The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system is called ________ memory
long-term
Name the three stages in the Atkinson-Shiffrin multistore model
1. Sensory memory
2. Short-term/working memory
3. Long-term memory
What are the three basic levels of encoding
1. visual
2. acoustic
3. semantic
what's the difference between recall and recognition?
Recall= retrieving info without cues; recognition=identifying info when seen
recall= fill in the blank or short answer questions
recognition = multiple choice
Elizabeth Loftus is best known for what?
For her research on memory construction and the misinformation effect
What's the difference between automatic and effortful processing?
Give 1 example of each
Automatic is unconscious encoding; effortful requires attention and conscious effort
automatic: you can picture where information was on a page in your notes, even if you didn't try to memorize it
Effortful: studying definitions of psychology terms for a test by making flashcards and rehearsing them until you can recall them from memory
What's the difference between iconic and echoic memory (how many seconds can you hold information of each type)
Iconic=visual sensory memory (1/2 second or less)
Echoic = auditory sensory memory (3-4 seconds)
What type of encoding is usually the most effective and why?
semantic encoding because it involves attaching meaning to information (tie the word to its meaning and your own experience)
Remember: chocolate choo choo train
Explain what the graphic below represents
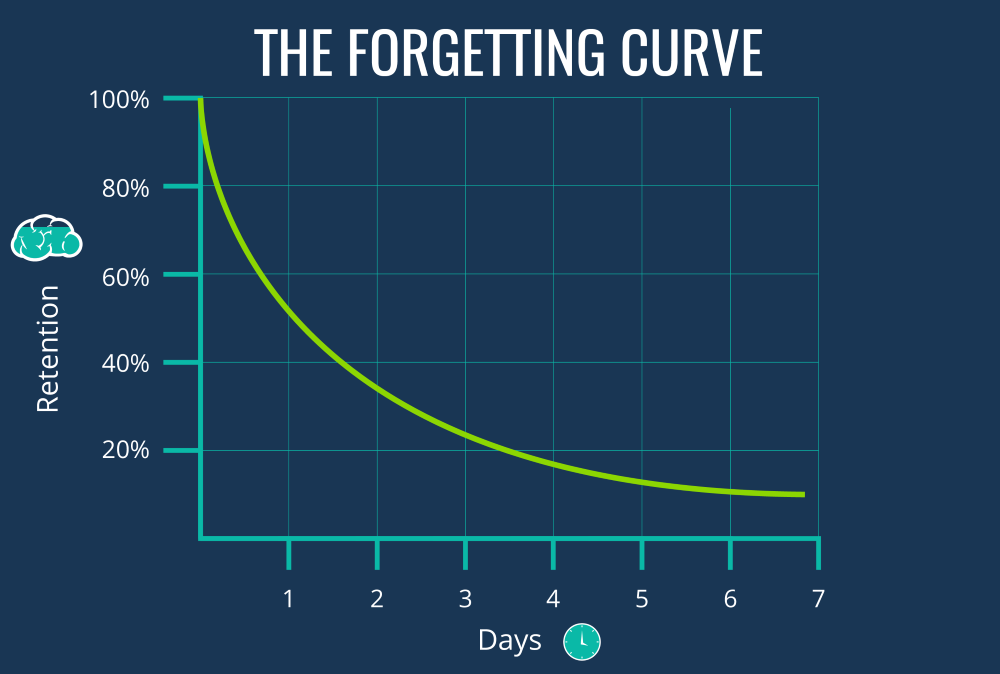
the rate of forgetting is initially rapids and then slows down overtime
What is the misinformation effect?
when misleading information distorts memory of an event
The researcher Hermann Ebbinghaus (Hottie Herman) is known for studying what?
Hermann Ebbinghaus is known for studying rehearsal and creating the forgetting curve
What is the information-processing model of memory?
1.encoding
2. storage
3. retrieval
What is the self-reference effect? Give an example.
remembering information better when we relate it to ourselves
example:
Implicit memory : "I don't have to think about how to ride my bike -- I just do it"
Arnold so easily remembers his old girlfriend's telephone number that he finds it difficult to recall his new girlfriend's number. Arnold's difficulty best illustrates
Proactive Interference
The smell of freshly baked cookies reminds you of your grandmother's kitchen. This is an example of what?
Retrieval cue
What is overlearning, and why does it help memory?
Studying/rehearsing beyond memory; strengthens retention and recall
What is a flashbulb memory, and why do we remember it so vividly?
It's a vivid memory of an emotionally significant event due to strong emotional arousal
Name two mnemonic strategies and how they work
chunking (organizing information into smaller, meaningful units to make it easier to remember)
Method of loci (remembering information by associating it with specific locations in a familiar place)
peg word (memorizing a list by linking items to a pre-memorized set of rhyming words -- "one is a bun" "two is a shoe" etc)
Hierarchies (structuring information into categories and subcategories to improve recall)
what is the difference between repression and motivated forgetting?
repression = the unconscious blocking of painful or anxiety-causing memories (a person who experienced childhood abuse might have no conscious memory of it because their mind repressed it)
motivated forgetting: when someone forgets information consciously or unconsciously because they don't want to remember it, often because it's unpleasant (student "forgets" about their bad grade on a test because they'd rather not think about it)
What's the difference between retrograde and anterograde amnesia?
retrograde: inability to recall past memories from before the event that caused the amnesia
anterograde: inability to form new memories after the event that caused amnesia
What does long-term potentiation (LTP) do for memory?
It increases synaptic strength, making memory storage more efficient
After a long, stressful week at summer camp, Maria looks back on the experience and remembers only the fun activities and friends she made, completely forgetting the early wake-up calls, homesickness, and mosquito bites.
Which psychological concept does Maria’s selective memory illustrate?
Rosy retrospection
What is rosy retrospection and how can we use the self-reference effect to remember this concept
recalling past events as more positive than they seemed at the time
think of a personal example of a time that you remember more positively now than it seemed at the time. By creating a personal example you are using the self-reference effect
A college student drinks energy drinks while cramming for an exam. On test day, after drinking another energy drink, they recall more of the material than if they hadn’t consumed one. What is this an example of?
State-dependent memory
Infantile amnesia refers to the inability to recall memories from early childhood. Which brain structure’s late development is thought to contribute to this phenomenon, and why?
The hippocampus, it is one of the last brain structures to fully mature, so early memories cannot be effectively encoded or stored.