Muscular and ______ systems work together to provide form, support, stability, and movement.
Skeletal
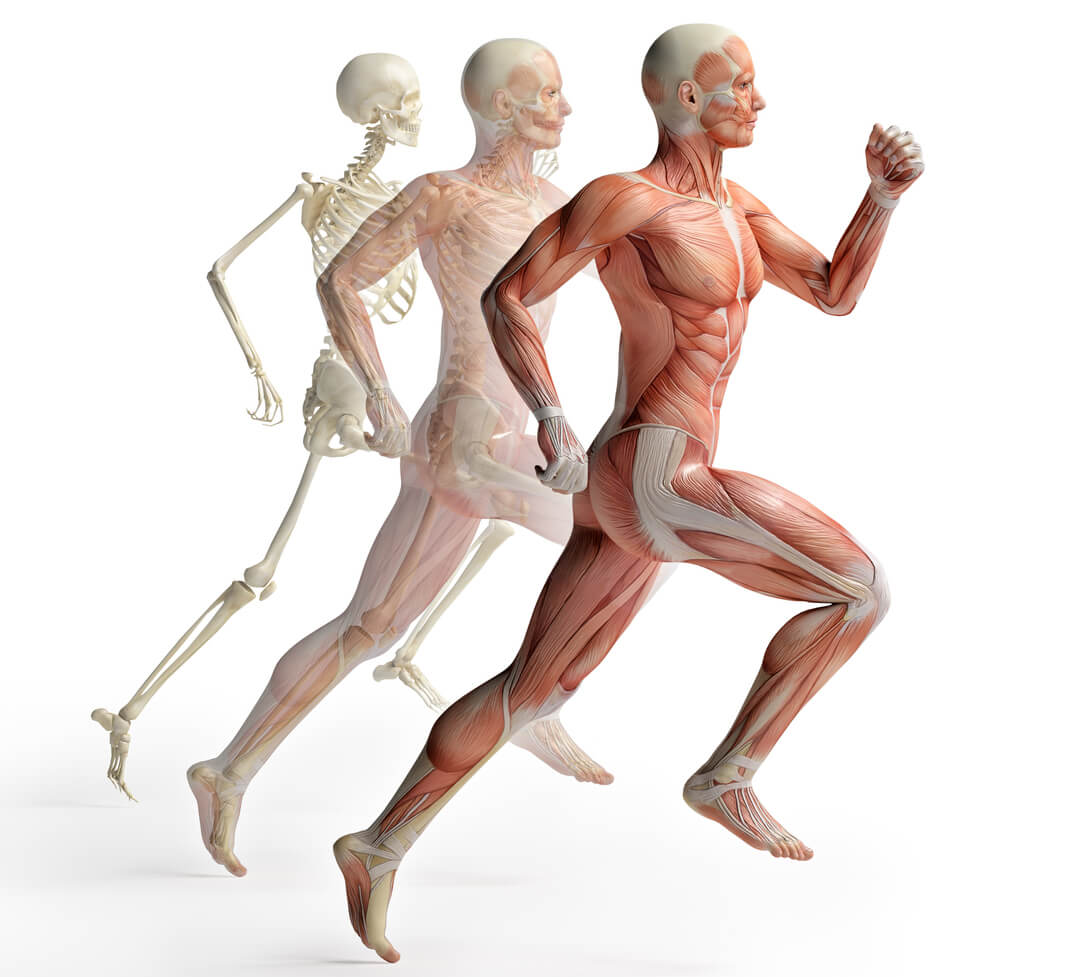

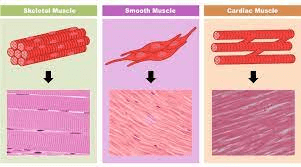
How many types of muscle are there? Name them.
3 muscle types. Skeletal, Smooth, Myocardial.
What is muscle innervation?
What does R-I-C-E stand for (concerning treatment of muscles)
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
Muscul/o, my/o, myos/o
Muscles
The muscular and skeletal systems are sometimes referred to jointly as the ______ ______. The body has more than ____ muscles, making up about 40-45% of the body's weight.
Musculoskeletal system.
600
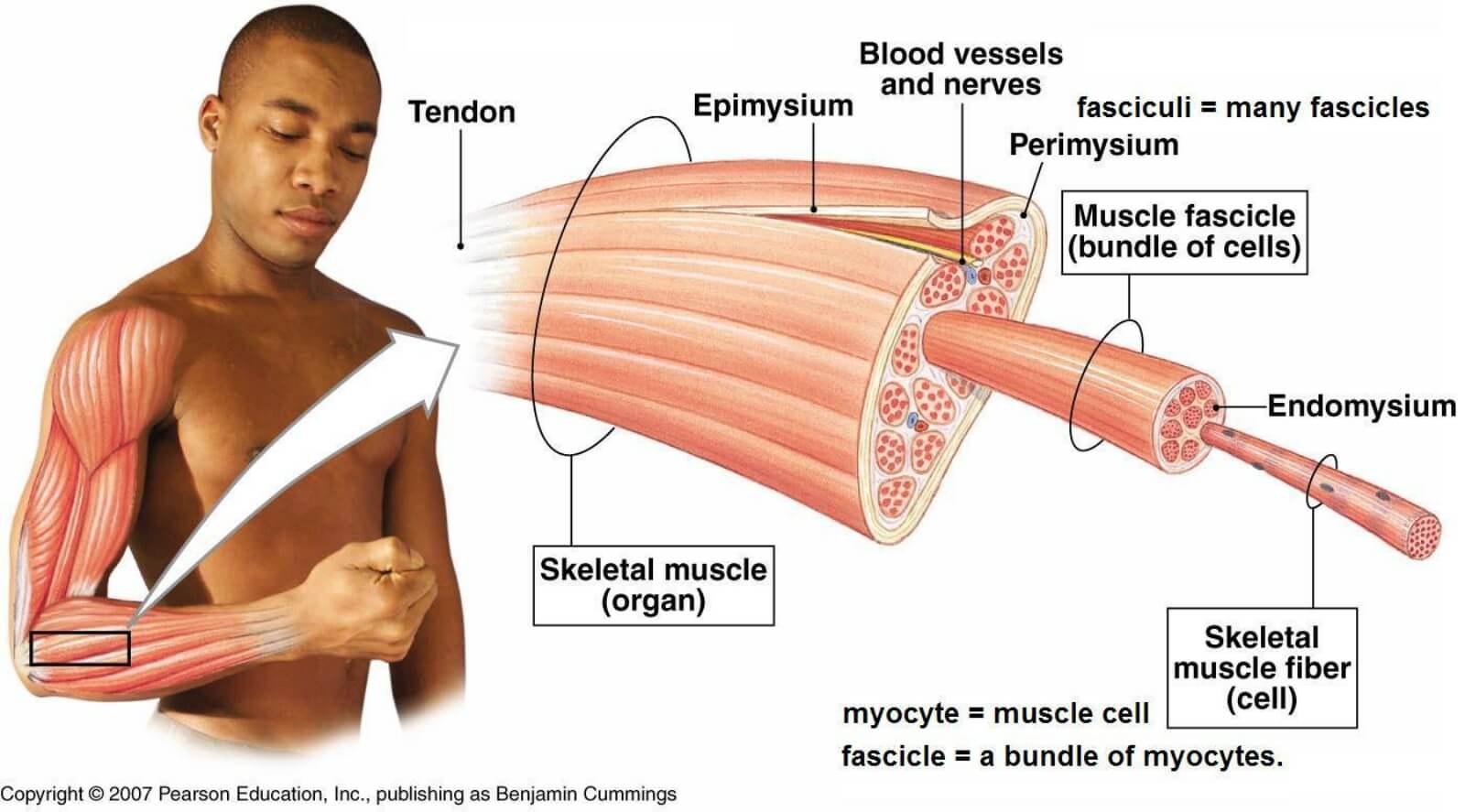
This muscle type is voluntary, striated, and attaches to bones to make body motions possible.
Skeletal Muscle

Muscles are arranged in _______ muscle pairs, meaning working in opposition of each other. When one muscle of the pair contracts, the other relaxes.
________ is the tightening of a muscle- becoming shorter, thicker, and causing the belly/center to enlarge.
________ occurs when muscle returns to original form, becoming longer & thinner.
Antagonistic muscle pairs, Contraction, relaxation

Muscles can be named according to their: Origin, Insertion, Action, Location, Fiber direction, Number of divisions, or size and shape. Define origin and insertion.
Origin= where the muscle begins, and it is located nearest midline of the body or on a less movable part of the body. (origin is less movable attachement)
Insertion=where the muscle ends by attaching to bone or tendon. (more movable attachment and farthest point from midline of body)
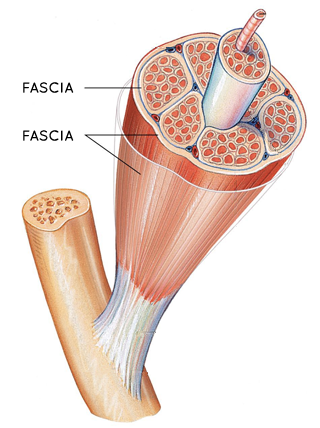
fasci/o
Fascia
A band of connective tissue that envelops, separates, or binds together muscles or muscle groups. Flexible to allow muscle movements.

The long, slender cells that make up muscles are called _____ ____.
Muscle Fibers
This type of muscle, also known as visceral muscle, is located in the walls of most internal organs, including digestive tract, blood vessels, and glands. It is involuntary and unstriated,
Smooth Muscle

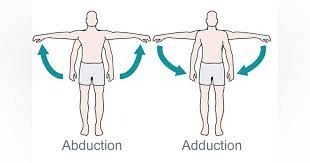
Abduction is movement of a limb ______ midline of the body.
Adduction is movement of a limb ______ midline of the body.
_____ means decreasing the angle between two bones by bending limb at joint.
_____ means increasing the angle between two bones or straightening out of limb.
Abduction= away from Flexion=decreasing the angle
Adduction= toward Extension=increasing the angle
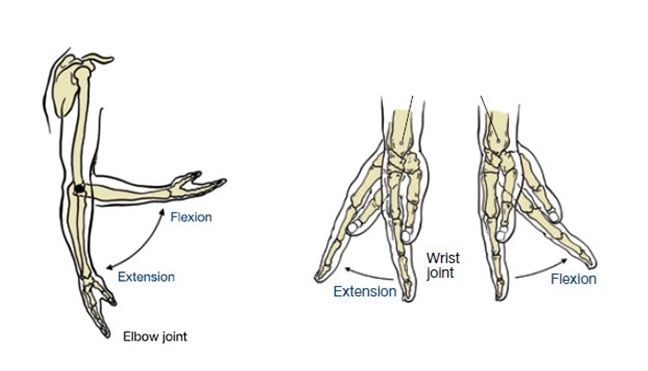
What is the difference/What happened during a sprain, strain, and shin splint?
Sprain- Injury to a joint, due to wrenching or tearing of a ligament.
Strain- Injury to overuse stretching or tearing of muscle or tendon attachment.
Shin splint- Injury when a muscle tears away from the tibia.
fibr/o
Fibrous tissue, fiber
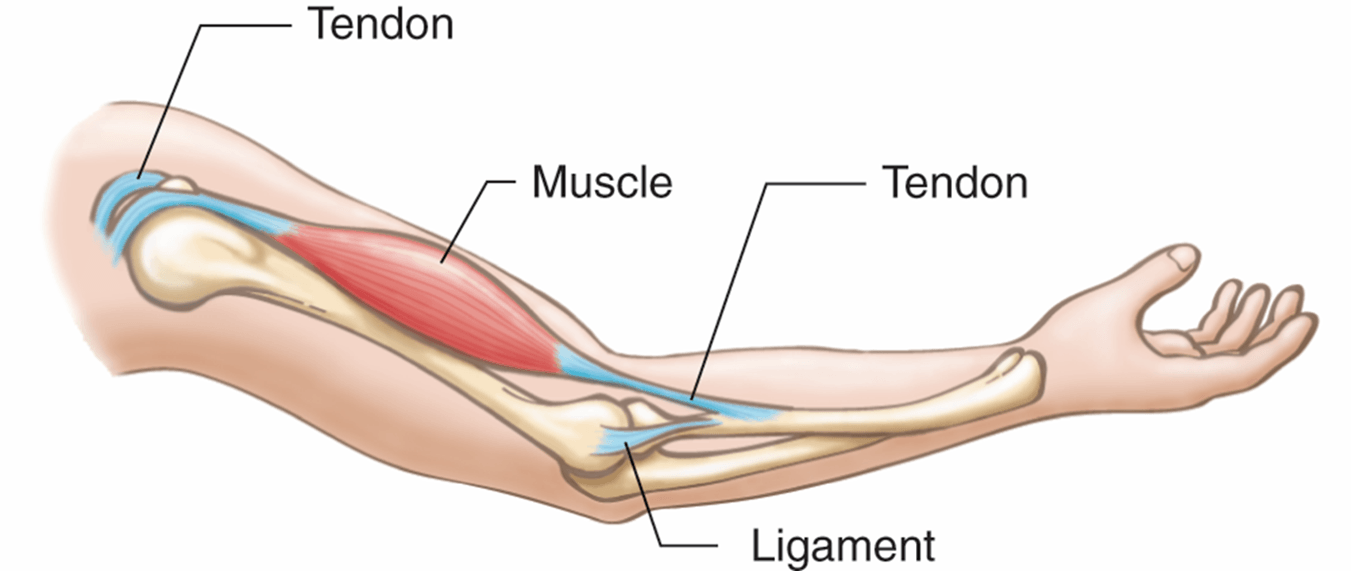
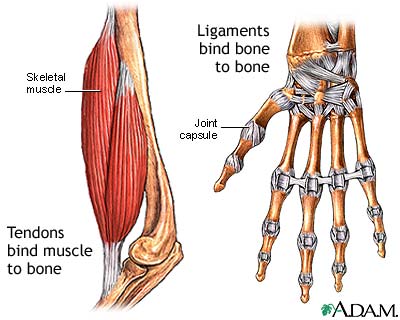
These are narrow bands of nonelastic, dense, fibrous connective tissue that attach muscles to bones.
Tendons
This muscle type forms the muscular walls of the heart.
Myocardial Muscle
My/o= muscle Cardi=heart -al= pertaining to

The act of raising or lifting a body part? The act of lowering a body part?
What is the relationship between rotation and circumduction?
Lifting=elevation Rotation=circular movement around axis (joint)
Lowering= depression Circumduction=circular motion at far end of limb
This is a diagnostic procedure to evaluate joint mobility and muscle strength. These exercises are used to increase strength, flexibility, and mobility.
What is a reflex?
Range of Motion (ROM) testing
A reflex is an involuntary response to a stimulus. No or abnormal responses can indicate a disruption of nerve supply to involved muscles. (reflexes can be lost due to coma or heavy sedation)
ten/o, tend/o, tendin/o
Tendons
A narrow band of nonelastic, dense, fibrous connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. (Do not confuse with ligaments- which connect bone to bone, forming joints)
Name 3 functions of the Muscular System.
-Holding body erect and making movement possible, -Generating body heat, -Moving food through digestive system, -Assisting with blood flow, -Moving fluids through ducts/tubes associated with other body systems.
Myocardial muscle is striated in appearance like _____ muscle, but similar to _____ muscle in that it is involuntary. The constant contraction/relaxation of the myocardial muscle causes the heart beat.
Skeletal (striated), smooth (involuntary)

Define supination & pronation.
Define dorsiflexion and plantar flexion.
Supination= rotating arm or leg so that palm or sole is turned forward or upward
Pronation= rotating arm/leg so that the palm/sole is turned downward/backward. 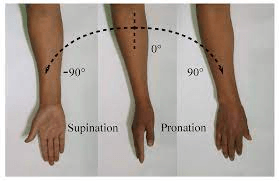
Dorsiflexion= movement that bends the foot upward at the ankle.
Plantar Flexion= movement that bends food downward at the ankle. 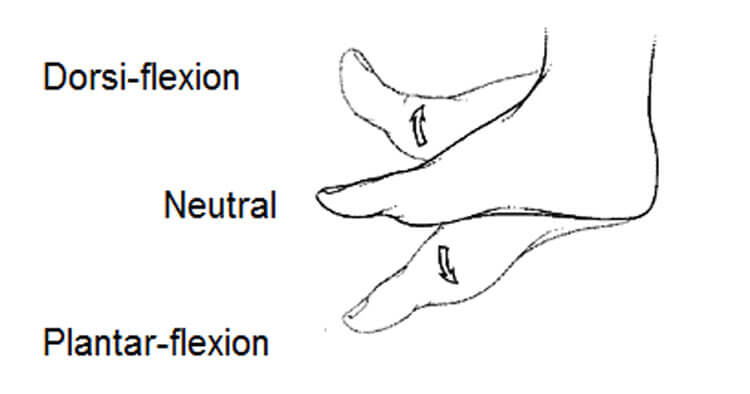
Abbreviations:
ADL, OT, RSD, ROM, CTS
ADL= Activities of daily living
OT= Occupational therapy, occupational therapist
RSD= Repetitive stress disorder
ROM= Range of Motion
CTS= Carpal tunnel syndrome
Kines/o, kinesi/o= _________
tax/o=_______
ton/o=______,_______,_______
tax/o=coordination, order
ton/o=tone, stretching, tension