee pain of insidious onset over the past 1-2 years. She remains active and exercises daily by walking, swimming, or biking. Her left knee swells after long walks and hikes. She also describes popping of her left knee. Results of the Thessaly test and McMurray test in the left knee suggest a meniscal tear. Lower extremity strength is normal.
A. Arthroscopic meniscal repair
B. Immobilization of the left knee
C. MRI of the knee
D. PT
PT
Degenerative meniscal tear can be associated with catching, locking and inability to extend the knee. Can be managed with PT and strengthening.
During a health visit, the mom of a 3 yo comments that her daughter is scratching her head. on exam, numerous nits are identified near the base of her hair shafts, predominately along the nape of her neck and behind her ears. She is also noted to have b/l posterior cervical LAD. Which of the following statements is characteristic of this condition?
A. Transmission is direct "head to head" with infected ppl
B. OTC agents are no longer recommended for initial treatment.
C. Infestation with lice is more common in AA kids
D. It is more common among lower socioeconomic groups who have limited accesses to personal hygiene.
E. After hatching, nits/eggs are easily removed from the hair shaft.
Transmission is direct "head to head" with infected ppl
A 5 year old comes for a well exam. Mom reports concerns about speech. He began stuttering at 9 months of ago but not outgrown it yet. It makes mom anxious. He is afraid to talk at school. Exam and hearing ar normal. What is the most appropriate intervention?
A. Reassurance
B. Start SSRI
C. Refer to neuro
D. Refer to developmental peds
E. Referral to speech
Referral to speech
if more than 4-8 weeks needs seen and also associated with anxiety and avoidance of things.
A 12-year-old boy is found to be colonized with MRSA after he and many other family members were treated for MRSA infections. Which of the following is more likely to decrease the risk of similar infections in the future?
A. Low-dose once daily TMP/SMX x 14 days
B. Topical Mupirocin to anterior nares BID x 5 days
C. Topical Gentamicin to the anterior nares and fingernails BID x 10 days
D. Topical mupirocin to the fingernails BID x 14 days
E. Low-dose daily Doxy for 5 days.
Topical Mupirocin to anterior nares BID x 5 days
A 32 weeks old male born via Cs after mom came to the ED for vaginal bleeding d/t abruption. in NICU, kid has multiple dysmorphic features. Prelim dx of T18 is made. chromosomal studies are done but awaiting confirmation. Which of the following findings is most likely to be identified?
A. Overlapping fingers and hypoplastic nails
B. Hypoplastic and fused cervical vertebrae
C. Polydactyly
D. Absent radius and thumb
E. Phocomelia
Overlapping fingers and hypoplastic nails
Hypoplastic/fused cervical vert= Klippel Feil
Polydactyly = T13
Absent radius/thumb= Holt oram
Phocomelia= previous seen with thalidomide
A 17 yo male has a concussion 3 wk ago. he was removed from the game. has mild HA, feels confused and dazed after the injury. no LOC/sz/v. Ct was normal. Symptoms resolved afer 2 days and is asx. Neg PMHx. on no meds. Exam is normal including neuro. which if the following most appropriate management?
A. Permit light aerobic but prohibit contact pending completion of return to play protocol.
B. Allow to go to FB and full contact drills, since asx.
C. Prohibit any physical activity for 3 more weeks.
D. Restrict participation until repeat CT is done.
E. Advise he refrain from FB the rest of the season but can play next year.
. Permit light aerobic but prohibit contact pending completion of return to play protocol.
A 65-year-old woman is evaluated for a mole beneath the right eye that has been present for several months but appears to be growing.
Skin findings are shown.
Which of the following is the likely diagnosis?
A. Malignant Melanoma
B. Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
C. Seborrheic keratosis
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
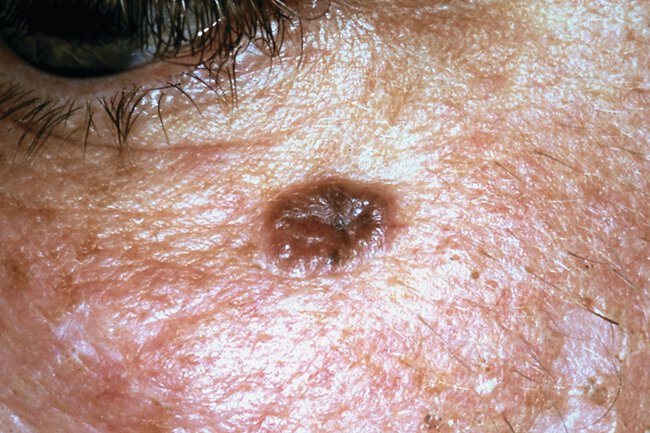
Pigmented basal cell carcinoma
can be pearly or translucent with arborizing telangiectasias.
can have central depression or ulceration
can have rolled waxy border
Can have pigment and can be dark
A 14 year old girl who is overweight presents to clinic with worsening headaches. She is on tetracycline for acne. HA are generalized. she has papilledema and b/l decreased visual acuity. A MRI/MRA/MRV is normal. Tap is done with an opening pressure of 54 cm h20. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Optic glioma
B. Non communicated hydrocephalus
C. Chiari malformation
D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
E. Pilocytic astrocytoma
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
A 39-year-old man is seen in a follow-up visit for an 8-week history of intermittent and fluctuating fevers that began after returning from Guyana 2 months ago. He also reports fatigue; muscle, bone, and joint aches; and depression. During his trip, he ate and slept in rural villages. He was adherent to his tafenoquine malaria prophylaxis.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.5 °C (99.5 °F); other vital signs are normal. Scattered lymphadenopathy is noted. The liver edge is palpable 2 cm below the rib cage. Low back discomfort is elicited with flexion and distension. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Hct 33%, WBC 3,400, ALP 167, ALT 71, AST 46. BCx neg, CXR is normal. abd u/s shows HSM.
which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Brucellosis
B. Coxiella infection = Q fever
C. Histoplasmosis
D. Malaria
Brucellosis- intermittent fever with periods of remission for weeks and may persist for months.
associated with HSM, arthralgia and depression
You are asked to see a male infant in the newborn nursey for follow up recs. He is term. He is well. He is going home. Parents are looking at a birthmark on his face. He has a port wine stain along the CN5 distribution of the right side of the face. Which is the most important risk/complication to discuss with the family?
A. Hypersplenism
B. Possible growth issues and need for steroids of eyelid
C. Tethered cord
D. Glaucoma
E. Heart failure
Glaucoma
A 6-year-old boy has 4 weeks of right knee pain. no trauma. getting worse and now limps. no fever. no illness. developed normally. Exam = ht/wt in 10th % since 2 months of age. no deformity, swelling, erythema, bruising. has limited hip internal rotation and abduction. Hip film shows misshapen and ratty appearance of the femoral head. WBC and ESR are nml. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Legg Calve Perthes dz
B. SCFE
C. Transient synovitis
D. Septic joint
E. Growing pains
Legg Calve Perthes dz- interruption of blood flow to capital femoral head with partial or incomplete avascular necrosis. boys 3-12 yoa. c/o hip or knee pain/limp.
An 18-year-old college kid comes for vesicles noted on sun exposed areas, which are present episodically for 7 years. he used Alcohol to excess for many years. no meds. not seen a doc in some time. Your eval confirms porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT). Which of the following other diagnoses should you also consider?
A. Paraneoplastic pemphigus
B. MEN syndrome
C. Acanthosis nigricans
D. Hep C
E. Hep B
Hep C
A 4-year-old boy w hx of intractable epilepsy presents to the ED for AMS x 1 day. He is difficult to awaken and only woke to take meds last night. His AED were recently changed. initial neuro exam, he opens eyes and withdraws his extremities to painful stimulation. His work up shows mild elevated of LFT and NH3 that is 3 x more then normal. A CT is normal. Which of the following meds is implicated in this presentation?
A. Carbamazepine
B. Valproic Acid
C. Clobazam
D. Levetiracetam
E. Gabapentin
Valproic Acid
A 2-year-old girl presents with a 1-day hx of rash and low-grade fever. On exam, there is an erythematous butterfly rash/malar with relative circumoral sparing, associated with a flat, erythematous, blancing, "lace-like" rash on the upper extremities. Although the child is treated only symptomatically, her mother, who is 19 wk gestation, is directed to inform her OB of the rash. Which of the following best describes findings on prenatal U/s consistent with congenital infection caused by the same organism responsible for this patient's rash?
A. Ascites and pleural effusions
B. Renal dysgenesis
C. Abdominal wall defect associated with gastroschisis
D. Hypoplastic limbs
E. Ventriculomegaly of the brain
Ascites and pleural effusions
What is this? 5ths disease/erythema infectiosum/Parvo B19
can cause anemia and hydrops
A 5 year old boy with hx of premature closure of b/l coronal sutures presents for exam. findings include: normal intelligence, hands/feet, midface hypoplasia and proptosis. What syndrome does this kid most likely have?
A. Crouzon syndrome
B. Apert syndrome
C. Carpenter syndrome
D. Pfeiffer syndrome
E. Sotos syndrome
Crouzon syndrome= premature closure of coronal sutures= brachycephaly. also midface hypoplasia, normal intelligence, hands and feet.
A 57-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-month history of neck pain and stiffness accompanied by unsteadiness on his feet, especially while climbing up or down stairs. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Muscle strength is 4/5 for both hip flexors and arm flexors. Hyperreflexia and clonus are present in the lower extremities, as are bilateral upgoing extensor reflexes in the toes. Diminished reflexes are present in the upper extremities. Forward flexion of the neck produces electric shock–like pain that radiates from the neck to the arm. which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Cervical myelopathy
B. Cervical radiculopathy
c. Cervical strain
D. Myofascial Pain
E. Whiplash injury
Cervical myelopathy= degeneration of cervical spine from spondylosis. has combined upper and lower motor neuron findings.
Cervical compression = lower motor neuron signs with weakness in arms/hands and upper motor weakness in legs with increased tone, hyperreflexia and clonus, and upgoing extensor reflexes.
A 78-year-old woman is evaluated for a rapidly growing, painful nodule on the right dorsal hand that appeared 6 weeks ago. Medical history is unremarkable, and she takes no medications.
Skin findings are shown.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Keratoacanthoma
D. Pyoderma gangrenosum
E. sporotrichosis
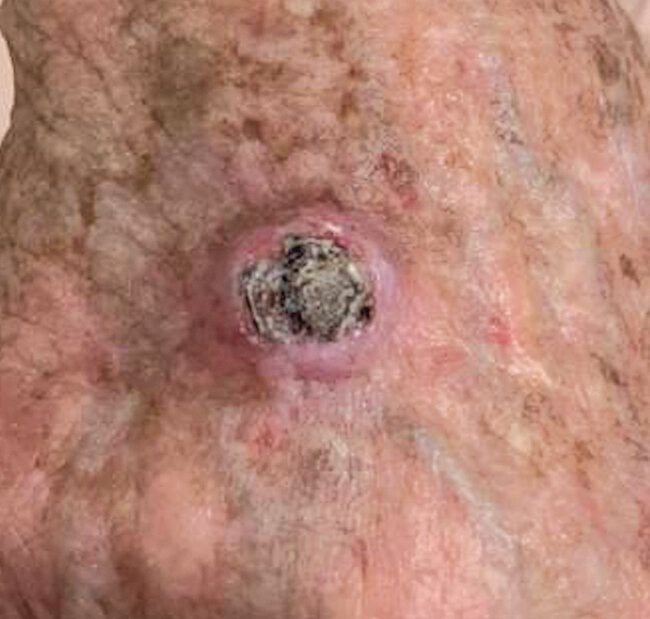
Keratoacanthomas- pink nodule with keratin filled center ("volcaniform” appearance)
rapid onset
painful
squamous cell carcinoma variant
A 67-year-old man comes to the office for a follow-up evaluation of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (MS). He was diagnosed with relapsing-remitting MS 20 years ago and had his last relapse 6 years ago. His disease converted to a secondary progressive course 4 years ago, and 2.5 years ago, he became nonambulatory. His only medication is interferon-beta 1b.
On physical examination, all vital signs are normal. Marked spasticity is noted in the lower extremities. Muscle strength is grade 1/5 with hip and knee flexion, bilaterally, and grade 2/5 with ankle dorsiflexion, bilaterally. An indwelling suprapubic catheter is noted.
A recent MRI of the brain shows multiple lesions consistent with MS that are unchanged from 2 years ago; gadolinium does not enhance the lesions.
which of the following changes to the patient's immunomodulatory therapy is most appropriate?
A. Administer IV glucocorticoids
B. D/c Interferon beta 1 b
C. Substitute natalizumab for interferon beta - 1 b
D. Substitute ocrelizumab for interferon beta - 1 b
D/c Interferon beta 1 b
d/c Disease modifying agents if secondary progressive MS who are non-ambulatory for more than 2 years and no relapsing activity during that time.
A 55-year-old man is evaluated in the ICU for low blood pressure requiring vasopressor support. He was hospitalized 3 days ago with a 3-day history of fever, headache, and myalgia. He owns a dairy farm in rural Arkansas and drinks unpasteurized milk. He is an active outdoorsman. On admission to the hospital, temperature was 39.2 °C (102.6 °F), pulse rate was 120/min, and other vital signs were normal. No lymphadenopathy or skin lesions were noted. Empiric doxycycline was initiated on admission; he takes no other medications.
On physical examination in the ICU, temperature is 38.9 °C (102 °F), blood pressure is 90/64 mm Hg, pulse rate is 128/min, and respiration rate is 24/min. The remainder of the physical examination is unchanged from admission.
labs: WBC 3400 admit day and 1200 now; Platelets 110,000 admit and 65k now, ALT admit 79 and now 202 and AST admit 62 and now 124. BCx are neg
Which is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Brucellosis
B. Ehrlichiosis
C. Heartland virus infection
D. RMSF
Heartland virus infection - Bandavirus is transmitted by Lone Star tick
tick bite, nonspecific sx
lack of response to doxy.
treatment is supportive
A 1-day old male is noted to have difficulty feeding due to micrognathia. A CXR is obtained from possible aspiration after an episode of choking during attempts to feed, reveals an absent thymus. soon after the xray, he is noted to have a T/C seizure. He is transferred to the NICU and additional evaluation includes a EKG. Which of the followin findings is most likely to be identified upon review of the EKG?
A. Prolonged Qtc interval
B. ST segment elevation
C. Peaked T waves
D. Prolonged PR interval
E. 2nd degree Mobitz type 1 block (Wenckebach)
Prolonged Qtc interval d/t hypocalcemia
(22q11.2 deletion= DiGeorge)
A 68-year-old man is seen for a preoperative medical evaluation before elective cervical laminectomy for chronic radicular pain without neurologic deficits. Medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia and hypertension. He had a cerebrovascular accident 3 weeks ago due to small-vessel atherosclerosis. Medications are rosuvastatin, lisinopril, atenolol, aspirin, and dipyridamole.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 31. Neurologic examination is normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation regarding surgery?
A. Avoid it
B. Delay for 1 month
C. Delay for 9 months
D. Proceed now
Delay for 9 month- elective surgery should be delayed at least 6 mo after stroke and as long as 9 months after stroke or TIA

Thought to have chix pox x 15 days. getting more and itchy. new lesions are 2-4 mm and round, red/brown macular/papular. old lesions are crusted, vesicular and necrotic. on trunk, symmetrical and flexor surfaces. What is the first line treatment?
A. EES
B. Topical steroids
C. Systemic steroids
D. Antihistamines
E. IVIg
EES- 1-2 months
what is it?
PLEVA= pityrasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta - unknown cause
keys= duration of sx, new successive crops of lesions
A parent of a 3 year old girl is concerned about DD. Parents report delays early in infancy. She only recently began to walk with a reverse walker. She has no speech and communicates with gestures/vocalizations. She is happy and easily excitable. On exam her height and weight is 25th % and HC is 3%. She ambulates with support and has a wide based gait.
Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this child's features?
A. Angelman syndrome
B. Fragile X
C. Prader Willi
D. Williams
E. Rett
Angelman syndrome
remember small head, severe ID, sz, wide based gait, happy
Maternally acquired chromosome 15
A 10 year old boy with a 4 day hx of malaise, HA, and myalgias has multiple erythematous macules and petechaie, noted on ankles, wrists, palms, and soles and also on proximal trunk and extremities. Additional c/o photophobia, n/v. Which of the following is also identified in patients with similar signs and symptoms?
A. Hypercalcemia
B. Hyponatremia
C. Gross hematuria
D. Dec C3 and C4
E. Hypocalcemia
what does this person have?
RMSF caused by Rickettsia rickettsia
Labs: low Hb, Plat, inc LFT, Low Na
High Ca in granulomatous dz
hematuria- uti/kidney infection
low complements- immune complex dz
Low Ca- TSS and sepsis
A 3-year-old boy is noted to have coarse facial features, a widened nasal bridge, and flattened midface. HSM and a large umbilical hernia are identified on abdominal exam. Which of the following radiographic findings would be the most suggestive of a diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) type 1/Hurler syndrome in this patient?
A. Fibrous dysplasia of the long bones
B. Dysostosis multiplex in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae
C. Pelvic and calcaneal apophysitis
D. Defects of the pars interarticularis in the Lumbar spine
E. Sacral Agenesis
Dysostosis multiplex in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae
Fibrous dysplasia of the long bones= McCune Albright
Apophysitis is common in overuse injuries
Defects of the pars= spondylolysis
Sacral Agenesis= moms with DM