Laboratory test that measures the amount of cross-linked fibrin fragments as clots break down.
What is d-dimer?
This medication is used for induction and to maintain general anesthesia. It has no pain management properties. It must be avoided in patients allergic to eggs.
What is Diprovan or propofol?
When prioritizing care the nurse should implement which first action?
1. Evaluate am labs on a client who is prescribed an potassium sparing diuretic.
2. Administer sliding scale insulin to a client with a blood glucose level of >350.
3. Report a hemoglobin level of 12.5 g/dL to the health care provider.
4. Admit a client who is scheduled for an elective hip replacement surgery tomorrow.
What is answer #2.
The name of this finding.
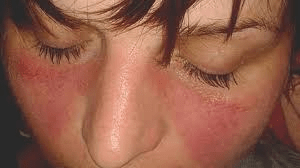
What is butterfly rash?
The only fluid that can be hung with blood administration.
What is normal saline?
Stimulates the inflammatory response and offers protection against various types of infection and foreign bodies.
What is a WBC?
The nurse cannot provide any new information that remains unclear to the patient but may may reinforce any information before the patient signs this. The nurse witnesses the signature.
What is surgical consent?
The nurse is caring for a client who is six hours postoperative following a thoracotomy. Which intervention noted in the plan of care does the nurse prioritize in order to promote circulation?
1. Remove the Foley when the patient is post-op day one.
2. Ensure the bowel sounds are present in all four quads.
3. Assist the client to turn, cough, and deep breath.
4. Assist the client with early ambulation.
What is assist the client with early ambulation?
The name of this type of lupus that only affects the skin.
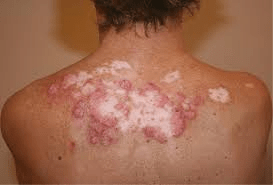
What is discoid or erythematous or cutaneous lupus.
The most common type of anemia due to inadequate intake and most common in pediatric and pregnant women.
What is iron-deficiency?
HIV targets these cells. Used to test for viral load of the disease.
What are CD4-T lymphocytes?
List five risk factors for surgical complications.
What are obstructive sleep apnea, pregnancy, respiratory disease, cardiac disease, DM, liver disease, kidney disease, immunocompromise, coagulation deficits, malnutrition, high BMI, substance use, genetic history of problems with anesthesia, allergies, older age with co-comorbidities.
Which of the following clients must be checked first?
1. The client who has been in the hospital for three days after diagnosis of COPD exacerbation.
2. The post-MI client who has been stable for two days.
3. The client who just came out of the operating room after having an agiocatheterization.
4. The client who has been in the hosptial for four days for asthma with a oxygen sat of 98%.
What is number 3?
Trauma, infection, certain medications, exposure to IV light, and stress.
What are triggers to lupus exacerbations?
The name of the medication that is given to replenish iron in the blood and iron stores taken between meals that may cause black tarry stools.
What is ferrous sulfate?
Repeated measurements are obtained because of dietary intake on results. Consistent elevation above 6.5mg/dL is associated with gout.
What is serum uric acid?
What are activity, consciousness, respiration, oxygen saturation, and circulation.
The nurse is employed in the ED. You are triaging patient's today. The nurse should assign priority to which client?
1. A client complaining of muscle aches, a headache, and general malaise.
2. A client who twisted their ankle when she fell rollerblading.
3. A client with a minor laceration to the index finger while cutting an eggplant.
4. A client with chest pain who states that she just ate hot wings that were made with really spice sauce.
What is number 4?
Clients with trauma, chest pain, respiratory distress, limb amputation, neuroloical deficits, or chemical splashes or burns are priority 1.
Medication is use for patients with Lupus that suppress the immune system and two nursing considerations with this medication.
What is methotrexate. Monitor for toxic effects and infections. It can cause bone marrow suppression and can increase liver enzymes.
The two most common blood labs that are checked six weeks after the initiation of treatment and are used to monitor response over time.
HGB and HCT.
These two tests are elevated in a response to inflammation or infection in the body.
What are Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive Protein.
The time prior to surgery when the team review the patient identity, procedure, and surgical site before the start of the procedure.
What is a "time-out"?
You are reviewing a CBC for a patient who has been admitted for knee arthroscopy. Which value is most important to report to the surgeon before the onset of surgery.
1. Hematocrit of 33%.
2. Hemoglobin level of 10.9 g/dL.
3. Platelet count of 426,000/mm3
4. White blood cell cont of 16,000 K/uL
What is number 4.
The CDC guidelines for prevention of surgical site infections indicate that surgery should be postponed if there is evidence of pre-exisiting infection as noted by elevated WBC prior to surgery.
The nurse is discussing autoimmune disorders with a new nurse. Which signs and symptoms are shared by rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematous (SLE).
1. Nodules in the subcutaneous layer and bone deformity.
2. Renal involvement and pleural effusion.
3. Joint stiffness and pain.
4. Raynaud's phenomenon and skin rash.
What is number 3.
The persistent eating of a substance not normally considered to be food (nonnuritent substances) such as soil or chalk for at lease one month which can limit the amoutn of healthy food choices the client makes.
What is pica?