This is defined as a slow pulse rate
Bradycardia (<60 BPM)
This is the normal total lung capacity
~6 Liters
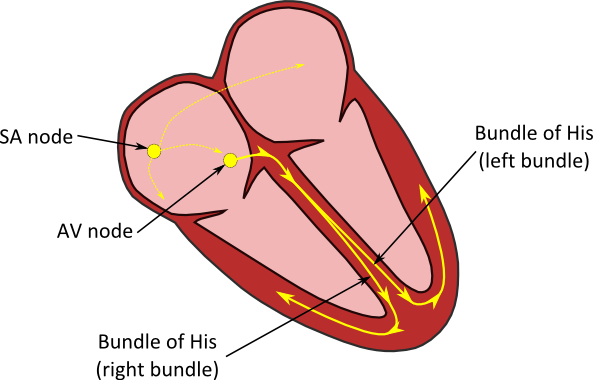
Electrical signal of the heart start here (the pacemaker)
SA (sinoatrial) node
Vocal cords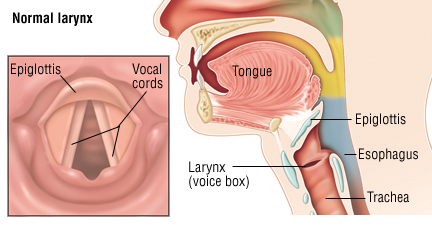
This side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
Left!
This is another name for low blood pressure
Hypotension
As opposed to balloons, the lungs inflate using this
Negative pressure
This machine is used to view the electrical activity of the heart
EKG (electrocardiogram)
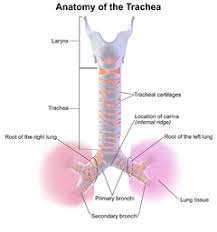
This is the medical term for the windpipe
Trachea
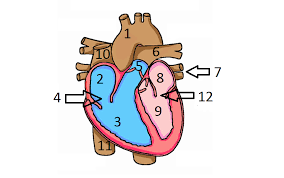
Which valve is number 12 pointing to?
Mitral valve
This is the normal range of breaths per minute
12-20
This is the term used for air outside the lungs, but within the chest cavity
Pneumothorax


This is what the p wave represents
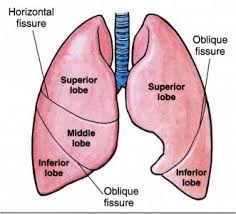
The left lung has this many lobes
Two
 This is structure number 2 (be specific)
This is structure number 2 (be specific)
Right atrium
This is what tachypnea means
Fast breathing! >20 breaths per minute
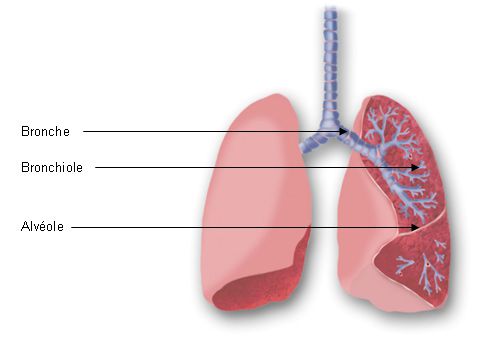
These are the small air sacs in your lungs that move oxygen in and carbon dioxide out
 Alveoli
Alveoli

This is what the QRS complex represents
Ventricular activation
Aspirated (inhaled) objects are more likely to go down this side
Right side! (bronchus more vertical and larger)
 This is structure number 1
This is structure number 1
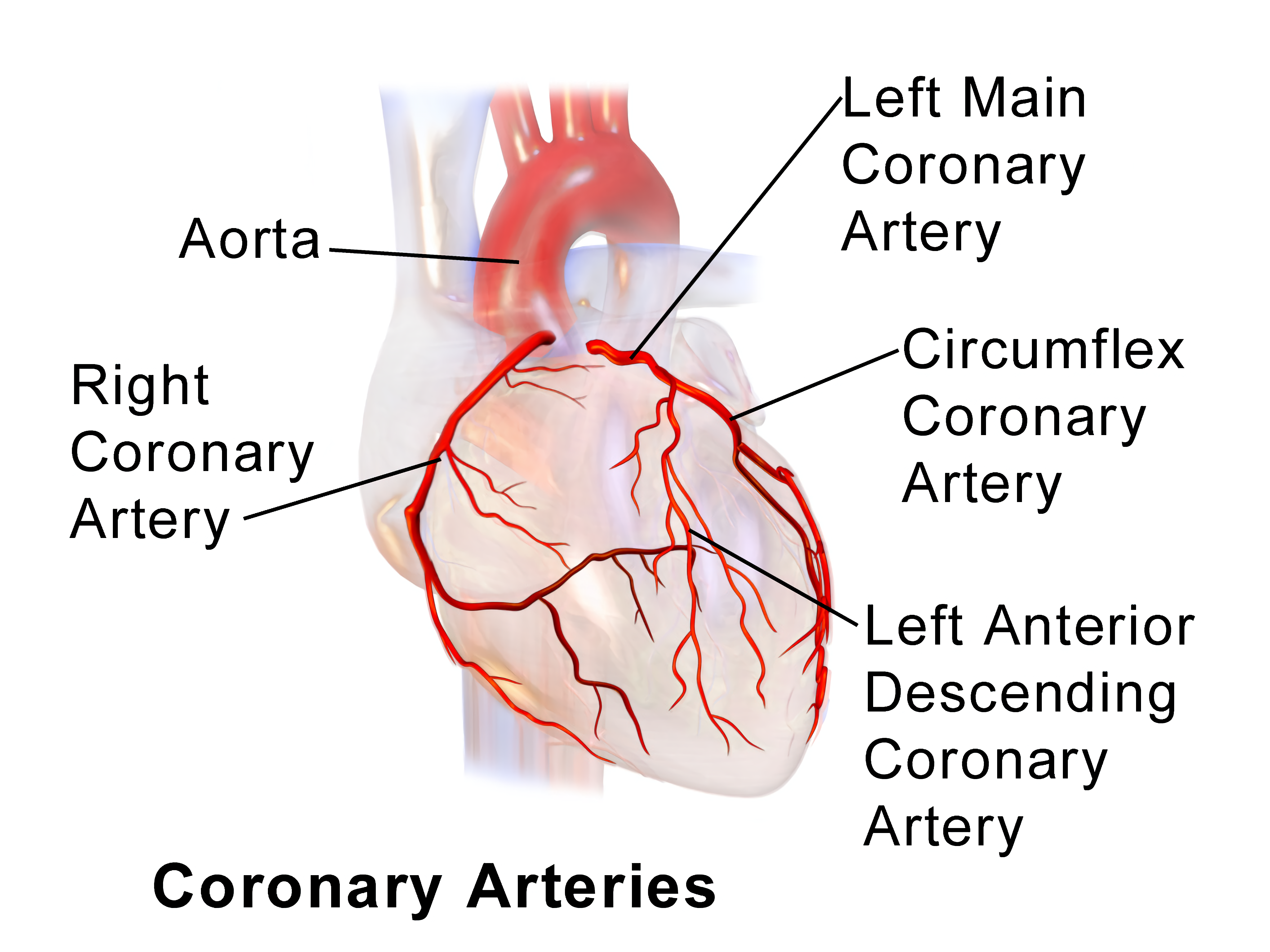
Aorta
In a blood pressure reading of 120/80, 80 is know as the ____ blood pressure
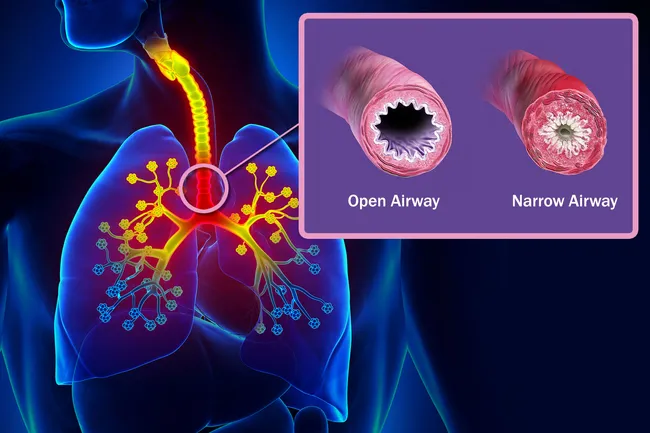
This disease is caused by narrowing/closure of airways making it difficult to breathe
Asthma!
An ST elevation usually represents this
Heart attack (myocardial infarction)
This part of the airway is between bronchi and alveoli
Bronchioles
These are the structures that get blocked during a heart attack
Coronary arteries