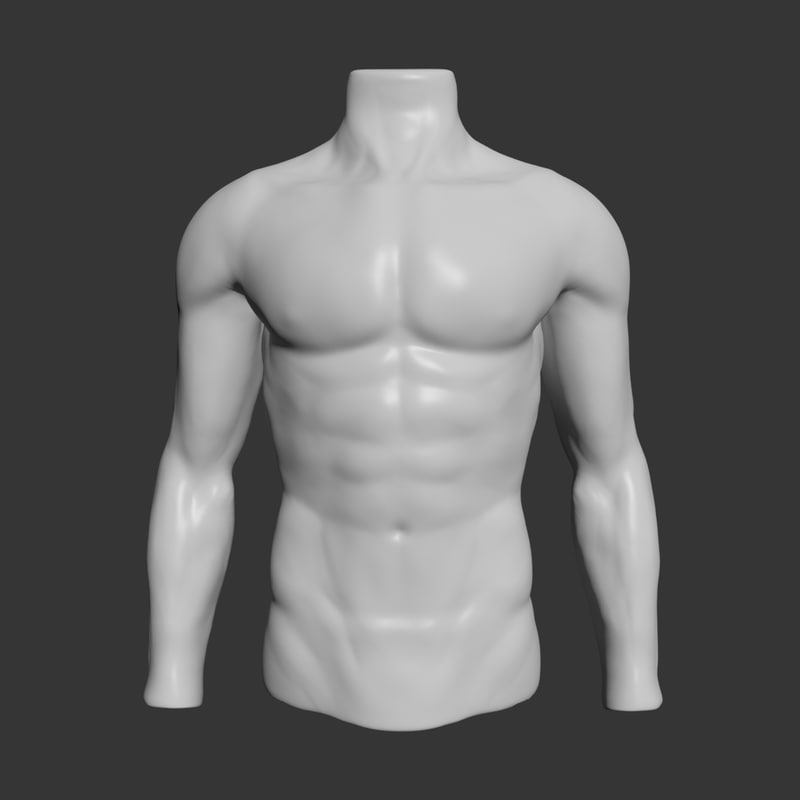
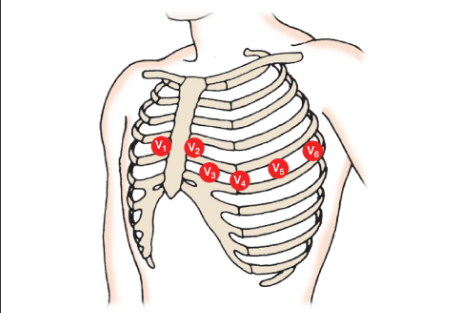
Where on this patient would you place stickers for a 12-lead EKG?

The HCT calls you into your patient's room and states their ostomy bag is about to explode. You find that it is filled with gas. What steps would you take to trouble shoot?
Burp it
Patient transfers from the ICU to your floor with an indwelling catheter. The ICU nurse last documented necessity as sustained instability. What is your next step?
Remove foley catheter per protocol
How often do you change continuous primary tubing?
96 Hours
A 78yr old female is admitted with sepsis after hernia repair with subsequent tracheostomy and PEG placement at an outlying facility. The unit secretary calls you and says the alarm is going off on the telemetry monitor, stating the pulse oximetry is reading 15%. You quickly run into the patient’s room and find the patient unresponsive with her trach lying on her chest. You yell for some help and discover the patient does not have a pulse, so you initiate CPR immediately. Who do you call?
Code blue 5-2345
Your patient has a tracheostomy. In case of an emergency, what 3 things do you need to have at bedside?
1. Suction
2. Ambu Bag
3. Two Trachs
Your patient has their NGT connected to continuous wall suction. When you assess your patient, they have gastric contents leaking out of blue vent port.
What steps would you take to trouble shoot?
Flush the blue port with air and ensure it is vertical in bed
You open your patient's chart and receive this alert.
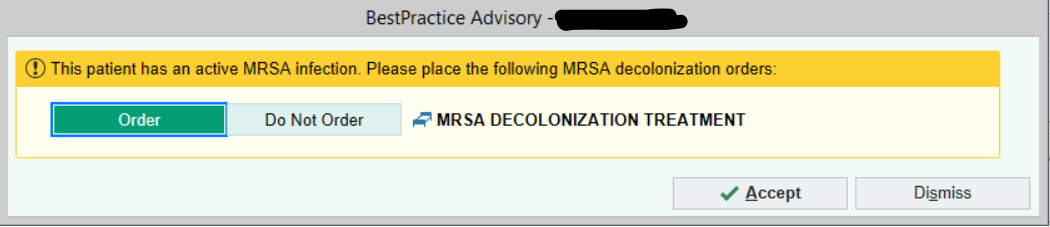
What is your next best step?
Order, accept, and SIGN!
How often do you document on non-violent restraints?
Every 2 hours
You are assigned a 63yr old female admitted for kidney transplant. During bedside report, the patient states she feels like her heart is beating “out of her chest.” The patient is in no other distress, alert and oriented x4, and moves all extremities. You ask the charge nurse to check the telemetry monitor, and she states the patient is in atrial fibrillation.
You obtain vital signs as below: VS: Temp 98.6F, BP 120/65, HR 150, RR 18, SPO2 94% on 2L NC
Who do you call?
A RRT 5-2345
When is a lap belt not considered to be a restraint?
Your patient, Mickey Dee, is admitted for fluid overload due to missing his dialysis appointments for the last week. They came back from dialysis and their vascath dressing looks like this.

What steps would you take to trouble shoot?
Change the dressing
63-year-old male admitted to 10 Tower 3 days ago for dyspnea secondary to COPD exacerbation requiring supplemental oxygen and dexamethasone. Can we D/C tele?
PMH: appendectomy (‘98), liver ligation (‘09), influenza pneumonia (‘17)
Current Trends:
VS: HR 80-110, BP 100-140/60-85, SaO2 89-95%
Telemetry shows NSR, Sinus Tachycardia
Receiving 2L NC
MIVF NS @ 60 mL/hr
K+ 3.3, Mg 1.8
Discontinue telemetry per protocol
On admission
Every Shift
With any changes
A 62yr old male is admitted with infected right femoral/popliteal artery bypass. The patient goes to OR for debridement at 0900am. At 1200, the patient returns from the OR. You enter the room and find the patient has a pool of blood under his right leg. You check VS and patient is hemodynamically stable. You apply pressure to the site and call the physician. The physician states to monitor the patient and notify them if the dressing becomes fully saturated. After 30 minutes, the dressing is completely saturated. You call the physician, and he says to continue to monitor. What is your next step? Who do you call?
Call rounding nurse 6-0666
Please give an example of SBAR
What is the difference between TPN and PPN?
central v peripheral, short term v long term, tubing change, infection risk
You are administering 2100 medications to Michael Mouse through his PEG tube. You flush the PEG with 30 mLs of tap water prior to medications and you meet resistance. What steps would you take to trouble shoot?
Contact provider to order viokace (pancreatic enzymes)
You got report that the previous nurse removed your patients foley at 0000. They performed an intermittent catheterization at 0600. It is now 1200 and the patient still has not voided. You perform a bladder scan, and it shows 551 mLs in the bladder. What is your next step?
Intermittent catheter
Nancy Drew is receiving continuous tube feeding through a Dobhoff tube. You gave meds at 9am, how long does the head of bed need to remain elevated?
Always!
Your patient has a JP drain in their abdomen s/p colectomy. The previous nurse reports to you they have had serosanguinous drainage 75ml over the last 8 hours. When you go to assess your patient, the JP now has frank blood. You empty the drain, and it no longer will hold compression and fills up again with blood. The patient is hemodynamically stable. Who do you call?
The provider
Please give an example of SBAR to the provider
What are the four instances that you need a witness for a PCA pump?
Initiation, Dose Change, Bag/Syringe Change, Change of Caregiver
After helping your patient ambulate to the bathroom you hear continuous bubbling from their chest tube system. What steps would you take to trouble shoot?
Assess from the patient to the system
You are assigned a patient with known, persistent bradycardia (HR 48) at baseline, and the low heart rate telemetry alarm is continuously going off. What is your next step?
Decrease the low heart rate alarm setting to 43 and continue to monitor the patient
How often do you change an inner cannula on an established trach (greater than 7 days)?
Every 24 hours
You are transporting a patient to CT who has a chest tube s/p thoracotomy. During transport, the chest tube gets caught under the wheel of the bed and the chest tube dislodges from the chest cavity. Who do you call?
Call a RRT 5-2345